Python is a programming language that supports the object-oriented programming language. There are four principles in OOPs language: Abstraction, Inheritance, Encapsulation, and Polymorphism. In this article, we will learn about the Polymorphism in Python language. Polymorphism is a fundamental concept in Object Oriented Programming language.
What is Polymorphism in Python language?
Polymorphism means different forms. In a programming language, Polymorphism refers to a function having the same name but being used in different ways and different scenarios. It makes programming more interactive and intuitive.

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Multi Cloud Architecture & DevOps
Master cloud architecture, DevOps practices, and automation to build scalable, resilient systems.
Types of Polymorphism
In the Python language, We can achieve Polymorphism in the Python language in two ways: method overriding and method overloading.
- Method Overriding: Method overriding means a subclass providence, a specific implementation of a method that is already defined in the superclass. This allows a subclass to modify or extend the behaviour of the method defined in the superclass.
- Method Overloading: Method overloading means defining multiple methods with the same name in a class but with different parameters. Python does not support method overloading in the traditional sense because it does not allow multiple methods with the same name and different parameters. However, we can achieve method overloading through the default arguments and variable-length argument lists.
Polymorphism Example in Python language
Let’s deep dive into some examples of Polymorphism in Python language.
- Method Overriding: The following program demonstrates the Overriding in Python language.
Program
class Animal:
def speak(self):
return "Animal speaks"
class Dog(Animal):
def speak(self):
return "Dog barks"
class Cat(Animal):
def speak(self):
return "Cat meows"
# Polymorphism in action
animals = [Dog(), Cat()]
for animal in animals:
print(animal.speak())
Output
Dog barks
Cat meows
In this example, we inherit the Dog and Inherit classes from the Animal class and override the speak() method. When we call the speak() method on objects of these classes, each object responds differently based on its specific implementation.
- Method Overloading: The following program demonstrates the Method overloading example
Program
class Calculator:
def add(self, x, y):
return x + y
def add(self, x, y, z):
return x + y + z
# Method overloading in action
calc = Calculator()
print(calc.add(1, 2))
print(calc.add(1, 2, 3))
Output
TypeError: Calculator.add() missing 1 required positional argument: 'z'
In this example, the interpreter gave us the error. We defined the two add() methods with different parameters in a class. However, in Python, only the latest defined method will be considered, and the earlier one is overridden. If we try to call the first method. Then, It will raise a ‘TypeError’ method because it expects three arguments.
Function of Polymorphism in Python
Some functions in the Python language are compatible with multiple data types. One such function is the len() function. It can run with many data types in the Python language. Let’s look at some examples of the Python language.
Program
print(len("HeroVired Article"))
print(len(["Python", "Java", "C", "Computer"]))
print(len({"Singh is King": "Akshay Kumar", "Tarzan Wonder Car": "Watermelon"}))
Output
17
4
2

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
Class Polymorphism in Python
We can also implement Polymorphism using the classes in Python language. Python allows classes to have different methods having the same name and so on.
The following example demonstrates Polymorphism in classes.
Program
class Cat:
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def info(self):
print(f"I am a cat. My name is {self.name}. I am {self.age} years old.")
def make_sound(self):
print("Meow")
class Cow:
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def info(self):
print(f"I am a Cow. My name is {self.name}. I am {self.age} years old.")
def make_sound(self):
print("Moo")
cat1 = Cat("Kitty", 2.5)
cow1 = Cow("Fluffy", 4)
for animal in (cat1, cow1):
animal.make_sound()
animal.info()
animal.make_sound()
Output
Meow
I am a cat. My name is Kitty. I am 2.5 years old.
Meow
Moo
I am a Cow. My name is Fluffy. I am 4 years old.
Moo
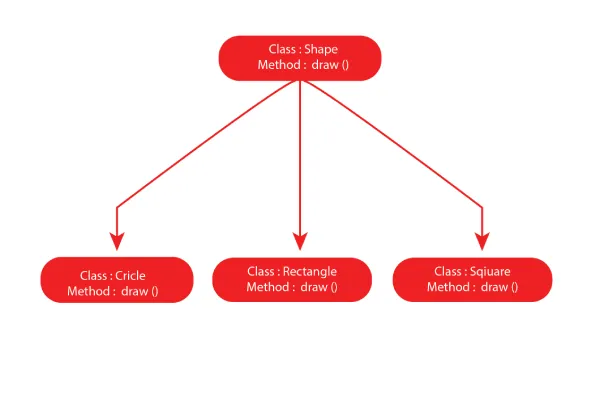
Polymorphism in Python with Inheritance
Python child classes also inherit methods and attributes from the parent class, which we can redefine. It is also known as Method Overriding.
Polymorphism allows us to access overridden methods and attributes that have the same name as the parent class. The following program demonstrates polymorphism in the Python language.
Program
from math import pi
class Shape:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
def area(self):
pass
def fact(self):
return "I am a two-dimensional shape."
def __str__(self):
return self.name
class Square(Shape):
def __init__(self, length):
super().__init__("Square")
self.length = length
def area(self):
return self.length**2
def fact(self):
return "Squares have each angle equal to 90 degrees."
class Circle(Shape):
def __init__(self, radius):
super().__init__("Circle")
self.radius = radius
def area(self):
return pi*self.radius**2
a = Square(4)
b = Circle(7)
print(b)
print(b.fact())
print(a.fact())
print(b.area())
Output
Circle
I am a two-dimensional shape.
Squares have each angle equal to 90 degrees.
153.93804002589985
Polymorphism with Class Methods
In this section, we will define two classes. In those classes, we have some methods. After that will put those class objects into a tuple. If we now iterate this tuple of objects, the for loop will execute all the given methods for the first object in the apple, then the second object in the tuple and so on.
This is an example of Polymorphism with class methods.
The following program demonstrates the Polymorphism in Class Methods
Program
class Cat:
def mood(self):
print("Grumpy")
def sound(self):
print("Meow")
class Dog:
def mood(self):
print("Happy")
def sound(self):
print("Woof")
hello_kitty = Cat()
hello_puppy = Dog()
for pet in (hello_kitty, hello_puppy):
pet.mood()
pet.sound()
Output
Grumpy
Meow
Happy
Woof
Polymorphism with Functions with Objects
In this section, we will use Polymorphism with functions and objects in Python to reverse the ability of a function to operate on objects of different types, treating them in a uniform manner. This allows for flexibility and modularity in the code design. Let’s explore an example to illustrate polymorphism with functions and objects.
The following program demonstrates the Polymorphism with function with Objects.
Program
class Fruits():
def type(self):
print("Mango")
def color(self):
print("Mango Color is Yellow")
class Vegetables():
def type(self):
print("Tomato")
def color(self):
print("Tomato is Red")
def func(obj):
obj.type()
obj.color()
#creating objects
obj_beans = Fruits()
obj_mango = Vegetables()
func(obj_beans)
func(obj_mango)
Output
Mango
The Mango Color is Yellow
Tomato
Tomato is Red
Conclusion
In this article, we learned about polymorphism in the Python language. Polymorphism means we can implement the same thing in different forms. Through methods, functions, and class inheritance, Python allows for the implementation of polymorphic behaviour, where the same interface can be used in different ways. Developers must know that polymorphism is essential for mastering object-oriented programming and writing efficient, modular code in the Python language.
What is Polymorphism in Python?
Why do we need polymorphism?
- It is beneficial to reuse the codes.
- The codes are simple to debug.
- A single variable can store multiple data types.
Updated on July 18, 2024
