Data analysis has become an integral part of corporate intelligence, providing much-needed insights to inform strategies. In today’s business world, power lies in data, and businesses skilled in extracting key insights from it hold a significant advantage over competitors.
Data is at the core of most activities today, highlighting the need for more skilled personnel. The demand is obvious in job portals filled with vacancies for data analysts. From entry-level to mid-level and senior level, ambitious minds get a chance to progress further- from being a data analyst to a senior data analyst and even to the Chief Data Officer.
This blog is more like your data analyst roadmap. It breaks down the must-have skills and competencies for being successful in a career in data analysis and creates a structured path for growth in data analysis.
What is Data Analysis, and Why is It Important?
Data analysis involves turning raw data into meaningful insights. It involves inspecting, cleaning, and modelling data to uncover patterns and trends that help businesses make smarter decisions.
Key skills of a data analyst include the working manipulation of tools such as Python or R, statistical analysis, and creating clear and impactful visualisations.
Techniques like data mining and even machine learning are dug deep to find the stories hidden within datasets. Data analysts discover insights that are at the very core of strategies to improve operational functioning and drive success across industries.

Get curriculum highlights, career paths, industry insights and accelerate your data science journey.
Download brochure
The Role of a Data Analyst: Responsibilities and Real-World Impact
A data analyst is one who takes raw data and transforms it into meaningful insights that help organisations make smarter decisions. They are across industries, solving problems and optimising processes by uncovering hidden patterns and trends in the number.
Data analysts are the most important in the fast-paced, technology-driven world today. The rapidly increasing need for data analysts provides fresh insights for businesses to gain a competitive advantage.
The career is built around real-world problem-solving and offers the opportunity to work on diverse issues across industries where meaningful impacts can be achieved.
Let’s break down what a data analyst does every day:
Data Collection and Cleaning
- Collect data from sources such as surveys, website logs, financial systems, or experiments.
- Cleaning and preparing the data to ensure accuracy and readiness for analysis.
Data Analysis and Pattern Discovery
- Utilise tools such as Python, R, and visualisation software for exploring datasets.
- Discover patterns, trends, and anomalies in uncovering hidden relationships.
Communication Insight
- Translate complex data findings into clear and actionable insights.
- Communicate insights by creating dashboards, reports, or visual storytelling.
Problem-Solving and Improvement
- Bridge insights to optimum processes to solve real-world problems.
- It can be in terms of analysing marketing campaigns, fraud detection, or preventing breakdowns in equipment.
A data analyst is not a number cruncher who sits in front of a screen. Rather, they go through the sales figures, traffic data, and patterns to reveal insights explaining the trend.
It isn’t just about numbers; it is connecting them in a way that decision-making has an intelligent voice.
Different Types of Data Analysts Working in Different Fields
Data analysts do not follow the same route; some focus their attention on business operations, while others enter the realms of marketing trends or even the sporting arena.
Here are some common job roles:
| Type of Data Analyst |
Focus Area |
Key Objective |
| Business Intelligence Analysts |
Business data |
Drive insights, improve performance and support decisions. |
| Financial Analysts |
Financial data |
Guide budgeting, investments, and market trend analysis. |
| Healthcare Data Analysts |
Patient and healthcare data |
Optimise outcomes and streamline operations. |
| Marketing Analysts |
Campaign and consumer behaviour data |
Evaluate performance and track market trends. |
| Operations Analysts |
Operational data |
Boost efficiency and reduce costs. |
| Sports Analysts |
Sports performance data |
Assess performance and improve strategies. |
| Crime Analysts |
Crime data |
Identify patterns and support prevention and investigations. |
| Environmental Data Analysts |
Environmental and climate data |
Study trends, patterns, and human impact. |
| Social Media Analysts |
Social media data |
Understand user behaviour and inform marketing strategies. |
| Economic Analysts |
Economic data |
Forecast trends and provide policy insights. |
Essential Skills for Aspiring Data Analysts: Technical and Soft Skills Defined
Every successful data analyst is a mix of technical knowledge and human insight. You don’t need to be a coder, but you do need a solid foundation in certain tools and techniques in your journey to complete the data analyst roadmap.
Soft Skills
Problem-Solving: The ability to dissect a problem and find actionable solutions.
Communication: Translating complex findings into simple, actionable insights.
Attention to Detail: Spotting errors or inconsistencies that could derail analysis.
Critical Thinking: Challenging assumptions and looking deeper into the data for hidden patterns.
Technical Skills
Programming Languages
- Python
- R
- MATLAB
- Scala
- Julia
- SQL
Data Analysis Tools
- MS Excel
- Tableau
- RapidMiner
- Power-BI
- SAP
- Google Analytics
Optional but Useful Tools
- Hadoop and Spark
- Jupyter Notebook
- Google Analytics
Mathematics and Statistics
Mathematics
- Calculus
- Standard Deviation
- System of Linear Equations
- Matrix Operation
- Solving Linear Equations using Gaussian Elimination
- Row Echelon Form
- Matrix Approximation
- Vector Operations
- Linear Mappings
- Linear Algebra
- Probability
Statistics
- Mean, Standard Deviation, and Variance — Implementation
- Descriptive and Inferential Statistics
- Probability Theory and Distribution
- Sampling Distribution
- Linear Regression
- Sample Error and True Error
- Bias Vs Variance and Its Trade-Off
- Hypothesis Testing
- Confidence Intervals
- Correlation and Covariance
- Correlation Coefficient
- Covariance Matrix
- Pearson Correlation
- Spearman’s Rank Correlation Measure
- Kendall Rank Correlation Measure
- Robust Correlations
Step-by-Step Data Analyst Roadmap to Build Your Data Analyst Career
Step 1: Strengthen Your Foundations
Before diving into tools, build a strong understanding of maths and statistics. You’ll use these daily for things like calculating averages or performing regression analysis.
Step 2: Learn SQL and Excel
SQL gets you the data, and Excel helps you clean and analyse it. Start with simple tasks like filtering rows or running SELECT queries.
Step 3: Add a Programming Language
Python is versatile and widely used in analytics. Focus on libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib for data tasks.
Step 4: Master Visualisation Tools
Learn how to tell stories with data using Tableau or Power BI. Good visuals make your insights easy to understand and act upon.
Step 5: Work on Real-World Projects
Apply what you’ve learned to real datasets. For example:
- Analysing cricket match statistics to predict player performance.
- Tracking store sales data to optimise inventory levels.
Step 6: Build a Portfolio
Showcase your work on GitHub or a personal blog. Highlight how you approached problems, cleaned data, and delivered insights.
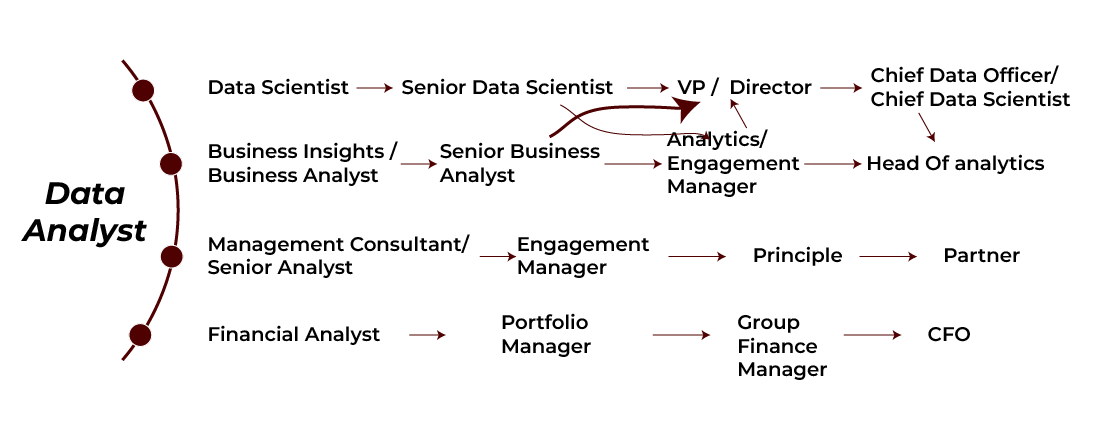
Different Job Roles, Skills Required, and Career Progression of Data Analysts
The journey of every data analyst is unique in its own way. They work in different positions that require different skill sets to deal with problems. Also, career growth is different for everyone.
Let’s quickly see the different working positions of a data analyst and the skills required in that particular role:
| Career Path |
Market Research Analyst |
Operations Research Analyst |
Quantitative Analyst |
BI Analyst |
Business Analyst |
Data Analyst |
| Level 1: Beginner |
Consumer data collection, Survey design |
Linear programming, Problem-solving |
Statistical algorithms, Financial modelling |
Report generation from BI tools, Dashboard setup |
Basic data interpretation, Business process analysis |
SQL, Excel proficiency, data visualisations |
| Level 2: Intermediate |
Market trend analysis, Competitor analysis |
Simulation models, Supply chain analytics |
Time series analysis, Risk analysis |
OLAP basics, Complex reporting |
Requirements gathering, Business case development |
Advanced SQL, R/Python, statistical analysis |
| Level 3: Advanced |
Complex consumer behaviour modelling, Sentiment analysis |
Optimisation algorithms, Stochastic models |
Derivatives pricing models, Portfolio optimisation |
BI software deep dive, Data warehouse management |
Data-driven business process reengineering, Cost-benefit analysis |
Predictive analytics, Data modelling techniques, Advanced visualisation tools |
| Level 4: Expert |
Predictive market dynamics, Advanced econometric modelling |
Advanced operations strategy, Prescriptive analytics |
High-frequency trading algorithms, Complex quantitative strategies |
Cross-system BI integration, Advanced analytics with BI tools |
Advanced market research, Business forecasting |
Big data technologies, Machine learning, Multi-dimensional data analysis |
| Level 5: Leader |
Market research strategy, Leadership in insights and analytics |
Operations innovation leadership, Strategic policy formulation |
Financial institution risk management strategy, Quantitative department leadership |
BI strategy formulation, BI department leadership |
Business unit leadership, Strategic business development |
Strategic decision-making, Analytics team leadership, Company-wide data initiatives |
The Importance of Networking and Mentorship in Your Data Analyst Journey
Most job opportunities come through connections. This is why networking and mentorship are important. Join platforms like LinkedIn and connect with professionals in your field.
Reach out to experienced analysts for guidance. A good mentor can help you navigate challenges, review your portfolio, or even recommend you for roles. Conferences and meetups are great for meeting like-minded people.
Building relationships takes effort, but the rewards are worth it.
Also Read: Data Analyst Course Syllabus: Exploring the Learning Path
Educational Background and Certifications: Paving Your Path to Success
Do you need a fancy degree to become a data analyst? Not necessarily.
While many employers prefer candidates with a degree in mathematics, statistics, or computer science, it’s not the only way in. In fact, many successful data analysts come from fields like engineering, economics, or even the humanities. What matters most is your skill set, portfolio, and ability to solve problems with data.
Degrees That Give You an Edge
- Bachelor’s in Mathematics or Statistics: Builds strong foundations in numbers and probability.
- Computer Science or IT: Covers programming and database management.
- Economics or Business: Helps you understand market trends and financial data.
- Master’s Degree: For advanced roles or leadership positions, a master’s in data science or analytics can help. But for most entry-level data analyst jobs, it’s not mandatory.
Certifications That Make You Stand Out
Here are some best courses available in the market to help you complete your data analyst roadmap and get the best jobs:
Business Analytics and Data Science Course Online with Certification
Duration: 10 months
Learning Hours: 470+
Key Highlights:
- In collaboration with edX and Harvard University and aligned with NASSCOM
- 70-90% instructor-led live classes
- 7+ portfolio projects and case studies
- Workshops on industry-trending topics
- Build Your Own Product capstone project
- Hands-on learning through expert guidance
- Data analysis through GenAI
Integrated Program in Data Science, Machine Learning, and Artificial Intelligence
Duration: 11 months
Learning Hours: 704
Key Highlights:
- Ranked #1 PG Data Science Course by Analytics India Magazine
- 80+ Live Sessions with faculty from industry and academia
- Eligibility for MITx MicroMasters® certification
- 70% to 90% Live Instructor-led Classes
- Gamified & Interactive Learning
- Discussion Forums and Community
- Industry Simulation Projects & Case Studies
- Practical Hands-on Learning Session
- Career Assistance and Workshops
Advanced Certification in Data Science and Analytics
Duration: 10.5 months
Learning Hours: 579+
Key Highlights:
- Certification in collaboration with the University of Chicago
- Learn data warehousing, predictive modelling, and advanced Python programming
- Includes capstone projects on topics like sports analytics and public health
Certification Program in Data Analytics
Duration: 5 months
Learning Hours: 200+
Key Highlights:
- In collaboration with Microsoft
- Comprehensive Learning Path
- Case-Based and Interactive Learning
- Industry-Standard Tools & Technologies
- 8+ Industry-Level Projects
- Practical Exposure and Masterclasses
- Doubt Resolution and Peer Support
- Generative AI for Data Analytics
Salary Trends in Data Analytics
Curious about what data analysts earn? The answer depends on your experience, location, and role.
| Experience Level |
Expected Salary Range (India) |
Notes |
| Entry-Level |
₹4–6 lakhs annually |
Ideal for freshers starting their data analytics career. |
| Mid-Level (3–5 years) |
₹8–12 lakhs annually |
Includes roles like Senior Data Analyst and Business Intelligence Analyst with higher responsibilities. |
| Senior-Level (Specialised) |
₹10–20 lakhs annually |
Specialised roles with advanced skills: |
|
|
– Machine Learning Analyst: ₹15–20 lakhs annually |
|
|
– Financial Data Analyst: ₹12–18 lakhs annually |
|
|
– Marketing Data Analyst: ₹10–15 lakhs annually |
Also Read: Data Analyst Interview Questions with Answers
Conclusion
Data analysis has become a cornerstone of corporate intelligence, delivering crucial insights that drive strategic decisions. In today’s business landscape, data powers success, and those skilled in extracting value from it hold a significant advantage.
With data coming in all around us, the need for skilled talent has increased rapidly. Hence, from entry-level, mid-level, and senior positions, there is immense scope for professional growth, from Data Analyst to Senior Data Analyst and even Chief Data Officer.
This blog acts as your data analyst roadmap, outlining for you the key skills and competencies required to ensure a successful journey and structured growth in data analysis.
FAQs
For beginners, it can take 6 months to a year with consistent learning. This includes mastering tools like Excel, SQL, and Tableau.
Basic coding skills in Python or R are helpful but not mandatory for all roles. SQL is more important for database management.
Dealing with messy or incomplete data is a common problem. Strong problem-solving skills and approach could take the mess out of it.
Updated on November 25, 2024









