Today, cloud computing technology is the main backbone of the industry, but still, many businesses are unable to use the technology to its fullest extent.
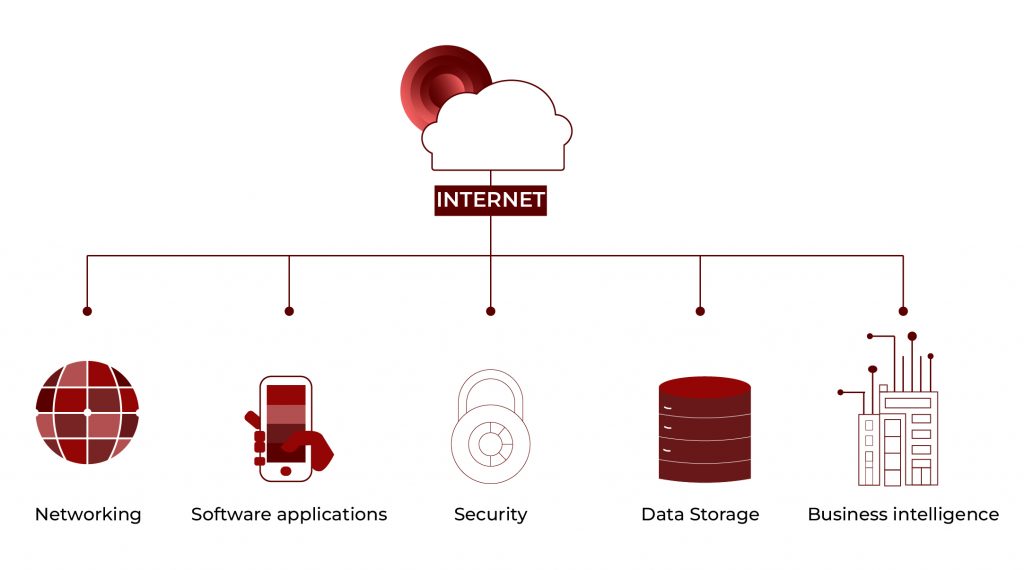
In cloud computing, we can store the data, manage the data, and analyse the data from the internet rather than from the local servers or personal computers.
That primarily benefits enterprises with a more flexible, efficient, and scalable solution. Today, more and more businesses, big or small, are also moving to the cloud to cut costs, boost efficiency, and even allow teams to work together regardless of where they are.
Basically, cloud computing technology takes the worry of hardware away from us and lets us focus on growth and the real business. With this constantly changing technology, one should at least be familiar with the basic features, technologies, and deployment models.
Also Read: 5 Major Types of Cloud Computing
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the technique of storing, managing, and processing data over a network of distant computers hosted on the Internet rather than a local server or computer.
Instead of companies establishing and maintaining their own physical data centres or hardware, they can simply use a cloud provider to give them the resources whenever they need them, and the company only pays for the amount of time that they use it. That way, corporations can expand and contract resources elastically, respond rapidly to variable demand, and ultimately do away with the cost and complexity of the old-fashioned IT infrastructure.
Basically, cloud computing technology completely changes the whole structure of managing data and applications, allowing for more flexibility, efficiency, and availability in all fields.
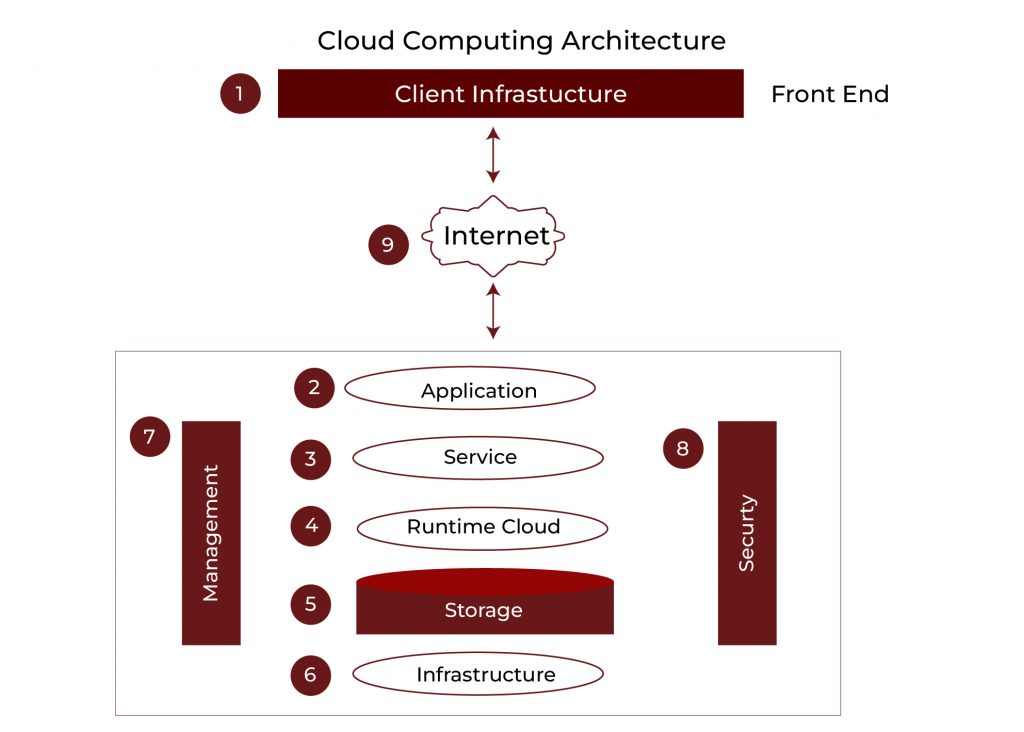
Also Read: Cloud Computing Architecture

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Multi Cloud Architecture & DevOps
Master cloud architecture, DevOps practices, and automation to build scalable, resilient systems.
Key Characteristics that Define Cloud Computing
Cloud computing technology is built on a number of defining characteristics that separate it and allow it to be so special and purposeful. Let’s dive into these defining characteristics.
Scalability and Elasticity
Cloud computing adjusts to meet demand.
It can accommodate as they expand and contract; if traffic just skyrockets, there is no downtime or anything. That adaptability is really nice for the firm with varying demands.
Cost-Efficiency
Cloud services run on a pay-as-you-go basis, meaning that a company pays only for what they use. That is a big savings because there is no large initial investment in servers or infrastructure.
That would also eliminate the recurring costs of upgrading hardware and supporting it.
Resource Pooling and Multi-Tenancy
Cloud providers use a resource pooling model so that a lot of clients can utilise the infrastructure, but with each client’s data being completely separated and secure.
And due to this fact resource pooling allows providers to host services at a fraction of the cost of hosting on dedicated servers.
Broad Network Access
Cloud computing is the capability of utilising computing resources from the internet to any machine having a network connection. This allows employees, clients, and stakeholders to log on from anywhere and still be able to work together.
Reliability and Redundancy
Cloud providers ensure high reliability through data redundancy.
The information is duplicated on two or more servers, so if one server goes down, the information is still available on the other. That dependability equals no loss of data and high app availability.
All these reasons as to why cloud computing is such a convenient and growing answer to the digital requirements of today.
Also Read: Major Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
The Basics of Cloud Computing Technology and Its Relation to Today’s Infrastructure
There are just so many keynote technologies that make cloud computing possible and so efficient. Understanding these can help us better leverage the cloud.
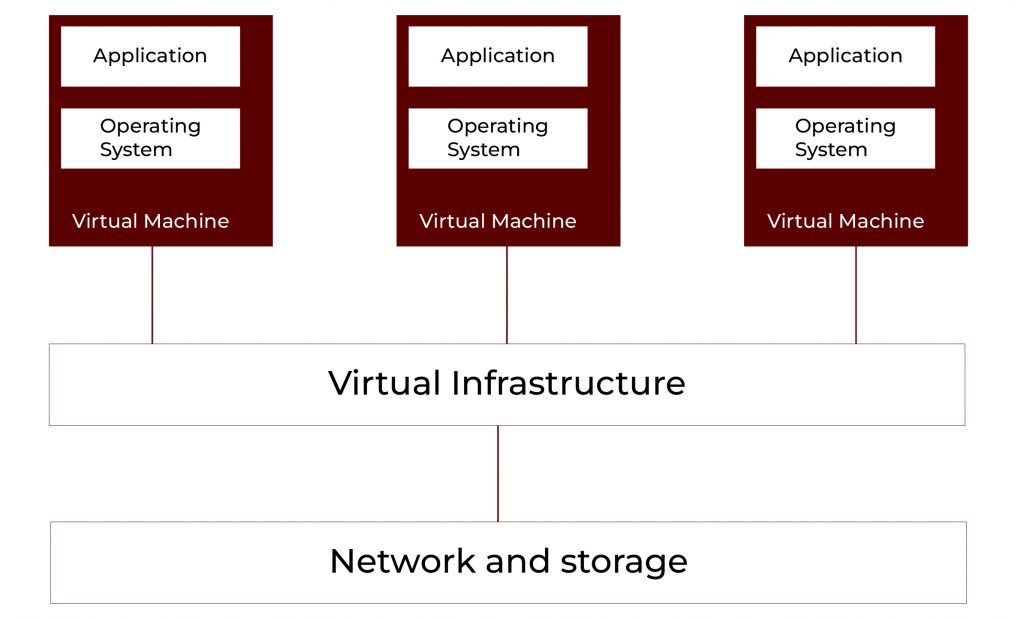
Virtualisation and How It Enables Cloud Efficiency
Virtualisation is a foundational technology for cloud computing. It does this by creating several “virtual machines” on one physical machine, essentially “partitioning” the hardware. Every one is its own server, so it utilises the system resources to the max, and it’s cheaper that way.
For example, instead of purchasing additional physical servers when demand increases, they can merely “add” virtual servers to the existing infrastructure.
This setup streamlines operations and keeps costs under control.
Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) and Its Impact on Cloud Computing
Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) is the foundation that allows cloud systems to deliver these services, which can operate independently or in conjunction if desired. This modular strategy allows businesses to tailor their services to each customer’s specific requirements.
An example may be a medical doctor who wishes to integrate a cloud EMR system with a patient scheduling program.
The SOA makes it easier by having these “loosely coupled” services that can be “plugged” in and out without disturbing anything else.
Containerisation and Orchestration with Docker and Kubernetes
Containerisation is the process of encapsulating an application and all of its dependencies in a container that can operate anywhere on any infrastructure.
Docker is a popular tool for creating these containers.
Kubernetes, on the other hand, controls and conducts these containers, making sure that nothing is wasted.
If a company’s app suddenly experiences high demand, Kubernetes will automatically launch, scale, and manage these containers. This enables considerable traffic without requiring manual help.
Also Read: Docker and Kubernetes
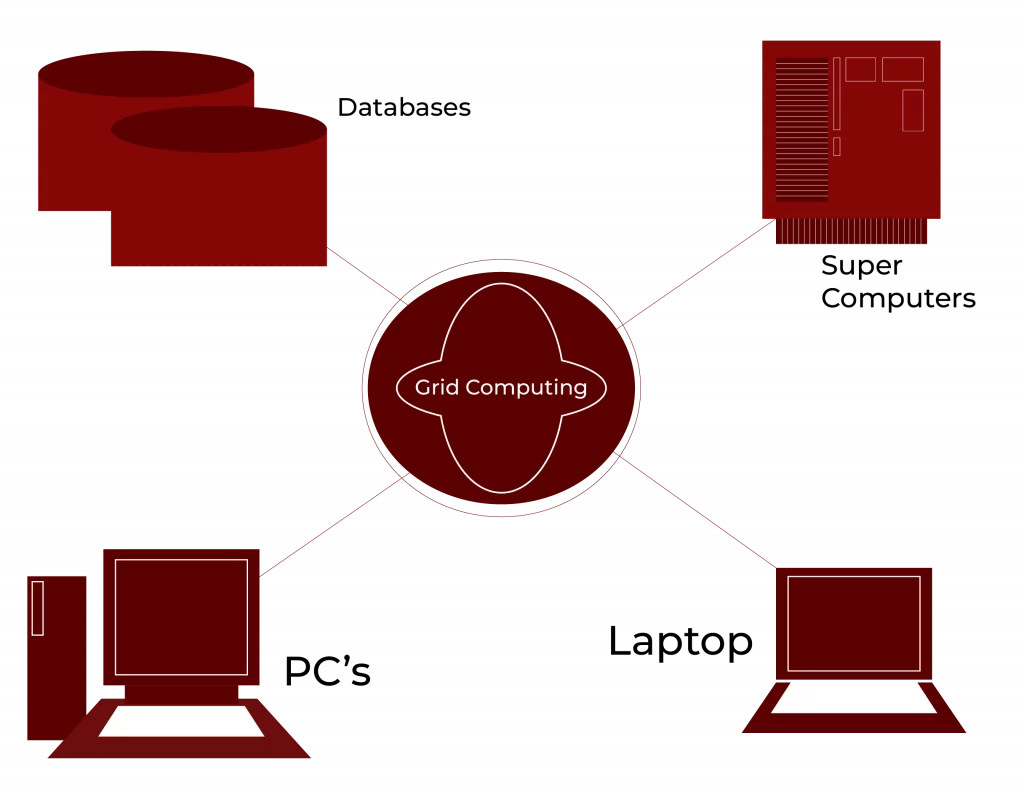
Grid and Utility Computing for On-Demand Resource Management
Grid computing is the use of several computers to work on a single large project, such as processing data for scientific research.
In contrast, utility computing is based on a pay-per-use model. It would be a brilliant idea for any type of enterprise that requires access to high-performance processing capacity on demand.
If they have a really big project and they need to do a lot of processing, with utility computing they can get all that power when they need it and not have to mess with buying all new hardware.
Serverless Computing and Event-Driven Applications
Serverless computing is a model in which developers can run their code without worrying about the infrastructure that runs behind it. Using serverless, a company would only pay for the code to run, so it would be much cheaper for sporadic applications.
It’s perfect for, say, processing payments or moderating a small event on an app.
Like in the case of an e-commerce website, transaction processing would be a perfect serverless computing application since the code would be dormant until a customer submits an order.
This reduces overhead and ensures resources are used efficiently. These building block technologies allow cloud computing to be elastic and extensible so that companies don’t concern themselves with infrastructure but rather with growth.
Exploring Different Cloud Deployment Models for Diverse Business Needs
All business is not alike and that is why cloud computing technology has several deployment models to cater to these differences.
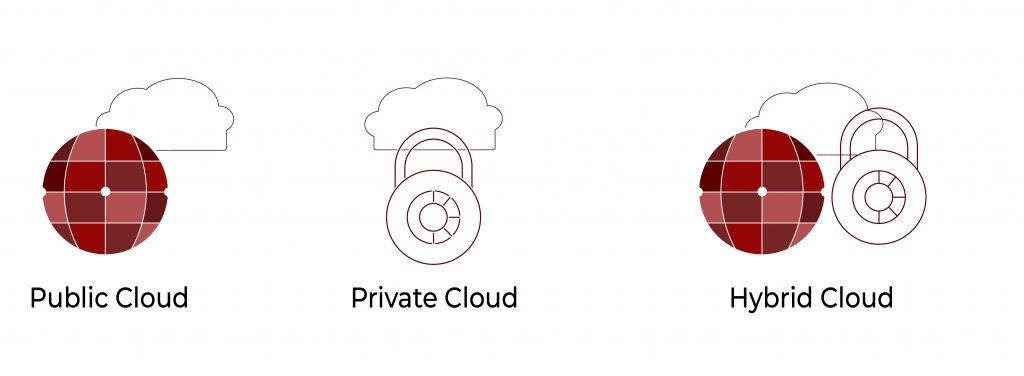
Public Cloud Model for Shared Infrastructure Need
Public cloud is the most widely used model.
In this setup, a cloud provider owns and manages the infrastructure, and multiple clients share resources on a subscription basis. Public clouds are so cheap and so scalable that they’re perfect for start-ups and growing companies.
For instance, a small firm might begin with little capital and flourish as it grows bigger.
With the public cloud, companies no longer need to worry about maintaining, securing and upgrading their systems since all of that responsibility is shifted to the provider, and they can actually focus on their business.
Private Cloud Model for Exclusive and Controlled Environments
Nice for a business that would have to have really strict control over their information like a bank or some kind of government branch.
A private cloud can provide security and the ability to allocate resources to a business’s specific needs. They are a lot more expensive, but the control and security factors are well worth it for the firms that have to deal with that kind of sensitive information.
Hybrid Cloud Model for Flexible and Scalable Solutions
Hybrid clouds are a mix between public clouds and private clouds. It lets the companies keep their “sensitive” information on some private cloud but utilise the public cloud for its less “sensitive” work.
For example, a retail firm could store its customer data on a “private” cloud but its online store on a “public” cloud.
Because it enables cost-effectiveness, scalability, and flexibility, it has gained a lot of popularity among businesses with highly variable workloads.
Multicloud Strategies to Prevent Vendor Lock-In
Using many cloud providers at the same time is known as a multicloud strategy. So, in this way, companies do not have to be reliant on one company, and they can take advantage of the strengths of each company.
For example, a company might use AWS for machine learning, Google Cloud for analytics, and Azure for virtual machines.
Multicloud is great because it is flexible in nature. By utilising the appropriate deployment model, a firm can exploit cloud computing technology to the fullest and in a manner most appropriate for its organisation and thus have more control, scalability, and efficiency.

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
Cloud Computing Service Models Explained for Business Efficiency
A choice of the correct cloud computing technology service model is vital to fully utilising this technology.
Every model has a purpose, and if you are familiar with them, you will be able to choose which one is best for your company.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS is like renting the foundation of a building.
It provides you with all the infrastructure you could possibly need, servers, storage, and networks, and you don’t even have to purchase or maintain any hardware.
With IaaS, you get:
- Full control over operating systems, storage, and applications.
- Capacity to grow or shrink as the business requires it.
- It makes it really cheap because you only pay for what you use.
Like an online retail business that uses IaaS during high usage periods (holidays). Rather than purchasing additional servers, companies may gradually expand the IaaS capabilities and then reduce it when demand is lower.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS functions similarly to a virtual environment where developers may create, test, and launch apps.
This is a good model, it gives the developers all the tools and infrastructure they need and just lets them build without worrying about the hardware.
With PaaS, businesses gain:
- Speed in developing applications.
- Simplified deployment processes.
- Lower IT costs because maintaining the infrastructure is the responsibility of the provider.
For example, an enterprise designing a mobile application could employ PaaS to easily distribute updates, perform tests, and swiftly build up an environment. They save time and money by avoiding hardware setup.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is a comprehensive solution in which a provider hosts and manages apps. These applications are accessed over the internet, so they require no technical setup to use.
SaaS provides:
- Accessibility from any device with an internet connection.
- Regular updates are managed by the provider.
- No installation or maintenance requirements for users.
Consider SaaS as a CRM platform or other subscription service. A sales team may manage contacts, follow prospects, and examine data analytics using SaaS CRM without needing to contact IT.
Function as a Service (FaaS) and Serverless Computing
FaaS takes cloud computing a step further by charging only when code runs. It’s event-driven, which is good because many applications don’t need to be awake the entire time.
Benefits of FaaS include:
- Cheaper, as you only pay for the time of execution.
- Scalability to handle sudden spikes in demand.
- No infrastructure management since everything runs on the provider’s servers.
For example, a web service uses FaaS to process images, but only when a user actually sends in an image. This approach minimises costs and simplifies management.
Also Read: Major Types of Cloud Service Models
Real-World Applications of Cloud Computing Across Different Sectors
Cloud computing technology has really changed industries with a lot of applications in various fields.
Let’s see how different fields benefit from cloud technology.
Healthcare Industry: Using Cloud for Patient Data Management and Real-Time Monitoring
Further, cloud computing technology can be utilised in healthcare to provide for a secure storage of patient records, as well as providing real time data sharing.
Updated information can be instantly available to doctors, labs, and clinics, which means better patient care.
Through wearable devices, continuous monitoring and quick response become possible with real-time health data sharing, like heart rate or glucose level, with the cloud.
Retail and E-Commerce: Cloud for Improved Customer Engagement
Cloud computing technology helps retailers improve their interactions with customers, with the goal of providing personalised services to them.
Inventory systems based on the cloud track stock levels between stores in real-time and eliminate stock out and delivery time delays. Cloud storage allows customer data that means tailored recommendations are made, resulting in better shopping experiences.
Cloud resources scale up to deal with heavy referral traffic as well without adversely affecting performance during periods like sales during festivals.
Education Sector: Cloud-Based Learning Management Systems
Cloud computing technology has revolutionised education by making resources available everywhere.
Cloud-hosted learning management systems (LMS) make it possible for students and teachers to study online remotely, submit assignments, and even take tests.
Just like with online courses, where it’s the complete opposite, Universities can utilise a cloud-based LMS to provide online courses and webinars, which brings learning far beyond physical classrooms.
Financial Services: Cloud-Based Fraud Detection and Prevention
Cloud computing technology is used by financial institutions for data driven insight as well as fraud prevention.
In these systems, transaction patterns are analysed in real-time so that suspicious activity is spotted and alerts are triggered in real-time. The cloud allows for the storing and processing of very large datasets in a way that provides a level of security necessary to support compliance with regulatory requirements.
With cloud-based machine learning, financial services are given powerful tools for proactive fraud detection.
Cloud Computing Advantages and Benefits for Small and Large Business
Growth and operations are made easier, and businesses of all sizes benefit from cloud computing advantages.
Here are some of the key benefits that make cloud computing technology adoption worthwhile.
Cost Savings
- No need for expensive hardware and maintenance.
- Pay-as-you-go model reduces capital expenses.
- Frees resources for revenue-driving areas.
Scalability and Flexibility
- Adapts to changing business needs.
- Scale resources up or down as needed.
- Ideal for seasonal or unpredictable demand.
Increased Collaboration and Accessibility
- Real-time collaboration from any location.
- Secure access from any device.
- Supports remote work and productivity.
Data Security and Reliability
- Features like encryption, access control, and backups.
- Data stored across multiple centres for reliability.
- Ensures business continuity.
Common Challenges and Potential Drawbacks in Cloud Adoption
While cloud computing technology is really awesome, there are some perks and some pitfalls that businesses aren’t aware of.
Understanding them will help to make informed decisions.
Security and Data Privacy Concerns
- Risks of unauthorised access and compliance issues.
- Importance of encryption and access control.
Downtime and Reliability Issues
- Internet-dependent; downtime can disrupt access.
- Redundancy is recommended for critical operations.
Managing Cloud Costs
- Unmonitored usage can lead to high bills.
- Cost management tools help control spending.
Integrating Cloud Computing with IoT for Enhanced Connectivity and Performance
How are companies going to store and manage and interpret all the data that is going to be generated by all the sensors and appliances and cars and whatnot that are all going to be smart and connected?
This is where cloud computing fits in the Internet of Things (IoT).
Cloud computing technology is the basis for all that data that the IoT creates, and it offers the storage, processing power, and connectivity that the IoT devices require to operate.
Let’s talk about some IoT cloud integration real-world stuff:
- Smart Cities: In a smart city project in India with IoT sensors, monitoring air quality, traffic lights, and street cameras becomes easy.
- Precision Agriculture: IoT can measure the moisture, temperature and nutrient levels of any field and store them in cloud. Analysing that data will help farmers to make accurate agricultural decisions.
- Healthcare Monitoring: Wearable technology can monitor patients and send all the vital signs to medical professionals via the cloud.
The Role of Cloud Computing in Big Data and Analytics for Data-Driven Decisions
Data is the foundation of almost every industry’s decision-making process, and it takes a lot of infrastructure to store and evaluate vast volumes of data.
Cloud computing technology makes all of this easier by offering scalable storage and processing tools, along with advanced analytics capabilities. Cloud analytics allows businesses to turn raw data into meaningful information without the need for expensive on-site equipment.
Lets say a telecom company in India wants to analyse call data to help better their customer service.
They could use cloud-based big data tools to store call records and analyse patterns and problems in real-time. This method is fast, cheap, and expandable, perfect for large amounts of data.
These are the main advantages of cloud computing to big data analytics:
- Real-Time Processing: Real-time data streams are processed by cloud platforms from many sources.
- Cost-Efficiency: Rather than companies paying large amounts of money for infrastructure, they pay only for the amount of cloud storage and processing that they use.
- Scalability: Cloud solutions are also easily scalable as data grows without having to worry about complicated infrastructure upgrades.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact of Cloud Computing
With sustainability becoming more of a focus in business, the green aspect of cloud computing technology is a significant one.
Cloud computing technology is not only easy for companies to host their data and applications, but when they do, they are much more likely to have green operations instead of the typical data centres that companies keep in-house. Cloud providers are also putting a lot of money into renewable energy, energy-efficient cooling systems, and carbon-neutral strategies so that their environmental impact is lessened.
For instance, Microsoft Azure says that it will be powered by 100% renewable energy by 2025.
For example, other cloud providers like Amazon Web Services also have very aggressive goals for reducing carbon emissions, so even cloud computing is green.
Some of the sustainability benefits include:
- Lower Power Consumption: If everyone shares the cloud infrastructure, then the resources are utilised to their fullest extent, and energy demand is not as high.
- Reduced Hardware Waste: Cloud services minimise the need for physical servers, decreasing electronic waste.
- Renewable Energy Initiatives: Many providers are shifting towards renewable energy. Thus, the carbon footprint of data centres is decreasing.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Cloud Provider
Finding a trustworthy partner that shares your company’s needs is more important when selecting a cloud provider than simply comparing prices.
Thus, while selecting a service, keep the following considerations in mind:
Security and Compliance
- Prioritise security features like encryption and multi-factor authentication.
- Look for compliance with standards like ISO and GDPR.
- Ensure compliance for handling sensitive data.
Performance and Reliability
- Check for guaranteed uptime and minimal disruptions.
- Review SLAs for uptime commitments and support.
Cost and Pricing Models
- Compare pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, and hidden fees.
- Use cost management tools to monitor usage.
Support and Customer Service
- Look for 24/7 customer support availability.
- Consider support options like dedicated managers and technical tiers.
Scalability and Flexibility
- Ensure the provider can scale with your business growth.
- Look for flexible options for different workloads and stages.
You really have to weigh all these factors very delicately so that you can select a provider that not only meets your operational needs but will also enable you to meet your business objectives in the most cost-effective and efficient manner possible.
Conclusion
Cloud computing technology is a very robust technology for solving many of today’s modern business problems. With its flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency, it enables organisations to focus on growth without heavy investments in physical infrastructure.
Key service models like IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, and FaaS cater to diverse business needs, while deployment options allow for precise control over data and applications. IoT-connected cloud solutions provide real-time tracking and analysis, which can lead to data-informed decision-making in industries ranging from healthcare to retail.
From growing sustainability practices to extreme security measures, cloud computing is not only fiscally responsible but environmentally responsible.
With the correct provider and strategy, companies should be more than able to innovate, compete, and accept the future.
For those who wish to delve further and master this subject, the Certificate Program in DevOps and Cloud Engineering by Hero Vired is a great way to go. It is a hands on course on cloud infrastructure, DevOps practices, and actual tools used in the field and gives you a job in one of the most exciting fields in tech today.
How do I determine which cloud deployment model is right for my business?
Is cloud computing secure, and what measures ensure data protection?
How does cloud computing support sustainable business practices?
Why is serverless computing gaining popularity, and what does it mean?
Updated on November 11, 2024
