Every business-big or small-is going to have to think about the long game. And that’s what strategic management is for: just a simple process of aligning our goals, resources, and everyday activities toward clear, measurable achievements.
What does “strategic management” really mean?
Simply put, it is the process that allows organisations to set goals, make intelligent decisions, and execute actions that direct the organisation toward those goals. It is like an ATM-GPS device: it gives us clear directions to take but, at the same time, allows flexibility in adjusting according to changes.
Through the use of the strategic management model, we’re not just planning for today; we look ahead, and anticipate what challenges might be there, and we position ourselves to thrive.
This includes setting the mission of our business, looking at the strengths and weaknesses, determining the market as well and selecting specific strategies to help achieve our objectives.
Strategic management integrates all these pieces by aligning our resources, people, and processes toward long-term growth and resilience. It is not just about having a plan but creating one that can grow with us.
Let’s walk through how the strategic management model can power this vision step by step.
Also Read: Different Types of Strategic Management
Key Components of a Strategic Management Model for Sustainable Growth
A robust strategic management model has three vital parts that must come together in harmony: formulation, implementation, and evaluation.
Setting Vision, Mission, and Long-Term Goals as the Foundation
Setting a clear vision and mission statement isn’t just for corporate show; it’s what aligns everyone in the business.
- The vision outlines where we aim to go long-term.
- The mission defines what we do, why we do it, and how we stand out from others.
- We define long-term goals that are realistic yet ambitious enough to drive us forward.
Strategy Formulation and Implementation Across Organisational Functions
Formulating a strategy means deciding on the big moves. This involves:
- Market analysis to understand industry trends and competitive landscapes.
- Internal analysis to pinpoint strengths, weaknesses, resources, and capabilities.
- Setting priorities that align with our vision and mission, like targeting a specific market segment.
Once we’ve got the plan, it’s time to put it into action—this is implementation. And it’s where many strategies struggle.
Why?
Because implementation isn’t just about good intentions; it’s about organising every function—marketing, finance, human resources, and operations—so they all play a part.
With clear roles and teamwork, the strategy shifts from paper to reality.
Strategy Evaluation and Control: Feedback Loops for Continuous Improvement
A sound strategic management model includes built-in feedback loops. Evaluation lets us know whether we are achieving our goals and what adjustments need to be made.
This ongoing evaluation would mean that we don’t only track the strategy but improve it over time.
Via regular review, we have a cycle where feedback leads to refinement, keeping us aligned with our objectives and with the changes in the market environment.

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Strategic Management & Business Essentials
Develop strategic thinking, leadership skills, and business acumen to excel in management roles.
Step-by-Step Process of Strategic Management Model
Strategic management is quite straightforward if broken down at each step. All it entails is a process of taking things a step at a time, where each step feeds into the previous step.
Here’s how it works step by step so that each step strikes the mark.
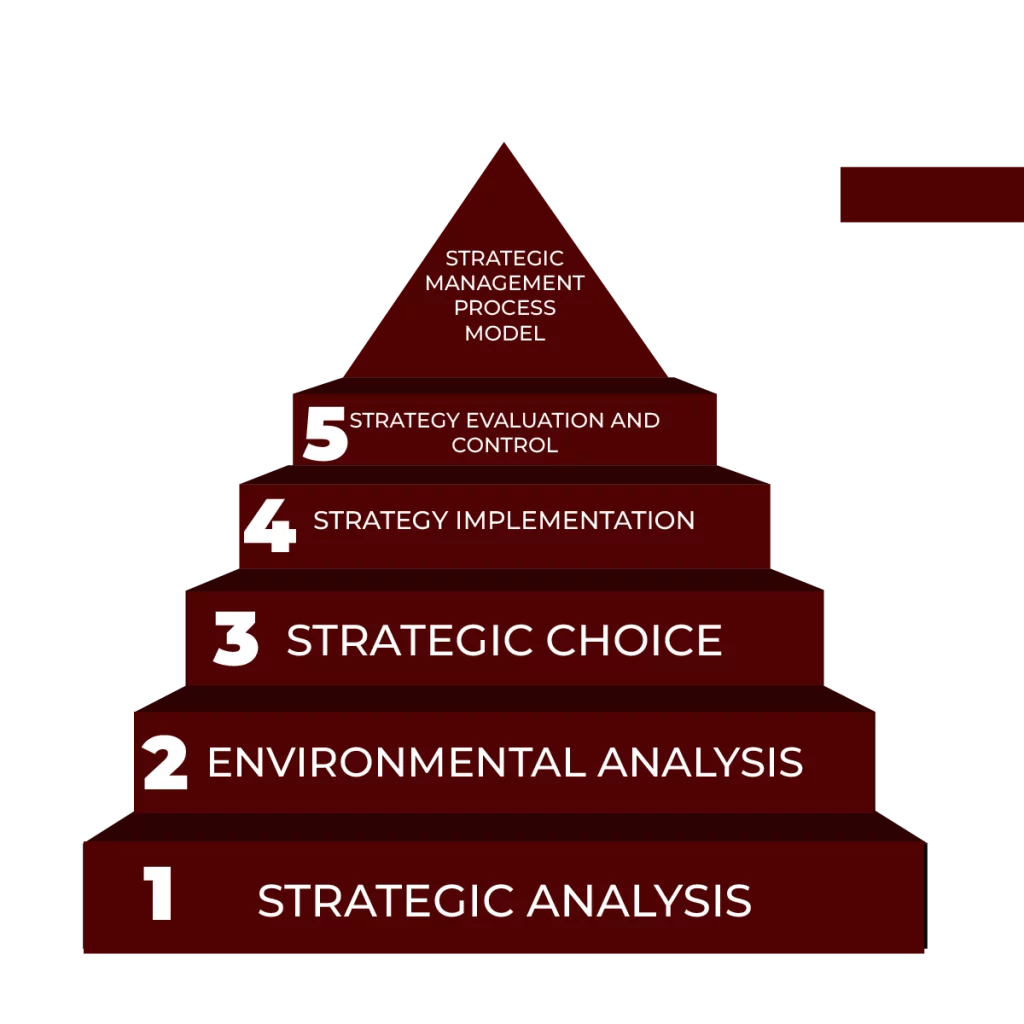
Defining Organisational Intent with SMART Objectives:
- Set clear, SMART goals—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound.
- Provides clarity and alignment across all departments, removing guesswork.
Conducting Comprehensive Internal and External Environment Analysis:
- Internal Analysis: Assess strengths (e.g., skilled workforce) and weaknesses (e.g., outdated technology).
- External Analysis: Use tools like SWOT and Porter’s Five Forces to evaluate competition, market trends, opportunities (e.g., eco-friendly demand), and threats (e.g., regulations).
Developing Actionable, Aligned Strategies for Targeted Goals:
- Turn insights into strategic actions that directly support goals.
- Ensure each action aligns with the core capabilities of the business.
Executing Strategies Effectively Across Departments:
- Assign clear roles and responsibilities across teams to execute the strategy successfully.
Monitoring, Evaluating, and Adapting Strategies:
- Track progress through KPIs to check if goals are met and make adjustments as needed.
Also read: The Stages & Process of Strategic Management
Strategic Management Models and Approaches Tailored to Business Needs
The best strategic management model is one that matches our unique goals, market, and even the speed of our industry.
Here’s a closer look at different strategic management models and how to choose one that suits our business.
Traditional Linear Model for Predictable, Stable Environments
The traditional, or linear, model is like a classic playbook. This model moves in a straight line from formulating to implementing to evaluating a strategy, all in a clear order.
It’s perfect for businesses in predictable industries, like cement manufacturing or utilities, where changes happen slowly.
With this model, we create a step-by-step plan and follow it, knowing that surprises are rare.
Adaptive Model for Fast-Moving, Dynamic Sectors
If we’re in an industry that shifts quickly, the adaptive model is a better fit. This approach isn’t about following a set plan; instead, it’s about flexibility and ongoing adjustments.
In fast-moving sectors like tech or e-commerce, sticking to a rigid plan can make us fall behind quickly.
Visionary Model for Disruptive Innovation and Bold Goals
The visionary model is for businesses aiming to make a big splash. It’s the approach that companies use when they want to change the game.
This approach is about thinking big and finding ways to create a market rather than adapt to one. It’s risky, but the reward can be massive if successful.
Shaping Model for Collaborative, Ecosystem-Based Businesses
The shaping model is for businesses that thrive in a network.
In this model, we don’t just think about ourselves but the entire ecosystem, like partners, suppliers, and even competitors.
The goal is to shape a network where everyone benefits. With this model, collaboration is key. The idea is to build something that serves a larger community, which, in turn, creates a stronger market presence for everyone involved.
Renewal Model for Companies Facing Crisis or Transformation
Sometimes, we’re not in growth mode but survival mode. The renewal model is for businesses facing crises, major challenges, or the need for a turnaround.
This model is about survival, with the goal of stabilising before any significant growth.
The renewal approach is strategic triage. It’s for situations where the business needs a reset before moving forward again.
Essential Strategic Management Frameworks and Tools for Success
Let’s break down some practical frameworks that make strategic management easier.
A tool for self-assessment, helping us evaluate internal and external factors:
- Strengths: Internal resources give us an edge
- Weaknesses: Areas needing improvement
- Opportunities: External factors we can leverage
- Threats: Potential external risks
It provides a full picture for strategising around strengths and managing weaknesses.
Porter’s Five Forces:
Analyses the competitive landscape, focusing on:
- Competitive Rivalry: Intensity of competition
- Threat of New Entrants: Ease of market entry for newcomers
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers: Dependence on suppliers
- Bargaining Power of Buyers: Customer alternatives
- Threat of Substitutes: Risk of replacement products
It helps to anticipate competitor moves and new market challenges.
Balanced Scorecard:
Links strategic goals to measurable outcomes across departments, tracking:
- Financial Performance
- Customer Satisfaction
- Internal Processes
- Learning and Growth
It ensures balanced progress, preventing any area from lagging behind.

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
Cross-Functional Integration in Strategic Management Execution
Having the right model and tools is one side of the coin. The other is making sure all departments work together to bring the strategy to life.
Marketing and Sales for Strategy Execution
- Act as the frontline, directly connecting with customers and spreading the strategic message.
- Aligning these teams ensures a broader reach and a stronger impact on our strategy.
Finance’s Role in Resource Allocation
- Allocates funds to essential areas to support strategic goals.
- Calculates expansion costs, secures funding, and closely monitors spending to prevent overreach.
HR’s Role in Shaping Organisational Culture
- Builds a culture aligned with strategic goals by recruiting talent that fits these aims.
- Fosters collaboration and innovation to support long-term strategy.
Technology and Operations as Drivers of Innovation
- Operations ensure strategic plans are feasible and smoothly executed.
- Technology provides essential tools and support for effective strategy implementation.
Choosing the Right Strategic Approach for Your Specific Business Context
Stuck trying to figure out the right strategic approach for your business? Maybe you’ve read about different models but aren’t sure which one will fit your specific needs.
Let’s go through how to choose a strategy that works for your unique business.
Evaluating Market Predictability and Business Flexibility
- Identify your market’s predictability and your business’s flexibility.
- Predictable markets suit traditional, structured models with clear, set steps.
- Unpredictable markets need adaptable models like adaptive or shaping approaches.
- Flexible businesses benefit from adaptive or visionary models for quick shifts.
- Less flexible businesses may prefer grounded, linear approaches.
Aligning Approach with Industry Needs
- Tech sectors: Fast-paced industries like software need adaptive strategies for agility.
- Retail: Shaping models work well when collaboration and market presence are priorities.
Integrating Ethics, Social Responsibility, and Sustainability in Strategy
Customers, investors, and even employees are becoming more concerned with ethics and sustainability. If we can bring these values into our strategic management model, it will strengthen the brand and create trust.
Ethical Decision-Making in Strategy
- Make ethics central by maintaining transparency from sourcing to employee treatment.
Balancing Profit with Social and Environmental Impact
- Achieve profitability while positively impacting society and the environment.
Sustainability as a Competitive Advantage
- Sustainable practices benefit both the business and the planet, preparing us for future challenges.
Conclusion
A strategic management model outlines and directs exactly what is required in both predictable and unpredictable times to guide a business.
By clearly defining objectives, combining this with a proper approach, and interweaving it with ethics and sustainability, businesses craft strategies that, in fact, support growth and resilience.
The uniqueness of each business and environment would make use of the chosen model—traditional, adaptive, or even visionary. Then, tools like SWOT and the Balanced Scorecard would help to keep the strategy focused and measurable.
Cross-functional coordination requires that all departments work towards shared goals to succeed in implementation.
Lastly, a powerful, adaptable strategy makes a business thrive, ensuring it remains agile, impactful, and ready for new challenges.
For professionals who want a deeper outlook toward expertise, the Certificate Program in Strategic Management and Business Essentials at Hero Vired promises an exciting step forward. The course would enable students, through practical learning, to be equipped with advanced strategic frameworks, decision-making tools, and real-world applications.
What are the key elements of a strategic management model?
How does an organisation determine the best strategic approach?
Why is strategic management evaluation necessary periodically?
What are the most used tools of strategic management, and what are the benefits for businesses?
What are the roles of ethics and sustainability in modern strategic management models?
Why is continuous evaluation crucial in strategic management?
Updated on November 21, 2024
