Management is one of the foundations of any organisation. It is what enables everything to function effectively and efficiently, where targets are met and objectives realised. There is always a saying that a good plan is only half of a strategy; the other half is the management of its implementation. But what does management actually mean, and how is it designed and arranged in an organisation? That is why it is necessary to explain what levels of management exist and what their role consists of.
In this case, when we refer to management levels, we are simply discussing organisational stratification. This hierarchy assists in defining the functions, powers, and delegation so that it becomes clear who is accountable for what task and who he or she should be reporting to. In this article, we look at what each of these levels means.
Meaning of Management
The planning, coordinating, leading, and managing of organisational resources in order to achieve organisational goals is referred to as management. Providing goods and services with effectiveness and efficiency is the core of management. However, management is not only about ordering and ensuring that people listen and obey instructions. There are basically three principles involved in management, which include assessing the needs and strengths of the employees, providing guidance, and developing the topmost abilities and overall top-notch performance.

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Multi Cloud Architecture & DevOps
Master cloud architecture, DevOps practices, and automation to build scalable, resilient systems.
Overview of Management Levels
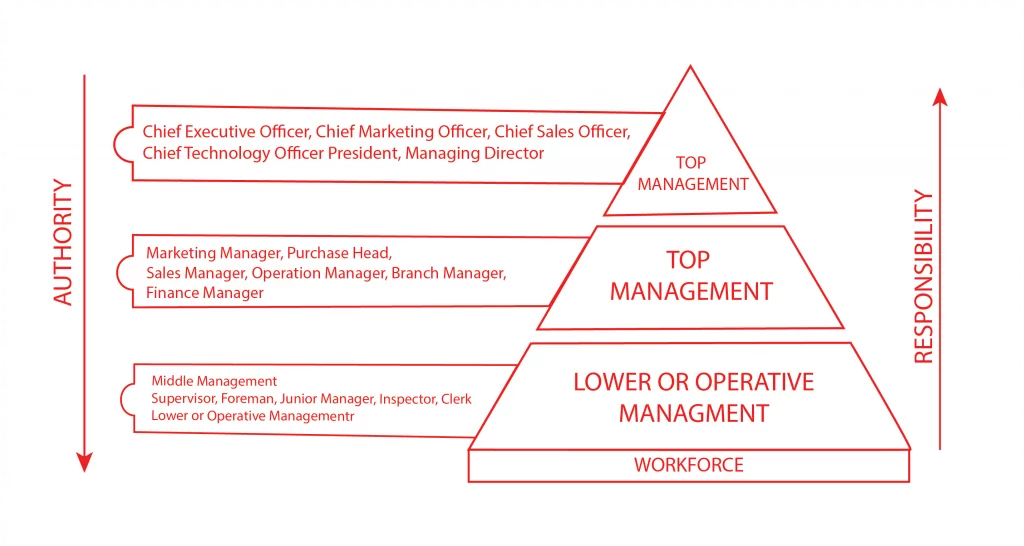
In the organisation’s functioning, management levels establish definite hierarchical structures and lines of reporting. This hierarchy means that the right decision is made at the right level, and everyone is clear about their responsibilities. The three main levels of management are:
- Top-Level Management: These are the individuals who are responsible for the management of organisations, including determining the organisational goals, strategies, and mobiles. This makes them strategic and bear the overall responsibility for the magnitude of the firm’s success.
- Middle-Level Management: They are usually positioned between the top management and the operational management levels within organisations. Employees at this level, for instance, act out the plans that have been put in place by the top management and manage the day-to-day execution of department responsibilities.
- Lower-Level Management: Also known as first-line managers, these individuals directly supervise employees. These help in ascertaining that activities are properly and satisfactorily accomplished.
All these levels of management have their responsibilities in the functioning of the organisation, and a truly appreciative understanding of these responsibilities can assist in understanding management as a constructive whole.
Top-Level Management: Strategic Decision Makers
The top level is also known as strategic management or managerial apex and is considered the highest tier in the executive hierarchy of an organisation. As indicated, they are the ones charged with the general managerial responsibility of the firm and the actualisation of its managerial objectives. The CEOs, CFOs, CTOs, Directors, and VCs fall under the top-level management of any company.
Roles and Responsibilities of Top-Level Management
Top-level management has a wide range of responsibilities, all geared towards ensuring the organisation’s long-term success. Here are some of their key roles:
- Formulating Organisational Mission, Vision, and Long-Term Objectives
- Set the overall direction for the organisation.
- Define the mission and vision.
- Establish long-term objectives.
- Developing and Implementing Strategic Plans and Policies
- Create high-level policies and strategies.
- Make decisions about the company’s direction.
- Ensure alignment with overall goals.
- Allocating Resources and Making Major Financial Decisions
- Distribute resources, including finances and personnel.
- Approve budgets and manage investments.
- Ensure necessary resources for success.
- Establishing Relationships with Stakeholders and Representing the Organization Externally
- Build relationships with key stakeholders.
- Represent the organisation at external events.
- Maintain the company’s public image.
- Overseeing Overall Organisational Performance
- Monitor performance metrics.
- Assess progress towards goals.
- Make adjustments as needed.
Middle-Level Management: The Bridge Between Strategy and Execution
The strategic vision of top management must be translated into workable plans, and this is where middle levels of management come in. These managers serve as an essential connection, making sure that the company’s ambitious ambitions are carried out successfully. Department heads, regional managers, and division leaders are examples of middle-level managers who are essential to the seamless operation of the company.
Key Responsibilities of Middle-Level Management
- Implementing Strategies and Policies
- Translate broad strategies into specific plans.
- Ensure alignment with organisational goals.
- Collaborate with top-level management.
- Creating Departmental Goals and Plans
- Set goals for each department.
- Develop detailed plans to achieve these goals.
- Ensure departmental contributions to overall success.
- Assigning Tasks and Responsibilities
- Delegate tasks to team members.
- Ensure everyone knows their roles.
- Maintain productivity and coverage of all tasks.
- Monitoring and Evaluating Performance
- Monitor team performance using metrics.
- Evaluate progress and identify issues.
- Make adjustments to stay on track.
- Serving as a Communication Link
- Act as the main point of contact between top and frontline employees.
- Ensure clear communication of directives.
- Relay feedback and concerns up the chain.

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
Lower-Level Management: Supervising Daily Operations
The real action happens at lower-level management, sometimes referred to as first-line or supervisory management. These supervisors are directly in charge of supervising the staff and keeping an eye on daily activities. They work as section officers, foremen, supervisors, and team leaders.
Primary Responsibilities of Lower-Level Management
- Assigning Specific Tasks and Work Schedules
- Create daily work schedules.
- Assign tasks to workers.
- Ensure smooth operations.
- Providing Training, Guidance, and Supervision
- Provide on-the-job training.
- Offer guidance to ensure optimal performance.
- Supervise workers closely.
- Addressing Employee Concerns and Resolving Conflicts
- Act as the first point of contact for employee issues.
- Resolve conflicts quickly and fairly.
- Maintain a positive work environment.
- Reporting Progress and Challenges to Middle-Level Management
- Keep middle management informed.
- Highlight achievements and challenges.
- Suggest potential solutions.
- Maintaining a Productive and Motivated Workforce
- Foster a supportive atmosphere.
- Use recognition and rewards to motivate.
- Keep morale high.
Also Read: Process of Strategic Management
Specific Functions of Each Management Level
It might be easier to understand how companies run well if you are aware of the various roles that each level of management plays. Every level has certain duties that go towards the business’s overall success. To understand how these roles work together, let’s dissect each one.
Top-Level Management: Setting the Course
The company’s long-term strategy and strategic direction are under the control of top levels of management. These top leaders are able to make important decisions that influence the future because of their comprehensive perspective of the company and the outside world.
- Setting Overall Goals and Objectives
- Establish vision, mission, and long-term goals.
- Identify key strategic initiatives.
- Ensure alignment across the organisation.
- Framing Organisational Policies and Strategies
- Develop policies and strategies guiding activities.
- Set frameworks for operations.
- Ensure departmental alignment with the overall strategy.
- Making Key Financial and Resource Allocation Decisions
- Allocate resources across projects and departments.
- Approve budgets and manage investments.
- Ensure necessary resources for achieving objectives.
- Ensuring Organisational Growth and Sustainability
- Identify opportunities for expansion and innovation.
- Focus on long-term growth and relevance.
- Maintain a competitive edge.
Middle-Level Management: Turning Strategy into Action
Transforming the general strategies from top management into detailed plans and activities are the responsibilities of middle-level managers. They guarantee that daily activities correspond with the strategic objectives.
- Translating Top-Level Strategies into Actionable Plans
- Break down strategic goals into actionable plans.
- Create detailed projects and tasks.
- Collaborate closely with top-level management.
- Coordinating Between Departments for Smooth Operations
- Ensure synchronised activities and efficient resource use.
- Regular communication and collaboration.
- Resolve inter-departmental issues.
- Participating in Recruitment and Training of Lower-Level Management
- Involved in hiring and training new managers.
- Ensure recruits understand their roles.
- Focus on continuous skill development.
- Evaluating Departmental Performance and Reporting to Top Management
- Monitor departmental performance using metrics.
- Prepare reports highlighting achievements and challenges.
- Provide feedback for informed decision-making.
Lower-Level Management: Executing the Plan
The managers who deal directly with employees are lower-level managers, sometimes referred to as first-line or supervisory managers. They guarantee that middle management’s plans and assignments are carried out successfully on the ground.
- Directing and Supervising Day-to-Day Operations
- Oversee daily activities of teams.
- Ensure employees understand tasks and resources.
- Maintain smooth operations.
- Ensuring Effective Communication of Directives
- Clear communication of higher management directives.
- Act as a bridge, translating strategic goals into daily tasks.
- Ensure understanding and compliance.
- Maintaining Discipline and Morale Among Employees
- Foster a positive work environment.
- Address issues promptly.
- Keep morale high through recognition and support.
- Monitoring Production Quality and Quantity
- Monitor production processes for quality and efficiency.
- Conduct regular quality checks.
- Ensure standards are met.
Importance of Clear Management Hierarchy
Effective and efficient operations depend on a clearly established management structure. It makes sure that everyone is aware of their duties, which promotes improved cooperation and communication.
- Ensuring Efficient Coordination and Communication
- Streamline communication within the organisation.
- Clear roles reduce confusion and increase efficiency.
- Departments work together seamlessly.
- Fostering Innovation and Adapting to Market Changes
- Provides stability for innovation.
- Separates strategic thinking from daily operations.
- Enables swift response to market changes.
- Contributing to Overall Organisational Success
- Top managers set the vision.
- Middle managers translate it into actionable plans.
- Lower managers execute these plans.
- Each level ensures cohesive movement towards goals.
Also Read: Best Management Courses for Working Professionals
Conclusion
In this blog, we’ve explored the three distinct levels of management: They include top-level, middle-level, and lower- level. There are certain tasks assigned to every level, and each of them plays a definite role in the organisational success. Strategic management occurs at various levels within the organisation: The top management provides the direction for strategies, the middle management filters down the strategies from the top management and translates them into operational strategies, and The lower-level management supervises and enforces the operational strategies provided by the middle management.
The management structure is rather important as it controls the way workers collaborate, create new ideas, and complete tasks on their way to achieving organisational objectives. Awareness of these levels of management assists in explaining how each layer contributes to the functioning of the organisation. An awareness of these roles will enhance one’s perception of the factors that contribute towards organisational success.
How do remote work and virtual teams affect management levels?
What are the key skills required for managers at different levels?
How does communication flow between different levels of management?
Updated on October 1, 2024
