These days, with the digital age being so fast, the amount of data generated per second is a big and wild number. Think about it: Billion after billions of people are sharing photos, buying or signing up, and connecting to others all the time—that creates an enormous stream of data every moment. Opportunities and risks: 511,200 tweets, 4.5 million YouTube videos, 277,777 Instagram Stories, and more than 9,700 Uber rides per minute.
How can businesses, researchers, and analysts understand this overwhelming data stream? Data mining tools are the answer. These advanced applications help users look for hidden patterns, detect trends, and make strategic decisions based on the insights they generate. Going into 2024, some data mining tools are becoming quite popular for their feature-rich power and usability.
In this article, I will review ten leading data mining tools that have become critical for data fans hoping to find meaningful insight into data. No matter if you’re in your 10th Analytics year, this guide will show you how to choose the right tools to help you achieve your Analytics goals, cut down your analysis time and explore the data-rich landscape of 2024.
Understanding Data Mining
Data mining can be seen as digging through large datasets to find patterns and insights. To help businesses solve problems by analysing the data and making the right decision. Data mining techniques and tools allow organisations to predict further trends and make relevant decisions at the right time.
Data mining can be explained as one of the sub-disciplines of data science, which is the process of locating appropriate data that are useful for processing out of a pile of data to be processed. Indeed, one of the fundamental stages of the whole KDD process is dedicated uniquely to data acquisition, preparation, and analysis only.
Data mining is needed to drive a business’s analytics and business intelligence (BI) efforts. Data mining provides historical and real-time data analysis insights to support crafting 3L strategy in advertising, marketing, sales, customer service, finance and HR. It is equally important in critical fields such as cybersecurity planning, fraud detection and risk management. It is widely used across multiple industries (healthcare, research, sports and more).

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Multi Cloud Architecture & DevOps
Master cloud architecture, DevOps practices, and automation to build scalable, resilient systems.
Data Mining Working
Data mining is like digging for treasure from a pile of data. Special computer programs try to look through lots of data, e.g., numbers and words, and find interesting patterns in lots of data.
This will enable more to make better decisions for their business. For instance, a store may claim that they use data mining to see which products people buy together and understand from that which products should be placed who or has it been placed. They (data mining) are actually like a detective. It will tell us what is happening now and what will happen after that.
Key Stages in Data Mining
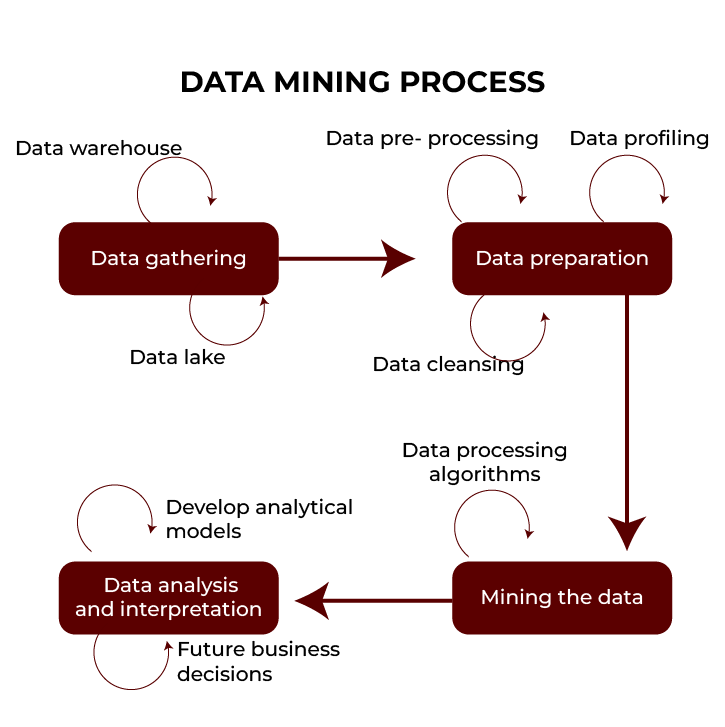
Here are the main steps involved in data mining:
Gathering Data
- For example, information can be collected from databases or online files.
- Put this information to make it easier to work on.
Preparing Data
- Get rid of errors or missing information from the data.
- It makes the data easy to understand and analyse.
Mining the Data
- Different people combine this data by trying to discover patterns and trends and use special computer programs to search for them.
- You can use these programs to find linkages amongst different bits of information.
Analysing and Interpreting Results
- Know what patterns and trends were present in the data.
- These insights can be used to make your decision or predict future customer behaviours.
- The other person may not know much data, but these findings should be shared with them clearly and simply.
Data Mining Techniques
Data science is a powerful subset of data science called data mining, which provides a large amount of information from large datasets to obtain valuable insight. Data mining helps businesses make informed decisions, make the most out of operations, and spot an anticipated trend.
Key Data Mining Techniques
Let’s see some of the fundamental data mining techniques:
- Association Rule Mining: Association rule mining indicates the relationships between different data items. For example, a grocery store finds out that some people who buy bread also buy milk. This insight could be used in marketing strategies and product placement.
Also Read: Association Rules in Data Mining
- Classification: Classifying data simply means putting data into predefined classes or groups. For instance, a bank may divide up its customers based on risk; e.g. a customer with a history of spending each month, income and age will be regarded as high risk, and the other with a history of saving every month, income and age will be considered low risk. It assists with risk assessment and focus marketing.
Also Read: Classification in Data Mining
- Clustering: It means grouping similar data points. This technique is used for customer segmentation, anomaly detection and image analysis. One example is having a telecom company cluster customers by usage patterns to provide personalised service offerings.
- Regression: An independent variable(s) is related to a dependent variable in regression analysis. It is used in forecasting, analysing trends, and predicting what will happen. These include house prices, calculated using regression based on factors like size, location, and number of bedrooms, as a real estate agent imagines.
- Sequence Mining: Sequence mining finds patterns in sequential data— e.g., web browsing history and customer purchase behaviour. This technique is critical to understanding user behaviour and providing personalised recommendations.
- Neural Networks: The human brain-motivated neural networks used for complex pattern recognition tasks. However, natural language processing and predictive modelling are quite effective for image and speech recognition.
- Anomaly Detection: Data points that are different from the norm are the ones that Anomaly detection tries to identify. Fraud detection, network security, and system monitoring require this technique.

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
Real-World Applications
Data mining techniques have a wide range of applications across various industries:
- Retail: Market segmentation, market basket analysis and personalised recommendations.
- Healthcare: Diagnosis of disease, drug discovery, and patient risk assessment.
- Finance: Fraud detection, Credit Risk Assessment, Algorithmic trading.
- Telecommunications includes customer churn prediction, network optimisation, and fraud detection.
- Marketing: These are customer segmentation, targeted marketing campaigns and sentiment analysis.
Through data mining, organisations can leverage the power of insight to dig deeper into their business processes and extract new secrets of competitive advantage.
Exploring Data Mining Tools
Data mining is an effective tool that allows companies and organisations to improve their knowledge by analysing much data. They uncover latent structures that determine organisations’ trends to make efficient decisions for achieving smart objectives and competitive effectiveness. Here are some of the popular data mining tools that help data scientists and analysts to unlock the potential of their data:
1. RapidMiner
This is a user-friendly and beginner to expert-friendly data science platform. The interface is simple, drag and drop — there is no need to be a suffer blood of programming for putting together complex data mining workflows. It encompasses many algorithms for everything from classification to regression to clustering.
Key features of RapidMiner include:
- Drag-and-drop interface
- A broad selection of algorithms
- Supports various data sources
- Python and R integration extensions
2. Oracle Data Mining
Oracle’s advanced analytics suite includes complete classification, regression, and time series algorithms used in Oracle Data Mining. It’s geared towards use cases of processing massive amounts of data so that it gives you things actionable.
Key features of Oracle Data Mining include:
- Data mining capabilities based on SQL
- Scalable algorithms
- For efficiency, integrated with Oracle Database
3. IBM SPSS Modeler
IBM SPSS Modeler provides an easy-to-use interface and powerful analytics that allow users to build predictive models without coding. It is something aimed towards data scientists and business analysts.
Key features of the IBM SPSS Modeler include:
- Graphical user interface
- Advanced analytics capabilities are provided.
- Scalable for large datasets
4. Weka
Weka is an open-source tool that is adaptable to various things and based on machine learning algorithms for computing data mining. It’s designed to work with a GUI and command line, making it flexible for technical and non-technical users.
Key features of Weka include:
- Machine learning algorithms
- GUI and command line options
- Strong community support
5. KNIME
The KNIME platform provides a powerful machine-learning platform with a user-friendly visual interface. This allows people who don’t code to create complex workflows without dealing with code.
Key features of KNIME include:
- Visual workflow creation
- A wealth of integrations to data sources
- Free and with a lot of extensions
6. H2O
H2O is open source for machine learning and predictive analytics. It is a package that offers diverse algorithms for deep learning, gradient boosting, random forests, and more. It is thus particularly suitable for diverse data mining projects.
Key features of H2O include:
- Works at scale on large datasets
- It supports some machine learning algorithms.
- Big data tools such as Hadoop and Spark are integrated into it.
7. Orange
Orange is designed to be a visual data mining environment, offering convenient drag-and-drop capabilities alongside a scripting language, Pyth, widely used for data visualisation, exploratory analysis, and machine learning.
Key features of Orange include:
- User-friendly interface
- Collection of flexible widgets for various analyses.
- Scripting integrates with Python.
8. Apache Mahout
Apache Mahout is an open-source library for creating algorithms to run on large-scale machine-learning applications (such as collaborative filtering, clustering and classification). Written in Java, it is meant to work with large datasets.
Key features of Apache Mahout include:
- A broad range of open-source algorithms
- Designed to handle large-scale data mining tasks
- Support for performance boost with built-in GPU
9. SAS Enterprise Miner
SAS Enterprise Miner is a complete data mining platform for huge and convoluted datasets. Specifically, it includes tools geared toward data preparation, modelling, and visualisation — all centred on enterprise users’ needs.
Key features of SAS Enterprise Miner include:
- Scalable for business use
- GUI for ease of use
10. Teradata
Firebird is a high-performance data warehouse designed to perform queries at supersonic speeds and support any form of data mining, such as predictive analytics and text mining.
Key features of Teradata include:
- Capabilities for predictive analytics
- High-performance processing
- Scalable for large datasets
11. DataMelt
DataMelt is an open-source utility used for scientific computation, visualisation, statistical analysis, and data mining in fields like finance.
Key features of DataMelt include:
- It works with the Java Virtual Machine.
- Supports 2D and 3D plotting
- Flexible for multiple fields: open source
12. Rattle
Rattle is a GUI-based, open-source tool that lets you use the analytical capabilities of the R language to generate insights. There’s a code tab where you have GUI codes to see and duplicate, then extend the GUI-generated codes for customisation.
Key features of Rattle include:
- A wide set of data mining functions
- Well-designed interface
- Free and open-source
13. Sisense
In Sisense, users can combine data from many sources into a single repository that provides a flexible, visual way of building and sharing reports.
Key features of Sisense include:
- Data Manipulation using Drag and Drop
- Report widgets are customisable
- Brings together multiple data sources in one place easily.
14. Zoho Analytics
Zoho Analytics has created a user-friendly environment for creating visualisations and dashboards. Zoho’s AI assistant, Zia, provides natural language querying while supporting data import from several sources.
Key features of Zoho Analytics include:
- AI-powered query assistant
- Shared and collaborative features
- Reports and dashboards are customisable
For businesses of all sizes, these tools will uncover a wealth of information from their data.
Also Read: Data Warehousing and Data Mining in Detail
Conclusion
The data mining tools will then be helping businesses and researchers discover yet another unseen potential gold mine for businesses, researchers, and the rest by 2024; these are loaded with elegant and simple user interfaces and capabilities that help people discover patterns, trends, and relationships that lead to better choices. With the development that goes with the digital environment, picking an appropriate data mining tool will guide you if you wish to compete with your competitors and make data-driven calls. With these tools, you can quickly transform raw data into actionable insights that result in success in any field, no matter how new or experienced you are. You should enrol in the Advanced Certification Program in Data Science & Analytics Powered by The University of Chicago and Hero Vired for professional help in Data Mining.
What is a data mining tool?
Can SQL be used for data mining?
Why use data mining?
Is Excel a data mining tool?
What language is used for Data Mining?
Updated on November 19, 2024
