One-dimensional arrays are a fundamental data structure in computer programming, particularly in the C language. They allow you to store the same type of data in the memory, providing a simple and efficient way to store multiple values in a single variable. In this article, we will delve into the world of one-dimensional arrays in C.
What is an Array in C?
An array is a collection of one or more elements in the same data type. It is stored in contiguous memory locations and can be any type, such as int, char, float, etc. We can also use arrays with user-defined data types, such as pointers, structures, etc.
Example of Arrays
// This program illustrates the Arrays in c language
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// declaring an array of integers
int arr_int[5];
// declaring array of characters
char arr_char[5];
return 0;
}

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Multi Cloud Architecture & DevOps
Master cloud architecture, DevOps practices, and automation to build scalable, resilient systems.
Types of Arrays
There are three types of Arrays in C language:
- One-dimensional Arrays
- Two-dimensional Arrays
- Multi-dimensional arrays
Introduction to One-Dimensional Array in C
We can imagine one-dimensional arrays in C as a single row storing the elements. In an Array, All the elements are stored in a contiguous memory location in Arrays. Array elements can be accessed using the indexing.
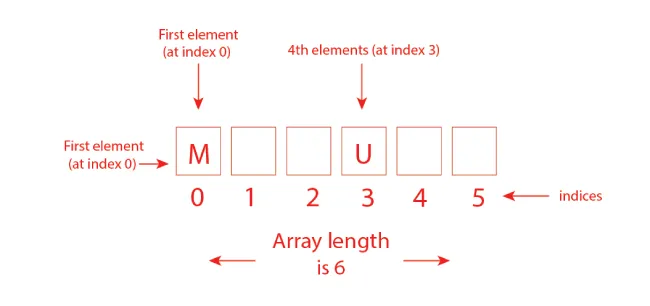
● Arrays Declarations
In the C language, Array declarations are very easy. Arrays can be any type, such as int or char. We can give any to the arrays, just like a random variable in C language.
Syntax of Array Declaration
int arr[5]; // Size of array is 5 in this declarations
Rules for Declaring One-Dimensional Array in C
The following rules must be followed before declaring the One Dimensional Array in C language.
- Before accessing and using an array, we must declare the array variable.
- The array can be accessed using indexing. The first element index is 0 in Array.
- Each element in the array is stored in contiguous memory locations.
- If you are defining the size of the array. It must be a non-negative number.
- Write a valid array name using the identifier. Which must be easily readable in the source code.

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
Array Initialization
Initizalations is the process where we define the elements of the array. When we declare an array or allocate the memory element of the array. Starting arrays contain some garbage value. So, we need to initialise the array to some meaningful value. In C language, we can initialise an array in different ways. Let’s explore each way one by one.
● Arrays Initialization with Declaration:
In this method, we will initialise the array along with its declarations. An array can be initialised using the curly braces {}. All those elements will be inserted in these curly brackets and separated by the comma
Syntax:
data_type array_name [size] = {value1, value2, … valueN};
The following program demonstrates the array initialization with declarations
Program
// This program illustrates the Arrays in c language
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// declaring an array of integers
int arr_int[5] = {33,45,55,99,100};
int length = sizeof(arr_int) / sizeof(arr_int[0]);
for(int i = 0;i<length;i++){
printf("%d ",arr_int[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Output
33 45 55 99 100
● Arrays Initialization with Declarations without Size
In this section, we will initialise the array without defining its size. In these cases, a compiler can automatically deduce the size of the array, and the compiler will allocate the computer’s memory according to the size of the elements.
Syntax of declaration
data_type array_name[] = {1,2,3,4,5};
The following program demonstrates the array initialization with declarations without size.
Program
// This program illustrates the Arrays in c language
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
// declaring an array of integers
int arr_int[] = {33,45,55,99,100};
int length = sizeof(arr_int) / sizeof(arr_int[0]);
for(int i = 0;i<length;i++){
printf("%d ",arr_int[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Output
33 45 55 99 100
● Arrays Initialization after Declarations (Using loops)
In this section, we will initialise the array using a loop, while loop, or do-while loop to assign a value to each element.
Syntax of loop
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
array_name[i] = valuei;
}
The following program demonstrates the Example of Array initialization in C language.
Program
// C Program to demonstrate array initialization
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
// array initialization using an initializer list
int arr[5] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
int arr1[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
// array initialization using for loop
int arr2[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
arr2[i] = arr[i] * arr[i] ;
}
for(int j = 0;j<5;j++){
printf("%d ",arr2[j]);
} return 0;
}
Output
100 400 900 1600 2500
Access Array Elements
We can access array elements using indexing in the C language. We pass the index value in the subscript operator [] and the index value i of the element.
Syntax
array_name [index];
Always remember that an array’s first elements start with index 0, and the last element is at N-1, where N is the number of elements in the array, and N-1 is the last number.
The following program demonstrates the Array Elements using Array Subscript.
Program
// C Program to illustrate element access using an array
// subscript
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// array declaration and initialization
int arr[5] = { 153, 2534, 35, 425, 255 };
// accessing element at index 2, i.e 3rd element
printf("Element at arr[2]: %d\n", arr[2]);
// accessing element at index 4, i.e last element
printf("Element at arr[4]: %d\n", arr[4]);
// accessing element at index 0, i.e first element
printf("Element at arr[0]: %d", arr[0]);
return 0;
}
Output
Element at arr[2]: 35
Element at arr[4]: 255
Element at arr[0]: 153
Also Read: Types of Operators in C
Update Array Element
We can also update the value of an element in the array using the subscript operator [] and assignment operator =.
Syntax:
array_name[i] = new_value;
The following program demonstrates the update of the array using the array element.
Program
// C Program to illustrate element access using an array
// subscript
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// array declaration and initialization
int arr[5] = { 153, 2534, 35, 425, 255 };
// accessing element at index 2, i.e 3rd element
printf("Old Value = %d\n",arr[2]) ;
arr[2] = 33 ;
printf("Update Value = %d",arr[2]) ;
return 0;
}
Output
Old Value = 35
Update Value = 33
Array Traversal in Array
In C language, we traverse the array, which is the process of visiting every element of the array. We can traverse the array using loops, while loops do while loops, and for loops.
Traversing using for loop
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
array_name[i];
}
The following program demonstrates the Array Traversal in Array
Program
// C Program to illustrate element access using an array
// subscript
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// array declaration and initialization
int arr[5] = { 153, 2534, 35, 425, 255 };
// accessing element at index 2, i.e 3rd element
int length = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]) ;
for(int i = 0 ;i< length;i++){
printf("%d ",arr[i]) ;
}
return 0;
}
Output
153 2534 35 425 255
Copying One-Dimensional in C
In this section, we will copy one array to another array. Suppose we have two arrays, array1 and array2. One is initialised with some elements. We have to copy the first array to another array. Let’s see “how we can do this “
The following program demonstrates the Copy one array to another.
Program
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int array1[5] = {100, 240, 330, 440, 550};
int array2[5];
printf("Copying One-Dimensional Arrays in C:\n");
printf("Array1 elements: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d ", array1[i]);
array2[i] = array1[i]; // Copying array1 elements to array2
}
printf("\nArray2 elements after copying: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d ", array2[i]);
}
}
Output
Copying One-Dimensional Arrays in C:
Array1 elements: 100 240 330 440 550
Array2 elements after copying: 100 240 330 440 550
Common Operations and Functions on One-Dimensional Arrays
In this section, we will discuss the common operations of one-dimensional arrays. We will perform some operations like searching, sorting, modifying elements, and mathematical calculations.
● Searching
Finding specific elements in one-dimensional arrays is a very basic operation in C. We will find specific elements using the linear search. The following program demonstrates the Source Code.
Program
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to perform linear search
int linearSearch(int arr[], int size, int key) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (arr[i] == key) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
int numbers[] = {5, 3, 9, 1, 7, 2, 8};
int key = 7;
int size = sizeof(numbers) / sizeof(numbers[0]);
int index = linearSearch(numbers, size, key);
if (index != -1) {
printf("Element %d found at index %d.\n", key, index);
} else {
printf("Element %d not found in the array.\n", key);
}
return 0;
}
<strong>Output</strong><strong> </strong>
Element 7 found at index 4.● Sorting
In this section, we will learn to sort with one-dimensional arrays. Sorting is the process of sorting the elements in ascending and descending order. Ascending order means smallest to highest element, and descending order means highest to the smallest element.
The following program demonstrates the Sorting in C language using Bubble Sort.
Program
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to perform bubble sort
void bubbleSort(int arr[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < size - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
// Swap arr[j] and arr[j+1]
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int numbers[] = {5, 3, 9, 1, 7, 2, 8};
int size = sizeof(numbers) / sizeof(numbers[0]);
printf("Array before sorting:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
printf("%d ", numbers[i]);
}
printf("\n");
bubbleSort(numbers, size);
printf("Array after sorting:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
printf("%d ", numbers[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
<strong>Output</strong>
Array before sorting:
5 3 9 1 7 2 8
Array after sorting:
1 2 3 5 7 8 9Points to Remember About Array in C
Every developer must know some points about Array. In this section, we will cover those points. Let’s discuss those points.
- Arrays in C are collections of similar data type elements stored at contiguous memory locations.
- In C array elements can be accessed by the index value.
- Array Indexing starts from 0, and the last value of the index is N-1. N is the number of elements present in the array.
- Array size can be defined in brackets of the array, for example, int arr[2].
Importance of One-Dimensional Arrays in Computer Programming
In this section, we will talk about the importance of One Dimensional Arrays in Computer programming
ng.
- Structure Data Storage: One-dimensional arrays provide a way to store data and store a sequence of elements in a linear format and ensure that data is organised and easily accessible for any developer.
- Efficient Memory Usage: Arrays are stored in a contiguous memory location, which makes them efficient in memory and provides fast performance and access to the elements.
- Iterating Easy: In Array, Iterating is very easy as compared to other data structures like linked lists.
- Simplicity in Implementation: Arrays are excellent data structures to learn about memory and organisation of data structures.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned about one-dimensional arrays in the C language. This is fundamental for anyone venturing into programming. Arrays provide a powerful tool for string manipulation and manipulating data in structured manners, with various types and sizes available. We also learned about the various operations on the array.
What is one Dimension Array in C language?
What is the syntax of an array?
How to calculate array size in C langauge?
How do you traverse a one-dimensional array in C language?
What are the advantages of using one-dimensional arrays in C language?
Updated on July 22, 2024
