Do you often struggle with managing your database? Are you confused about how to interact with it efficiently? Many of us indeed do face the same issues when dealing with databases.
Not to worry, we are here to clear things up. Let’s talk about database languages in DBMS.
They are tools used to define, manipulate and control data. They help in creating and maintaining databases, thereby making our lives very easy.
Database languages help us define, manipulate, and control data. They are like the bridge between us and our data. Understanding these languages can empower us to manage data better and make informed decisions.
Database languages in DBMS fall into four main categories. Each language has specific commands that help us manage our database efficiently.
What are Database Languages in DBMS?
Database languages, often known as query languages, are programming languages for creating and accessing databases. They enable users to save, organise, and retrieve the data.
A database management system or DBMS can be defined as a special type of software that can interact with the database and offer an interface to users and applications. DBMS offers security features like access control and authentication, guarantees effective data storage and retrieval, and preserves data integrity.

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Multi Cloud Architecture & DevOps
Master cloud architecture, DevOps practices, and automation to build scalable, resilient systems.
Types of Database Languages in DBMS
Mainly, there are 4 types of database languages in DBMS, which consist of multiple commands for efficient operations:
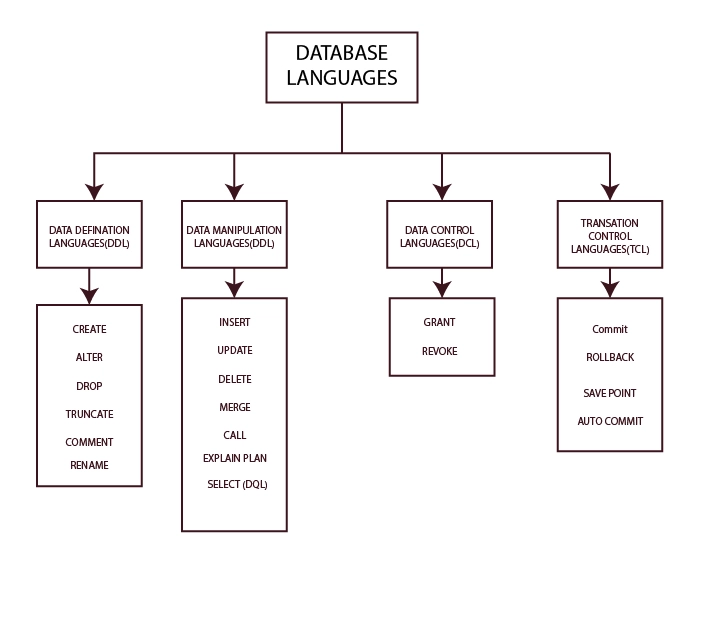
Now we have explored what is database languages in dbms as well as types of database languages in dbms. Let’s deep dive and learn more about these database languages in dbms with examples.
i. Data Definition Language (DDL)
The main focus of Data Definition Language (DDL) is on specifying and controlling the database’s structure. It’s similar to laying down the foundation before adding the finishing touches.
Database objects like tables, indexes, and schemas may be created, modified, and deleted using DDL.
Key Commands in DDL
- CREATE: This command creates a new database or database object.
- ALTER: It modifies an existing database object.
- DROP: This command deletes objects from the database.
- TRUNCATE: It removes all records from a table but keeps the table structure intact.
- RENAME: This command changes the name of a database object.
- COMMENT: It adds comments to the data dictionary.
Examples of DDL Commands
Let’s dive into some examples to see how these commands work.
1. CREATE TABLE
We use this command to create a new table in the database.
CREATE TABLE Employees (
ID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Name VARCHAR(50),
Age INT,
Salary DECIMAL(10, 2)
);
This command creates a table named “Employees” with four columns: ID, Name, Age, and Salary.
2. ALTER TABLE
This command modifies the structure of an existing table.
ALTER TABLE Employees ADD COLUMN Department VARCHAR(50);Here, we’re adding a new column named “Department” to the “Employees” table.
3. DROP TABLE
We use this command to delete a table from the database.
DROP TABLE Employees;This command removes the “Employees” table from the database.
4. TRUNCATE TABLE
This command removes all records from a table but keeps the table structure intact.
TRUNCATE TABLE Employees;The “Employees” table will be emptied, but the table itself will remain.
5. RENAME TABLE
This command changes the name of a table.
RENAME TABLE Employees TO Staff;The table “Employees” is now renamed to “Staff”.
6. COMMENT ON TABLE
This command adds a comment to the table for documentation purposes.
COMMENT ON TABLE Staff IS 'Table containing staff details';Using DDL commands, we can efficiently manage the structure of our database.
Now, let’s look at a complete example that takes user input.
Example with User Input
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Employees (
ID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Name VARCHAR(50),
Age INT,
Salary DECIMAL(10, 2)
);
-- Adding a new column
ALTER TABLE Employees ADD COLUMN Department VARCHAR(50);
-- Inserting a record with user input
INSERT INTO Employees (ID, Name, Age, Salary, Department) VALUES
(1, 'Aryan', 30, 70000.00, 'HR'),
(2, 'Shweta', 25, 65000.00, 'Engineering');
-- Displaying the records
SELECT * FROM Employees;
Output:
| ID | Name | Age | Salary | Department |
| 1 | Aryan | 30 | 70000.00 | HR |
| 2 | Shweta | 25 | 65000.00 | Engineering |
In this example, we can see how to create a table, modify it, insert records, and then retrieve data.
ii. Data Manipulation Language (DML)
Facing issues in effectively updating your database? Is data management without messing it up making you nervous?
Let us delve deep into the details of DML now, which is a very powerful tool for handling such tasks.
We can use DML commands to manipulate data in a database. We can insert new data, update existing data, delete unwanted data, and even retrieve data using DML. It is like a toolkit for all our needs in handling data.
Key Commands in DML
- SELECT: Retrieves data from the database.
- INSERT: Adds new data into a table.
- UPDATE: Modifies existing data within a table.
- DELETE: Removes data from a table.
- MERGE: Combines insert and update operations.
- CALL: Executes a subprogram like a stored procedure.
Examples of DML Commands
Let’s break down some examples.
1. SELECT
This command fetches data from the database.
SELECT * FROM Staff WHERE Age > 30;This command retrieves all staff members older than 30.
2. INSERT
We use this command to add new records.
INSERT INTO Staff (ID, Name, Age, Salary, Department) VALUES (3, 'Suman', 28, 60000, 'Finance');This adds a new record for Charlie in the Staff table.
3. UPDATE
This command updates existing records.
UPDATE Staff SET Salary = Salary * 1.1 WHERE Age > 30;Here, we increase the salary of staff members older than 30 by 10%.
4. DELETE
This command removes records from a table.
DELETE FROM Staff WHERE ID = 3;This removes Charlie’s record from the Staff table.
5. MERGE
This command combines insert and update operations.
MERGE INTO Staff USING NewStaff ON (Staff.ID = NewStaff.ID)
WHEN MATCHED THEN UPDATE SET Staff.Name = NewStaff.Name
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT (ID, Name) VALUES (NewStaff.ID, NewStaff.Name);
This merges data from NewStaff into Staff, updating or inserting as needed.
6. CALL
This command runs a stored procedure.
CALL UpdateSalary(50000);
Example with User Input
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Staff (
ID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Name VARCHAR(50),
Age INT,
Salary DECIMAL(10, 2),
Department VARCHAR(50)
);
-- Inserting a record with user input
INSERT INTO Staff (ID, Name, Age, Salary, Department) VALUES
(1, 'Aryan', 30, 70000.00, 'HR'),
(2, 'Shweta', 25, 65000.00, 'Engineering');
-- Updating records
UPDATE Staff SET Salary = Salary * 1.1 WHERE Age > 30;
-- Deleting a record
DELETE FROM Staff WHERE ID = 1;
-- Displaying the records
SELECT * FROM Staff;
Output:
| ID | Name | Age | Salary | Department |
| 2 | Shweta | 25 | 65000.00 | Engineering |
iii. Data Control Language (DCL)
Worried about who can access your data? Let’s explore Data Control Language (DCL).
DCL commands manage user permissions. We can grant or revoke access to our data, ensuring security and control.
Key Commands in DCL
- GRANT: Provides user access privileges.
- REVOKE: Removes user access privileges.
Examples of DCL Commands
1. GRANT
This command gives the user access.
GRANT SELECT, INSERT ON Staff TO user123;It allows user123 to select and insert data into the Staff table.
2. REVOKE
This command removes user access.
REVOKE SELECT, INSERT ON Staff FROM user123;
It removes the select and insert permissions from user123.
iv. Transaction Control Language (TCL)
Ever faced issues with incomplete transactions? Transaction Control Language (TCL) is here to help.
TCL commands ensure that database transactions are processed reliably. They help us commit changes or roll them back, maintaining data integrity.
Key Commands in TCL
- COMMIT: Saves all changes made during the transaction.
- ROLLBACK: Undoes changes made during the current transaction.
- SAVEPOINT: Sets a point within a transaction to roll back to.
- AUTOCOMMIT: Automatically commits each individual statement.
Examples of TCL Commands
1. COMMIT
This command saves changes.
COMMIT;
2. ROLLBACK
This command undoes changes.
ROLLBACK;
3. SAVEPOINT
This command sets a savepoint.
SAVEPOINT SavePoint1;
4. ROLLBACK TO SAVEPOINT
This command rolls back to a savepoint.
ROLLBACK TO SavePoint1;
5. AUTOCOMMIT
This command sets autocommit.
SET AUTOCOMMIT = 0;
Example with User Input
-- Starting a transaction
START TRANSACTION;
-- Inserting a record
INSERT INTO Staff (ID, Name, Age, Salary, Department) VALUES (3, 'Suman', 28, 60000.00, 'Finance');
-- Creating a savepoint
SAVEPOINT BeforeDelete;
-- Deleting a record
DELETE FROM Staff WHERE ID = 2;
-- Rolling back to savepoint
ROLLBACK TO BeforeDelete;
-- Committing the transaction
COMMIT;
-- Displaying the records
SELECT * FROM Staff;
Output:
| ID | Name | Age | Salary | Department |
| 1 | Aryan | 30 | 77000.00 | HR |
| 3 | Suman | 28 | 60000.00 | Finance |
Practical Applications and Use Cases of DBMS Languages
Struggling to see how database languages in DBMS fit into real-world scenarios? Let’s explore some practical applications of DBMS languages.
Managing Employee Records
Think about a company’s HR department. They need to manage employee records efficiently.
Using DDL, we can create tables for employee details. With DML, we can insert, update, and delete employee records as needed. DCL helps give HR staff access while keeping the data secure. Finally, TCL ensures transactions are processed reliably.
Example
1. Creating the Employee Table
CREATE TABLE Employees (
ID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Name VARCHAR(50),
Age INT,
Department VARCHAR(50),
Salary DECIMAL(10, 2)
);
2. Inserting Employee Data
INSERT INTO Employees (ID, Name, Age, Department, Salary) VALUES
(1, 'Aryan', 30, 'HR', 70000.00),
(2, 'Shweta', 25, 'Engineering', 65000.00);
3. Updating Employee Salary
UPDATE Employees SET Salary = Salary * 1.05 WHERE Department = 'HR';
4. Granting Access to HR Staff
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE ON Employees TO hr_staff;
5. Ensuring Transaction Reliability
START TRANSACTION;
UPDATE Employees SET Salary = 72000 WHERE ID = 1;
COMMIT;
Online Retail
Online stores manage vast amounts of data daily.
DML commands handle product updates and customer orders. DDL helps in creating product catalogs. DCL ensures that only authorized staff can access sensitive data. TCL maintains transaction consistency during purchases.
Example
- Creating the Product Table
CREATE TABLE Products (
ProductID INT PRIMARY KEY,
ProductName VARCHAR(100),
Price DECIMAL(10, 2),
Stock INT
);
1. Inserting Product Data
INSERT INTO Products (ProductID, ProductName, Price, Stock) VALUES
(101, 'Laptop', 1500.00, 50),
(102, 'Smartphone', 800.00, 200);
2. Updating Stock Quantity
UPDATE Products SET Stock = Stock - 1 WHERE ProductID = 101;
3. Granting Access to Inventory Managers
GRANT SELECT, UPDATE ON Products TO inventory_manager;
4. Ensuring Transaction Consistency
START TRANSACTION;UPDATE Products SET Stock = Stock – 1 WHERE ProductID = 101;
COMMIT;
Key Differences Between DBMS Languages in DBMS
Are you finding it tough to differentiate between the various database languages in DBMS? Let’s break it down clearly.
| Language Type | Purpose | Key Commands |
| DDL | Define and manage database structure | CREATE, ALTER, DROP, TRUNCATE, RENAME, COMMENT |
| DML | Manipulate and retrieve data | SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, MERGE, CALL |
| DCL | Control access to data | GRANT, REVOKE |
| TCL | Manage transactions | COMMIT, ROLLBACK, SAVEPOINT, AUTOCOMMIT |
Also Read: Join Dependency in DBMS

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
Conclusion
In this web blog, we have touched on the basics of Database Languages in DBMS.
We have looked at how DDL, namely Data Definition Language, helped in defining the structure of the database. We have seen how DML, namely Data Manipulation Language, helped us manipulate the data.
We clarified how DCL, namely Data Control Language, treated access and permission-related issues and hence secured the data. Last but not least, we learned how TCL, namely Transaction Control Language, ensured the integrity of the data by making sure reliable transaction management.
Understanding these languages will give us efficient tools for creating, managing, and securing databases. Mastering these commands assures us that our databases can run smoothly and effectively manage data. Want to learn more about DBMS? Try the Accelerator Program in Business Analytics, Data Science & Data Engineering offered by Hero Vired.
What are some common DCL commands and their uses?
What is the purpose of DDL in a database?
Why are TCL commands necessary in Database Management?
How does DML differ from DDL?
Can you provide an example of a MERGE command in DML?
How many types of database languages are there?
- Data Definition Language (DDL)
- Data Manipulation Language (DML)
- Data Control Language (DCL)
- Transaction Control Language (TCL)
Updated on February 24, 2025
