Has your computer been seeming to run a little slow, even though you are only running a few programs? Maybe everything seems laggy, and you are wondering what is going on. Is it some virus? Is my hardware too old?
What if I told you the problem might be something you’ve never heard of before thrashing in OS?
Thrashing in OS isn’t a term you hear every day, but it’s a real headache.
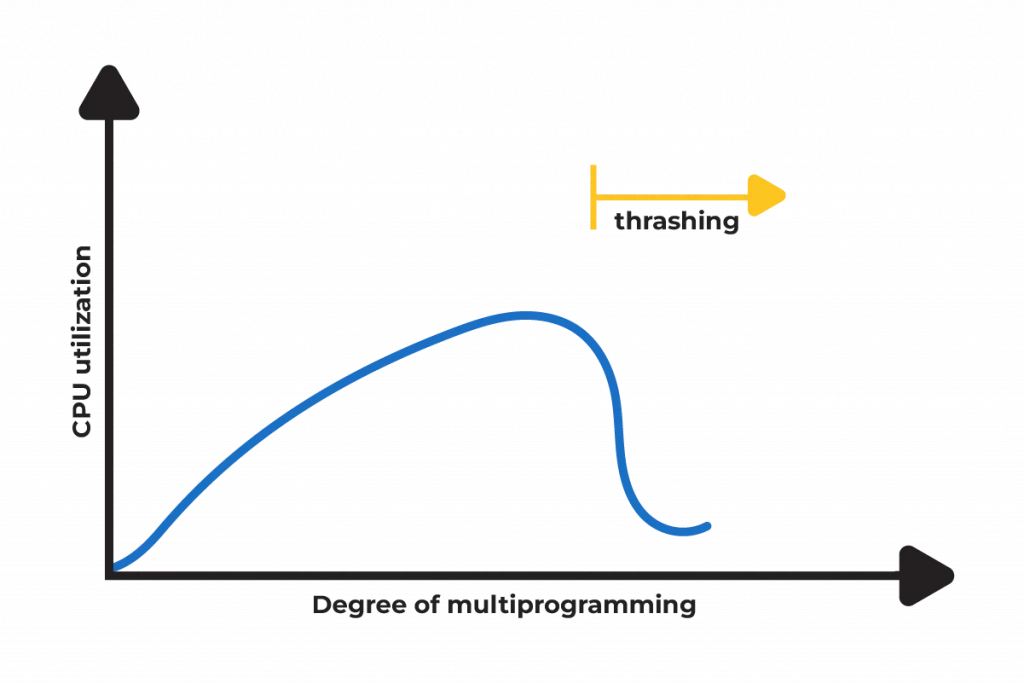
Thrashing in OS is a common phenomenon in computer systems whereby the system spends more time in swapping pages than it actually does performing some useful work.
The reason for thrashing is a high number of page faults: the system constantly has to get a page from the disk that is not in memory. This means that rather than processing your work, your operating system is busy swapping data back and forth between RAM and the hard drive.
The result? Sluggish performance that can frustrate you.
Let’s dive into that so next time your computer drags; you will have an exact idea of what is going on and how to get it over with.
How Thrashing Occurs in an Operating System
The Reason Behind Thrashing in Your Operating System
So, what exactly is thrashing in OS? To understand it, we first need to talk about virtual memory and paging.
Your computer’s RAM is where active data is stored for quick access. But RAM isn’t infinite.
When you run more applications than your RAM can handle, your OS uses a trick called virtual memory. It swaps out less important data to a part of your hard drive, freeing up RAM for what you’re doing right now.
This swapping process is known as paging.
Now, here’s where things get tricky. When the OS starts swapping too much—constantly moving data in and out of RAM—it can’t keep up. The CPU is waiting on data and the system performance drops.
Instead of running your programs smoothly, your computer is stuck in a loop of moving data around. This is thrashing.
The Relationship Between Page Faults and Thrashing
Every time your computer can’t find the data it needs in RAM, it experiences what’s called a page fault. Usually, that isn’t a big deal unless the number of page faults is too high.
If too many page faults occur, then the OS must repeatedly fetch data from the hard drive, slowing things down.
The more this occurs, the more your system thrashes.
The Role of Memory Management in Thrashing
Memory management is the key to avoiding thrashing. If you will, it’s the brain of your computer’s operations: it makes a decision about which data should be retained in RAM and which should be swapped out.
If memory management is poor, then the chances of thrashing are very high.
Consider working on a big project; multiple applications are running simultaneously. If your OS is not performing well in the case of memory management, then it will result in excessive swapping of data.

Get curriculum highlights, career paths, industry insights and accelerate your technology journey.
Download brochure
Key Factors That Contribute to Thrashing in OS
There are various reasons for thrashing in OS. Knowledge of them might help you avoid making your system crawl.
- Insufficient Physical Memory: Every time your computer runs out of RAM, it relies more on virtual memory. The more it will have to swap, the greater the possibility of thrashing.
- High Degree of Multiprogramming: If many programs are running on your system all at once, then it may become overwhelmed by this and cause excessive paging and, hence, thrashing.
- Poor Memory Management Techniques: If your OS isn’t managing the memory, then the system can cause continued additional shuffling of data, thereby raising the occurrence of thrashing.
- Aggressive or Ineffective Paging Algorithms: The high degree of aggressiveness in some paging algorithms results in unnecessary swapping and hence leads to thrashing.
- Overcommitment of System Resources: This is when your system tries to do much more than it is capable of- for example when running many heavyweight applications simultaneously. The system has a very good chance, under such circumstances, of thrashing.
Recognising the Symptoms of Thrashing in Your System
Knowing the signs of thrashing in OS will save you a lot of frustration. If you notice any of the following, thrashing could be the reason:
- High CPU Utilisation With Very Little Productive Work Accomplished: If the CPU is running hot, yet your tasks are not being executed, then the problem could be thrashing. The CPU spends time swapping instead of processing your commands.
- Increased Disk Activity Indicating Frequent Swapping: The high usage of a hard drive can be viewed by the disk activity light, which constantly blinks. This might mean your system is thrashing.
- Slowing Down System Response Times: When everything appears to open slowly, such as files, apps, or even typing, your operating system may be caught within a thrashing loop.
- High Page Fault Rates as a Red Flag: In nearly all cases, high page fault rates are indicative of thrashing. It’s easy to find monitoring tools that make issues like this easier to catch long before they’re bigger issues.
When thrashing kicks in, your computer stops being a tool and starts being a problem.
Instead of running your programs smoothly, the system is bogged down with swapping data between memory and storage.
This isn’t just annoying; it can make your system nearly useless.
How Thrashing Leads to System Slowdowns and Freezes
Imagine trying to drive a car that keeps stalling every few seconds.
That’s what your computer goes through during thrashing.
The CPU spends most of its time swapping pages in and out of memory, leaving little room to actually process tasks.
This constant swapping can slow your system to a crawl.
You might even see complete freezes, where the system becomes unresponsive for long periods. Every click feels like it takes forever to register. And if you’re working on something important, this can be a real nightmare.
The Effect of Thrashing on User Experience and Productivity
When thrashing takes over, productivity goes out the window.
Simple tasks like opening a document or browsing the web become tedious. Programs take ages to load. Switching between applications becomes an exercise in frustration.
And the overall user experience? It plummets.
The more your system thrashes, the less you get done.
It’s like trying to work in a noisy room—every distraction pulls you away from what you’re trying to achieve.
Potential for System Crashes Due to Severe Thrashing
Thrashing isn’t just a performance issue; it’s also a stability risk.
As your system gets caught in a loop of constant swapping, the chances of a crash increase. Your OS might simply give up, leading to sudden shutdowns or reboots. In the worst-case scenario, this can lead to data loss.
Comprehensive Methods to Handle Thrashing
Now that we know what thrashing is and what it does let’s take a closer look at how to manage it.
Optimising Memory Management for Better Performance
The very first line of defence against thrashing is efficient memory management.
How? Here’s the way:
- Increase Physical Memory (RAM): Adding more RAM to your system reduces the possibility of thrashing since more data could reside within the memory and wouldn’t have to be swapped out frequently.
- Use a More Efficient Page Replacement Algorithm: Certain algorithms efficiently estimate or predict which page will be used next. Similarly, with the usage of an intelligent algorithm, we can avoid unnecessary page faults and, hence, thrashing.
- Monitor Memory Usage: Regularly check your memory usage to understand how well your system is using the memory. If the consumption is at a high rate, then you should shut down some applications or upgrade the hardware.
Techniques to Reduce the Degree of Multiprogramming
Another strategy for preventing thrashing is based on running fewer programs simultaneously.
This may sound ordinary, but it is so effective:
- Limit Background Applications: Close any extra applications running in the background. The less tasks that are being dealt with by your OS, the better.
- Prioritise Important Applications: Let your system draw more resources to the applications that matter the most. By giving priority to important tasks, we are guaranteed that they will run smoothly, even on heavy loads.
Working Set Model Implementation to Avoid Thrashing
Another tool in our arsenal is the working set model.
It’s a methodology that enables your OS to retain the most frequently used data in memory.
Here’s how it works:
- Determine the Working Set: A working set is a set of pages that a process currently works with. By keeping this data in memory, constant swapping is reduced.
- Adjust Memory Allocation Based on the Working Set: We can prevent thrashing if we dynamically reallocate memory to each process based on its working set.
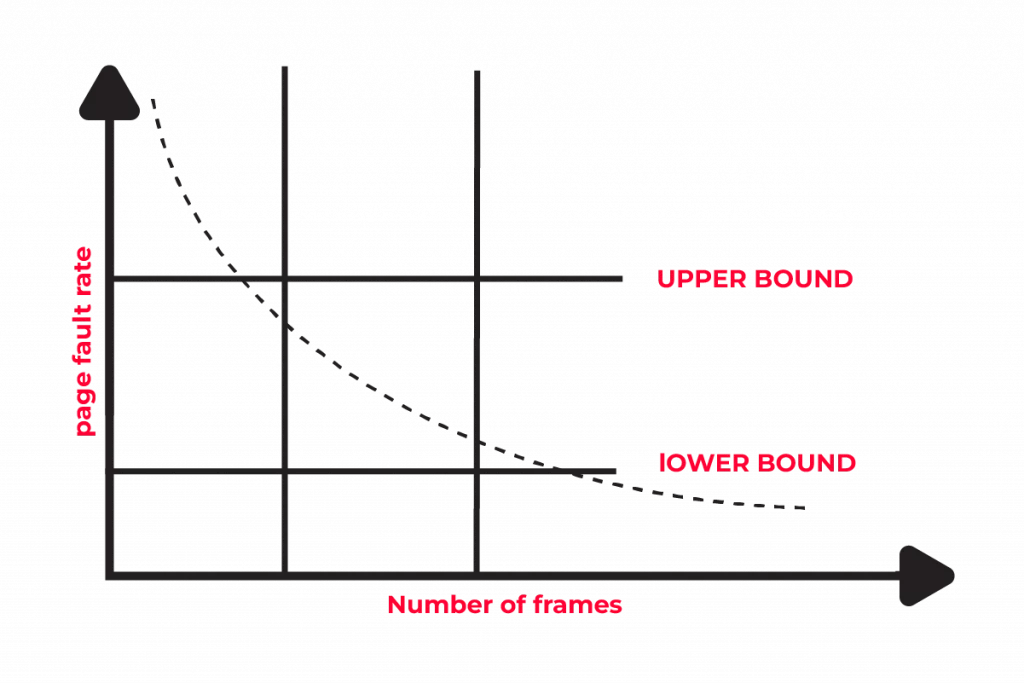
Using Page Fault Frequency Control to Manage Thrashing
Page fault frequency control is a direct approach to managing thrashing.
It’s all about keeping an eye on how often page faults occur.
- Set Upper and Lower Limits: We can set thresholds for page faults. If the page fault rate gets too high, the OS can take action, like reducing the number of active processes.
- Suspend Processes if Necessary: In extreme cases, we might need to suspend some processes to bring the page fault rate down. It’s a tough call, but it can save your system from crashing.
Prioritising Processes to Prevent Excessive Swapping
Not all processes are created equal. Some are more important than others.
By prioritising critical processes, we can ensure they get the resources they need without getting caught up in thrashing.
- Assign High Priority to Important Tasks: Make sure critical applications have top priority. This helps them avoid getting bogged down by less important tasks.
- Defer Non-Essential Processes: If a process isn’t urgent, it can wait. By deferring less critical tasks, we can keep the system running smoothly.
Swapping and Load Control Techniques for Stability
Finally, let’s talk about controlling the load on your system.
It’s all about balance:
- Control Swapping Frequency: Limit how often the OS swaps data in and out of memory. By controlling this frequency, we can reduce the chances of thrashing.
- Manage System Load: Keep an eye on the overall load. If things get too heavy, consider offloading some tasks or upgrading your hardware.
Real-World Examples Illustrating Thrashing in Different Scenarios
Let’s look at some scenarios where thrashing in OS can cause problems and how we can handle them.
Thrashing in Video Editing Applications with Limited RAM
Suppose you’re editing a high-definition video on a computer with limited RAM.
The system constantly swaps video data in and out of memory, trying to keep up with your edits. As the project grows, so does the thrashing.
The result?
A laggy editing experience where every change takes ages to process.
The solution?
Upgrading your RAM and closing unnecessary applications can make a world of difference.
How Database Servers Experience Thrashing During Heavy Query Loads
Think about a database server handling thousands of queries per second.
If the server’s memory can’t keep up, it starts thrashing. Queries that should take milliseconds stretch into seconds.
For a business, this could mean lost revenue as customers get frustrated and leave.
The fix?
Optimising queries, increasing memory, and fine-tuning the database settings can help reduce the load and prevent thrashing.
The Impact of Thrashing on Web Servers During Traffic Spikes
Your website is suddenly flooded with visitors.
Great news, right?
But if the server is not able to manage the load, thrashing might be the result. It takes ages to load a page, or even worse, the whole website freezes.
To avoid this, consider load balancing, increasing server resources or leveraging a content delivery network – CDN to distribute the load.
Virtual Machines Competing for Resources on Overloaded Hosts
In a virtualised environment, one or more virtual machines are run on a physical host and can use the same physical resources. If there are too many VMs that are operational, they begin to fight for memory space, and this results in thrashing.
The result?
All the VMs slow down, affecting every service running on them.
One way to avoid this is to carefully manage the allocation of resources to each VM and ensure the host machine has enough memory to handle the load.
Thrashing in Gaming Applications Rendering Complex Scenes
Suppose you are playing a game that is seeking to represent a massive, detailed world.
If your system doesn’t have enough memory, it starts thrashing. The game becomes choppy, with frames dropping left and right.
It’s not just frustrating—it’s unplayable.
The fix?
Make sure your gaming rig has enough RAM and that the game settings are optimised for your hardware.
Future Trends and Developments to Reduce Thrashing Risks
Is thrashing in OS a problem we’ll have to deal with forever?
Or can technology finally put an end to this frustrating issue?
Every new generation of operating systems and hardware brings with it a set of new trends that promise to make thrashing less of a headache. Let’s discuss some of these trends that might alter the future landscape.
Increasing Availability of Non-Volatile Memory to Combat Thrashing
One of the most exciting trends to hit computing lately has been that of non-volatile memory.
Unlike traditional RAM, the data in NVM persists after the power is turned off. It is faster compared to hard drives and can reduce, up to a large degree, the use of swapping data constantly.
With NVM, your system could handle more data in memory, cutting down on the page faults that lead to thrashing.
Emerging Memory Management Techniques in Modern OS
As we move forward, operating systems will get smarter in terms of memory management.
New algorithms and techniques come up to predict quite accurately which data can be kept in RAM and which should be swapped out. These enhancements translate to fewer superfluous page faults and, all in all, increased efficiency and speed for the end user.
For example, some OS developers are working on memory compression techniques.
This allows more data to be stored in RAM without increasing physical memory, reducing the chances of thrashing.
Another technique being developed is adaptive memory management. The operating system dynamically adapts its memory allocation strategy based on the workload.
Leveraging Machine Learning to Predict and Prevent Thrashing
Now, ML is no longer just the domain of self-driving cars and recommendation systems, but it’s steadily making its way into operating systems.
ML algorithms can analyse how your system uses memory and predict when thrashing might occur.
This allows the OS to take proactive steps to prevent it before it happens.
For example, an ML model could learn your usage patterns over time. It could then allocate memory more efficiently based on what you’re likely to do next.
This means your computer stays fast and responsive, even under heavy load.
Conclusion
Thrashing in OS is a major performance bottleneck where, most of the time, it gets utilised by the system in swapping rather than the execution of tasks. Such situations may result in slowdowns, freezes, and even crashes if it is the worst case.
No single remedy exists to solve this problem. Increasing physical memory, trying better memory management techniques, or trying to meet emerging technologies like non-volatile memory or machine learning are some ways one can try to tackle the problem.
Knowing what thrashing is and how to take action to prevent it allows our computing experiences to be smoother and more predictable; it aids in minimising all the frustrations that come with a system that can get really sluggish.
The future of memory management could be enlightening, truly minimising or even eliminating the impact of thrashing.
FAQs
When there are too many tasks for a system to handle, the system suffers from too much paging, hence slowing down its performance.
Yes, machine learning can analyse usage patterns and predict when thrashing might happen, allowing the OS to take preventive measures.
Non-volatile memory remembers data when power is off, reducing, therefore, the amount of swapping that needs to occur, hence reducing thrashing.
Some modern operating systems are beginning to implement these techniques, though they are still in the early stages of development.
Yes, more RAM always helps, but with advancements in memory management, future systems might rely less on sheer RAM capacity and more on smarter allocation strategies.
Updated on December 10, 2024


