The Cloud Reference Model (CRM) is a theoretical model that identifies the layers and constituent factors of cloud solutions. It acts as a planning tool for cloud services with the aim of offering a clear framework for outlining the relations between the multiple models of cloud. To simplify its interactions with disrupted cloud structures, the CRM divides the Cloud Ecosystem into tiers, which include IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, and the Cloud Management Layer, thus assisting organizations with mass, formidability, polymorphism, and assurance in cloud applications.
What is the Cloud Computing Reference Model?
The Cloud Computing Reference Model constitutes the layers, elements and dependencies within cloud computing systems. It offers a systematic way of learning the concepts of clouds and their architectures and services, together with the relations between them. This model proved to be very valuable both to the service providers and consumers, as it allows them to bring their infrastructure, services and processes into the well-coordinated and incorporated whole of the standard depth.
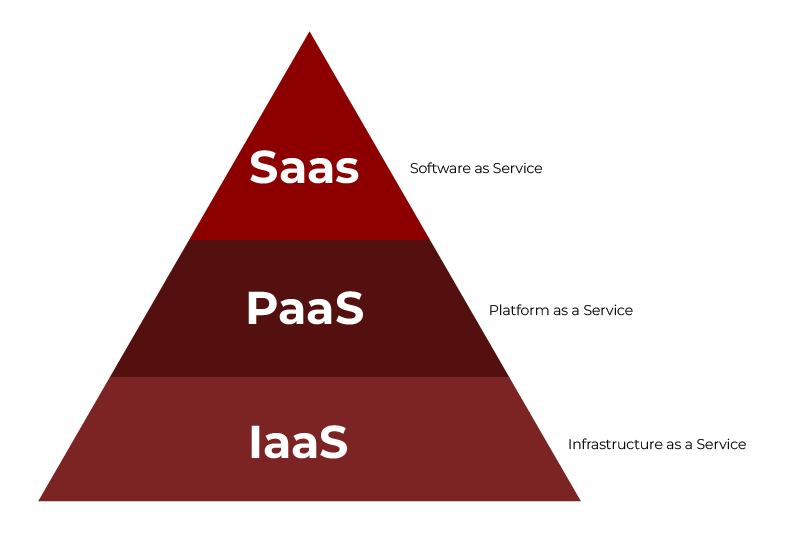
Currently there is no widely accepted cloud reference model, but there are a number of constructs designed by professionals and organizations of the IT industry. Perhaps the most often cited model is based on the idea of three foundational layers of cloud services, namely the Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), the Platform as a Service (PaaS), and the Software as a Service (SaaS) and around ten supplemental components generally connected with cloud computing governance, security, and management.
The Cloud Computing reference model is divided into 3 major service models.
- Software as a Service (Saas)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure as a Service (laaS)

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Multi Cloud Architecture & DevOps
Master cloud architecture, DevOps practices, and automation to build scalable, resilient systems.
 Cloud Computing Reference Model Overview
Cloud Computing Reference Model Overview
IaaS, PaaS and SaaS are three primary cloud delivery models and both have been highly embraced and institutionalized. The cloud delivery service model is a specific, predefined type of IT service that the cloud service provider organize and offers to the users. However, the level of features that the three types of delivery offer cloud users differ in terms of the level of administrative control.
These abstraction layers can also be viewed as a stack, in which services of one tier can be used with services of another tier to construct services from both. For example, SaaS may provide infrastructure for services from a higher tier. Let me briefly explain the layer of the Cloud computing reference model as described below.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
It is possible to define Software as a Service (SaaS) as the model of cloud computing in which the application is delivered by a third party by directly accessing the application from the web rather than installation in local or organization local servers. In SaaS, the users will have access to application software through an environment accessible by a web browser and the software environment and support are activities of responsibilities of the service provider.
Features of SaaS:
- Hosted on the Cloud: SaaS applications are hosted and managed by the service provider, usually on cloud infrastructure, eliminating the need for users to maintain hardware or software locally.
- Accessed via the Internet: SaaS applications are accessed by users around the Internet using a web browser, which makes it easy to use from anywhere there is an Internet connection.
- No Local Installation Required: SaaS applications are delivered through the cloud, so users don’t need to install or maintain software on local devices or servers.
- Reduced IT Overhead: SaaS reduces the need for organizations to manage software installations, upgrades, and security patches, lowering the burden on It teams and reducing administrative costs.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
Platform as a Service is a strategy that provides a greater level of virtualization to make a cloud easily programmable in other than infrastructure focused clouds that provide only compute services and storage (PaaS). The customers can build and host the applications in the cloud environment without necessarily having to forecast the number of processors or the memory that their applications need. One example of a PaaS offering that can support the quick creation and hosting of web applications is Google App Engine.
Features of PaaS
- Development Framework: PaaS describes a form of development that is a set of tools, libraries, and environments that enable developers to streamline the development, testing and deployment processes.
- Managed Hosting: Most of the underlying assets of PaaS are hosted by the providers, so the business is not concerned with the hardware and software environment, and the developers are not concerned with the infrastructure system software and network layers but have to code only at the application layer.
- Scalability: Resources like CPU, storage and network bandwidth are self-provisioned in PaaS solutions, and these change constantly to solve the needs of the application without any human interference.
- Cost Effective: Consumption-based is a kind of economic business model where businesses only pay for what they consume, and this model is helpful when the costs of a business fluctuate due to a small number of users or varying workloads PaaS allows such a formation of costs.
Also Read: Cloud Service Providers
laaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a platform where developers and IT organizations utilize storage and computer resources to provide unique business solutions. IaaS offers computer hardware as a service these include servers, networking technology, storage, and data centers. It may also include the delivery of OS and virtualization technology with which the resources are managed. Here the more important issue is that customers of IaaS do not purchase and install computing resources in their own data centers. The service is typically
paid for on a usage basis. The service may include dynamic scaling so if the customers need more resources than endowed, they can obtain them instantly.
Features of IaaS
- Virtualized Compute Resources: Scalable virtual machines with customizable CPU, memory, and storage configurations.
- Scalability & Elasticity: Auto-scaling and flexible resource scaling based on demand.
- Networking: Virtual networks (VPC), load balancing, VPN connectivity, and IP management.
- Security & Compliance: Identity management, data encryption, IAM, and compliance with industry standards.
- Global Access: Multi-region deployment, low-latency access, and global content delivery networks (CDN).
Types of Cloud Computing Reference Model
A reference model in the context of cloud computing is an architecture that categorizes and represents the various facets, elements and tiers of cloud computing. These models assist organizations and cloud providers to understand everyone’s responsibilities and the service demarcation line. The reference models may be at a different level of abstraction, a different model of the type of service offered, or a reference model of security and governance.
The types of cloud computing reference models typically align with the three main cloud service models: These include IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service), and SaaS (Software as a Service). Likewise, they may also contain facets like cloud deployment types, security reference types, and service delivery types.
The principles of NIST Cloud computing reference architecture are.
- Creator of a vendor-neutral architecture that adheres to the NIST standard.
- Create a solution that does not inhibit innovation by establishing a required technological solution.
- The NIST Cloud computing reference architecture provides characteristics like elasticity, self-service, and resource collaboration.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defines four cloud deployment models in its Cloud Computing Standards (SP 800-145). These deployment models describe the types of cloud environments and how they are used. The four models are:
- Private Cloud: A private cloud is a cloud infrastructure that is used exclusively by one organization. It may be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider, but it is dedicated to a single organization’s needs.
- Public Cloud: A public cloud is a cloud infrastructure that is made available to the general public by a cloud service provider. The infrastructure is shared among multiple organizations (tenants) but is fully managed by the cloud provider.
- Hybrid Cloud: A hybrid cloud is a combination of both private and public clouds that are interconnected, allowing data and applications to move between them. This model provides more flexibility and optimization of existing infrastructure.
- Community Cloud: A community cloud is shared by several organizations that have similar cloud requirements (e.g. compliance, security, or regulatory needs). The infrastructure is shared between the organizations, and it can be hosted internally or by a third-party provider.
CSA Cloud Reference Model
CSA Cloud Reference Model is a model that was developed more for the purpose of helping individuals and companies to identify the components, including roles and responsibilities in a given cloud computing environment, particularly addressing security matters. It offers a step-by-step methodical way of addressing cloud services and checking for security threats and compliance with set standards. CSA Cloud Reference Model is composed of multiple layers and entities such as Cloud Consumer, Cloud Provider, Cloud Service and Cloud Service Components.
The model defines and describes the roles of cloud service consumers and cloud providers to help improve the understanding of cloud services. It allows organizations to evaluate risks to security, approach data protection and include required security measures. It also lists the recommendations for the security of cloud infrastructure, platforms, applications, and data; major areas covered are identity and access management, encryption, audit and compliance, and incident management.
As it has been mentioned, one of the primary strengths of the CSA Cloud Reference Model is its modularity depending on cloud service models – IaaS, PaaS, SaaS – and deployment models – public, private, hybrid, and community. The model has shifted the focus towards both the provider side and the consumer side to make decision-making on the fulfillment of security policies, risks and operations in cloud environments precise and efficiently. With the help of the CSA Cloud Reference Model, organizations will be able to increase the level of protection of their cloud and investigate whether the aspect of cloud computing, both from the technical and the governance viewpoints, was comprehensive enough.
Also Read: Cloud Computing vs. Artificial Intelligence

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
Security Reference Model in Cloud Computing
A Security Reference Model in Cloud Computing is a schematic view that implements the essential security factors, safeguards, and measures required in the cloud computing paradigm. This model assists organizations in appreciating when and how the CSP and the customer share security responsibilities and how to attain total security solutions.
The cloud security reference model defines several areas of security that require consideration during the transfer to or usage of cloud computing infrastructure, platform, or software. It gives guidelines for implementing the protection of data, applications, and services while adhering to regulatory requirements.
The OCCI Cloud Reference Model
The OCCI Cloud Reference Model is a reference blueprint that offers the basis for handling cloud services and coordination in different environments. Some of them are: Cloud Service Interface: This is used for the provisioning, monitoring, and management of cloud services Provisioning and management of cloud resources such as compute capability, storage, and networking Resource Management. Service Management ensures that service delivery is coordinated and efficient to provide lifecycle management of actual service. It also has guidelines under Security and Compliance that encourage proper security and compliance standards.
Also Read: Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Major Actors of Cloud Computing Reference Model
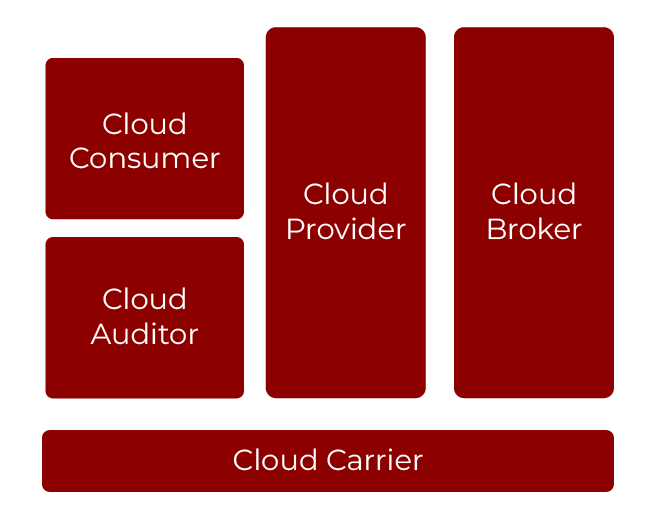
There are five major actors in NIST cloud computing reference architecture.
- Cloud Consumer
- Cloud Provider
- Cloud Carrier
- Cloud Auditor
- Cloud Broker
Cloud Consumer
The typical end-user for which the cloud computing service is designed for is the cloud consumer. A cloud consumer, on the other hand, is an individual or corporation which has a working relationship with a cloud provider and depends on the cloud to provide him/her/its services. A cloud customer browses through a cloud provider’s service offerings, makes the right request for service to the provider, signs the service level agreement with the provider and finally uses the service. The cloud customer may be invoiced for the service delivered and there is a necessity to have the payment detail. They need to have a cloud Service Level Agreement (SLA).
Cloud Provider
Cloud provider refers to any individual, group, or other entity that controls the provision of a service to be delivered to cloud users. A cloud provider develops the requested software, platforms, and infrastructure services and assumes the responsibility to support the technical infrastructure required to deliver these services. It commits to delivering the services at a promised level of quality and bears the responsibility for protecting the services’ confidentiality and data.
The cloud software is executed by the cloud provider through service interfaces and virtual network interfaces to aid in resource abstraction to make computing resources available for consumption through the infrastructure as a service to cloud consumers.
Cloud Carrier
A cloud carrier is an organization that is an agent that provides connection and Transmission of cloud services from an offering provider to a consumer. According to the cloud access method, the carriers for the cloud can be accessed through the network, telecommunication and other access equipment. Customers of cloud services, for example, can access them through network access devices such as laptops, mobile phones, PCs, MIDs, etc. Cloud services are usually distributed by network and telecommunication carriers, while a transport agent is an entity that organizes the shipping of storage devices like high-capacity hard drives.
Remember that a cloud provider will make service level agreements (SLAs) with the cloud carrier to deliver the services to the level in which the SLAs offer them to the cloud consumers. The cloud provider may also require that cloud carriers offer distinct and secure channels of communication between Cloud consumers and cloud providers.
Cloud Broker
A cloud broker is a kind of intermediary that provides services that enable the consumer to make choices on various cloud services offered by various service providers. Brokers can act as agents assembling desired cloud services, modifying offerings, or as intermediaries between the end user and service provider, which in addition can provide various services such as billing, security, and service orchestration. This they do to complement the services that consumers already have in place for the consumption of contents in their clouds. Example: A company that aggregates multiple SaaS offerings and integrates them into a unified platform could be considered a cloud broker.
Also Read: Cloud Computing Architecture
Conclusion
The concept of dividing the cloud environment into easily recognizable tiers helps various organizations indeed understand the elements of cloud computing or launch, deployment models, service types, governance, and operations. It helps the organizations direct their use of the cloud architecture and, in particular, helps determine the right services that should be used in the cloud to achieve the organizational objectives. Additionally, the CRM supports security and compliance and improves the overall performance of cloud solutions and their efficiency as well as their scalability. If you want to know more about cloud computing, consider pursuing Hero Vired’s Certificate Program in DevOps & Cloud Engineering offered in collaboration with Microsoft.
What is the Cloud Reference Model (CRM)?
Why is the Cloud Reference Model important?
What are the main components of the CRM?
How does the CRM help with cloud adoption?
What benefits does the CRM offer?
Updated on January 29, 2025
