Hashing is defined as a technique in DBMS that is used to search for records in databases that are very large or even small. In larger databases, which contain thousands and millions of records, the indexing data structure technique becomes inefficient because searching a specific record using indexing consumes more time. So, to counter this problem, hashing techniques are used. In this article, we will go through various hashing techniques.
What is Hashing in DBMS?
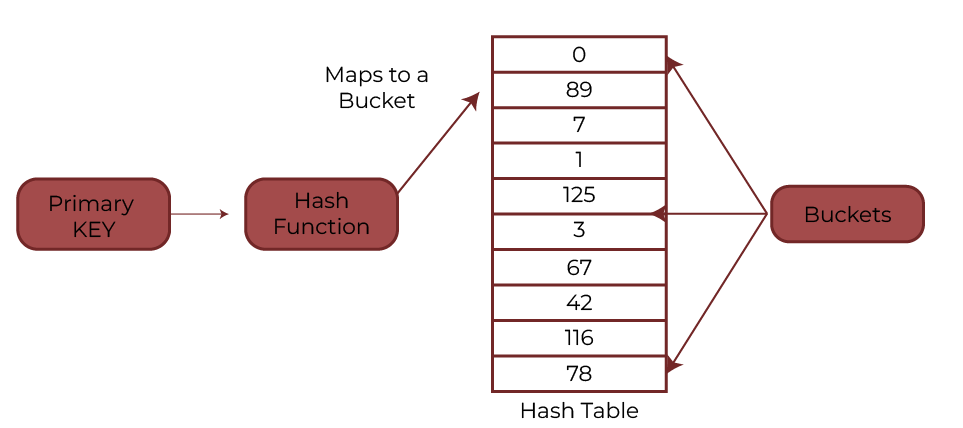
The hashing technique uses a hash function to store data records in an auxiliary hash table. There are three major components in hashing:
- Hash Table: The total number of data records in the database determines the size of a hash table, which is an array or data structure. The precise location of a data record is stored in each memory location in a hash table, which is referred to as a “bucket” or hash index and is accessible via a hash function.
- Bucket: In the hash table where the data record is stored, a bucket is a memory index. Typically, a disk block that holds numerous records is stored in these buckets. Another name for it is the hash index.
- Hash Function: A hash function is an algorithm or mathematical equation that computes the hash index as the output after receiving the main key of one data record as input.
Also read: Cardinality in DBMS

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Multi Cloud Architecture & DevOps
Master cloud architecture, DevOps practices, and automation to build scalable, resilient systems.
Properties of Hashing in DBMS
In this strategy, data is stored in blocks called addresses that are generated by the hashing process. These records are kept in memory at locations called data buckets or data blocks.
In this instance, the address can be generated from any column value using a hash function. The hash function frequently generates the address of the data block using the primary key. A hash function is a fundamental mathematical function to any sophisticated mathematical function. The address of the data block, or any row that shares the same address as a main key within the data block, can alternatively be thought of as the primary key.
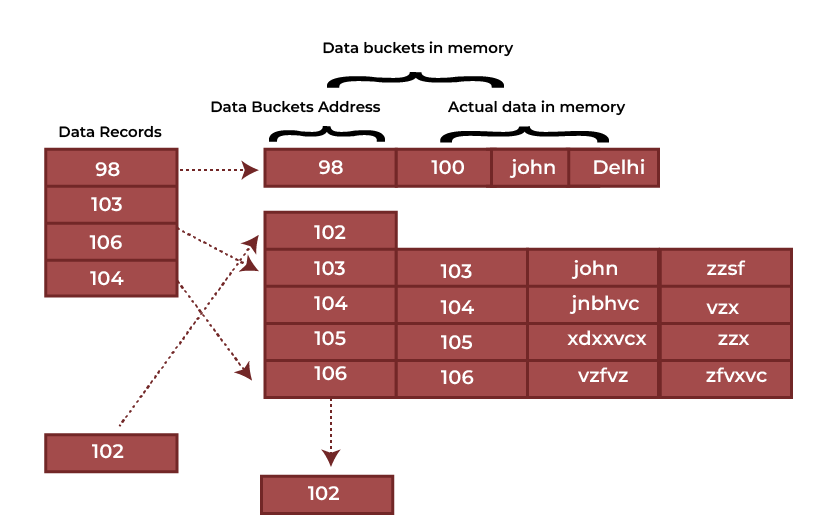
The main key value in the image above corresponds to the data block addresses. An alternative to this hash function might be a straightforward mathematical function, such as exponential, mod, cos, sin, and so forth. Let’s say we want to determine the address of the data block using the mod (5) hash function. The mod (5) function is used in this situation to hash the primary keys, producing the results 3, 3, 1, 4, and 2, respectively. Records are then saved at those data block positions.
The main key value in the image above corresponds to the data block addresses. An alternative to this hash function might be a straightforward mathematical function, such as exponential, mod, cos, sin, and so forth. Let’s say we want to determine the address of the data block using the mod (5) hash function. The mod (5) function is used in this situation to hash the primary keys, producing the results 3, 3, 1, 4, and 2, respectively. Records are then saved at those data block positions.

Important Terminologies
Data Bucket
Data buckets are storage locations within a hash table where actual data records are kept. Each bucket can hold one or more records, depending on the implementation.
Hash Function
A hash function is a mathematical algorithm that converts a given input (often a primary key) into a specific address within the hash table. This address indicates where the corresponding data record is stored.
Hash Index
The hash index is the result produced by the hash function, representing the address of the data block within the hash table. It serves as a quick reference to locate the desired data.
Linear Probing
Linear probing is a collision resolution technique used when the initial bucket calculated by the hash function is already occupied. It sequentially checks the next available buckets in the hash table until an empty one is found.
Quadratic Probing
Quadratic probing is another collision resolution method similar to linear probing. However, instead of checking the next bucket linearly, it uses a quadratic function to determine the next bucket to check, reducing clustering issues.
Bucket Overflow
Bucket overflow occurs when the bucket identified by the hash function is already full. This situation requires additional handling strategies, such as linear or quadratic probing, to find an alternative bucket for storing the new record.
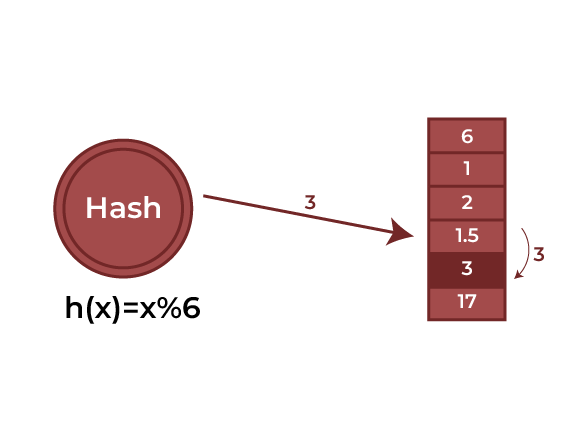
Working of Hash Function
A hash index is produced by the hash function using the data record’s primary key. There are now two options:
- There isn’t a value that already occupies the generated hash index. Thus, this is where the data record’s address will be kept.
- There is already another value occupying the hash index that was generated. This is referred to as a collision, so a collision resolution technique will be used to combat it.
The hash function now applies whenever we query a specific record, returning the data record much faster than indexing because we can use the hash function to find the exact location of the data record without having to search through all of the indices one by one.

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
Types of Hashing in DBMS
There are two primary hashing techniques in DBMS:
- Static Hashing
- Dynamic Hashing
Static Hashing in DBMS
Static hashing in a Database Management System (DBMS) is a technique where the size and structure of the hash table are fixed when it is created. Here are some key points about static hashing:
- Fixed Number of Buckets: The number of data buckets remains constant throughout. Each bucket is a storage location where records are stored.
- Hash Function: A hash function is used to map search-key values to bucket addresses. For example, if the hash function is mod 5, it will always map a given key to the same bucket address.
Operations in Static Hashing
- Insertion: When a record needs to be entered using a static hash, the hash function h determines the bucket address (where the record will be stored) for search key K.
Address of a bucket = h(K)
- Search: The address of the bucket containing the data can be obtained using the same hash function when a record needs to be retrieved.
- Delete: This is simply a search followed by a deletion operation.
- Update: The record is searched using the hash function and then updated.
Dynamic Hashing in DBMS
Dynamic hashing is a technique used in DBMS that handles the limitations of static hashing like bucket overflow. Here are the key aspects of dynamic hashing:
- Variable Number of Buckets: Unlike static hashing, the number of buckets in dynamic hashing can grow or shrink based on the number of records.
- Directory: A directory is used to keep track of the buckets. The directory itself can grow or shrink dynamically.
- Hash Function: The hash function generates a hash value, and the directory uses a certain number of bits from this hash value to determine the bucket address.
- Bucket Splitting: When a bucket overflows, it is split into two, and the directory is updated to reflect this change. This helps in distributing the records more evenly.
Operations in Dynamic Hashing
- Querying: Means looking at the depth value of the hash index and then using those to compute the bucket address.
- Update: To perform a query as above and update the data.
- Deletion: Perform a query to locate the desired data and delete the same.
- Insertion: Compute the address of the bucket
- If the bucket is already full.
- Add more buckets.
- Add additional bits to the hash value.
- Re-compute the hash function.
- Else
- Add data to the bucket,
- If all the buckets are full, perform the remedies of static hashing.
Static Vs Dynamic Hashing in DBMS
| Static Hashing | Dynamic Hashing |
| In static hashing, hash tables have a fixed size. When a table is filled up, an overflow page is allocated to take in the brimming data. | Dynamic hashing employs an alternative methodology. Instead of being fixed, dynamic hash tables grow to hold more data. |
| Because static hashing only requires two input/output operations—read and write—it is a quick way to perform insert and delete operations. | If a dynamic hash table is empty, it can be resized to save memory usage. |
| The overflow chain can grow rather lengthy if the hash table isn’t optimized, which will lower performance and complicate scaling. | The advantage of dynamic hashing lies in its flexibility: you don’t have to plan its size in advance |
Best Use Cases for Hashing
- Hashing algorithms excel in various scenarios where fast data retrieval, security, and efficiency are essential. Graphics processing, where quick access to pixel data or image properties is crucial, benefits from hashing’s speed. Similarly, game boards, particularly in complex video games, rely on hashing to quickly determine the state of the game and make efficient moves.
- In cybersecurity, hashing plays a pivotal role in generating message digests, ensuring data integrity, and detecting tampering. Moreover, during compiler operation, hashing helps expedite symbol table lookups and optimize code generation. Password verification is another prime application, enhancing security by storing and comparing password hashes instead of the actual passwords.
- Lastly, when linking file names and paths in file systems, hashing enables rapid access and reduces the need for exhaustive searches. In these use cases, hashing offers a powerful solution to streamline operations and enhance both performance and security.
Also Read: Data Integrity in DBMS
Conclusion
Hashing in databases is a technique that helps in speeding up data retrieval in large databases by using hash functions to search for records. It overcomes the inefficiencies of traditional indexing methods. There are two main hashing methods Static and Dynamic, Static uses fixed-sized tables while Dynamic adjusts itself based on the data volume. Each type has its advantages like static is simple and dynamic is flexible. Hashing is widely used in areas that need fast access, security, and performance, like cybersecurity, graphics processing, and file systems.
What is a pointer in C?
What are null pointers?
A null pointer is a pointer that does not point to any valid memory location. It is often initialized with NULL to signify that it is not currently pointing to a valid object.
Updated on February 17, 2025
