Choosing the right programming paradigm is one of the initial but highly important decisions in building any software program. Some developers embrace OOP, while others find POP easier to grasp.
Here comes the question: what is the difference between OOP and POP, and which approach should we use?
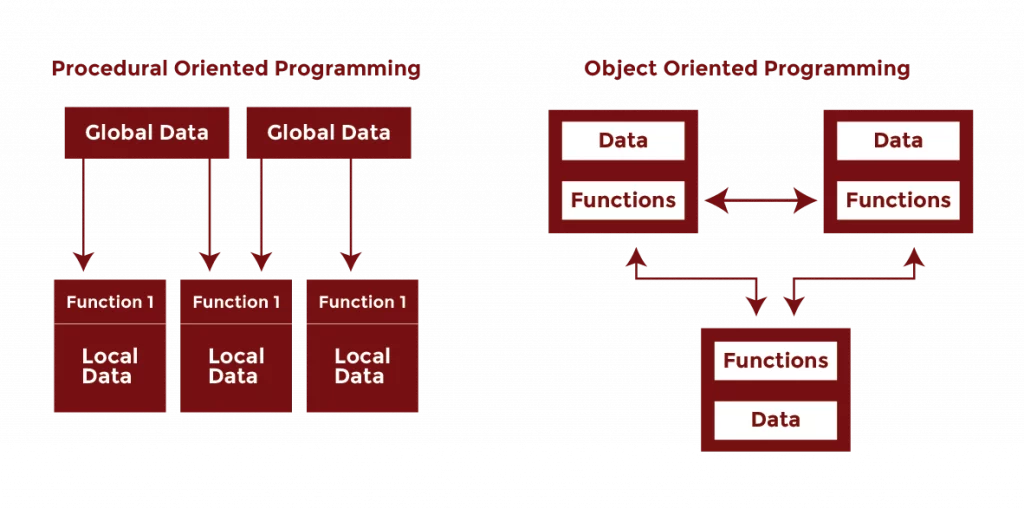
OOP is object-based; it revolves around objects and their respective interactions. It binds data together with the methods that operate on it. This characteristic allows complex applications to be structured in a way that improves code reuse, security, and scalability.
POP is nonetheless a step-wise method that breaks a program down into a series of procedures or functions. Thus, such programming methods are easy to follow and are rather efficient for smaller applications.
What Is Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)?
OOP functions as a programming method that keeps code arrangements inside objects. Real-world entities become objects that contain both data elements referred to as attributes as well as functions known as methods.
Rather than writing different procedures for different tasks, the related data and methods are grouped into objects, which makes code modular and much more easily managed.
Java, alongside C++, Python, and C# are the OOP programming languages. Codes written in OOP languages have features of encapsulation, inheritance polymorphism, and abstraction, which boost code maintainability and reuse capabilities.

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Multi Cloud Architecture & DevOps
Master cloud architecture, DevOps practices, and automation to build scalable, resilient systems.
Key Characteristics of Object-Oriented Programming
OOP stands on four fundamental pillars:
- Encapsulation
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Abstraction
Each of these characteristics makes OOP a powerful choice for large, complex applications.
Encapsulation
- Bundles data and methods together.
- Prevents direct access to data, improving security.
- Example: A bank account class restricts direct changes to the account balance.
Inheritance
- Allows a new class to reuse features of an existing class.
- Reduces redundancy and improves maintainability.
- Example: A Car class inherits features from a Vehicle class.
Polymorphism
- Let the same method work differently for different objects.
- Example: A function calculateArea() works for both Circle and Rectangle classes but produces different results.
Abstraction
- Hides complex details and exposes only necessary information.
- Example: A mobile banking app lets us transfer money without showing the backend calculations.
Features of Object-Oriented Programming
Code Reusability
With inheritance, we don’t have to write the same code multiple times. A single base class can serve multiple derived classes.
Data Security
Encapsulation ensures that critical data isn’t accessible from outside the object. For example, a banking system prevents direct access to a user’s balance.
Modularity and Maintainability
Breaking a program into objects makes it easier to debug, modify, and extend.
Scalability
OOP makes it easy to add new features without affecting existing functionality.
Real-World Applications of Object-Oriented Programming
OOP is widely used in industries where software needs to be modular, secure, and scalable.
Banking and Finance
- Used in core banking systems for transactions, loans, and account management.
Game Development
- Objects represent players, enemies, weapons, and game elements.
E-commerce Platforms
- Handles products, users, and transactions efficiently.
Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
- Objects represent data structures and models.

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Object-Oriented Programming
The difference between OOP and POP is most noticeable in code organisation, security, and maintainability.
Advantages of OOP
Encapsulation Provides Better Data Security
- OOP hides sensitive data inside objects using private and protected access modifiers.
Code Reusability Saves Development Time
- OOP supports inheritance, allowing existing code to be reused.
Easier Maintenance for Large Projects
- OOP structures programs into modular classes, making updates easier.
- Large-scale applications like banking systems and enterprise software rely on OOP for scalability.
Better Real-World Problem-Solving
- OOP models real-world entities through objects, making it more intuitive than POP.
Disadvantages of OOP
Higher Memory Usage Due to Object Storage
- OOP stores object metadata, making it memory-intensive compared to POP.
Slower Execution Due to Dynamic Method Calls
- OOP relies on polymorphism and method overriding, increasing CPU processing time.
More Complex for Beginners
- Understanding objects, classes, inheritance, and polymorphism takes time.
Not Always Necessary for Small Programs
- For simple applications, OOP can add unnecessary complexity.
What Is Procedure-Oriented Programming (POP)?
POP is a traditional programming approach where a program is divided into functions or procedures. These functions execute in a top-down order, following a structured sequence.
Instead of objects, data is shared globally between functions. While this makes the code simple, it also increases the risk of unintended modifications.
POP is still widely used in C, FORTRAN, and Pascal. It’s common in embedded systems, operating systems, and low-level programming, where efficiency is crucial.
Key Characteristics of Procedure-Oriented Programming
The difference between OOP and POP lies in how they handle data, structure, and execution flow.
Here are the key characteristics that set POP apart from OOP.
Step-by-Step Execution with a Top-down Approach
- POP follows a sequential flow, meaning the program runs line by line.
- The main function is written first, followed by smaller functions that break down the task.
- Example: In C, we define a main() function, then call sub-functions one after another to execute the program in a structured manner.
Global Data Sharing Instead of Encapsulation
- All functions can access global variables, which simplifies data sharing.
- This leads to potential data modification errors, as any function can alter shared data.
- Example: In C, multiple functions accessing a global variable can result in unintended data changes, making debugging harder.
No Code Reusability Through Inheritance
- POP does not support inheritance, meaning functions cannot inherit properties from other functions.
- Every time a new function is needed, code must be written from scratch.
- Example: If we need a function to calculate tax in different departments, we must write separate tax functions rather than reusing a parent function.
Procedures Are Independent, Not Part of Objects
- POP programs consist of separate functions, each handling a specific task.
- Functions do not belong to any class, unlike OOP, where methods are tied to objects.
- Example: In C, a billing system may have functions like calculateTotal(), applyDiscount(), and printBill(), each working independently.
Features of Procedure-Oriented Programming
POP is widely used for small-scale applications, system programming, and situations where direct hardware access is required.
- Simplicity in Execution
- POP programs are easy to understand as they execute functions sequentially.
- Best suited for simple applications like calculators or utility scripts.
- Efficient Memory Management
- POP consumes less memory because there are no objects or class overhead.
- Ideal for low-memory environments, such as embedded systems.
- Direct Hardware Access
- System-level programming, such as operating systems and drivers, benefits from POP’s direct interaction with hardware.
- Example: The Linux Kernel is written in C, which follows a procedural approach.
- Easy to Debug and Modify
- Since functions run independently, debugging one function does not affect others.
- Suitable for smaller projects where modifications are minimal.
Common Applications of Procedure-Oriented Programming
Despite the rise of OOP, POP remains relevant in various fields:
Embedded Systems and Firmware Development
- Example: Microcontroller programming in C for automated irrigation systems.
Operating System Development
- Example: The Windows and Linux kernels are primarily written in C, following a procedural structure.
Scientific and Numerical Computing
- Example: FORTRAN is still widely used in NASA’s space simulations due to POP’s computational efficiency.
Utility and Scripting Applications
- Example: Batch processing scripts in Shell or Python for file management.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Procedure-Oriented Programming
POP is known for its efficiency and simplicity, but its limitations make it less suitable for modern large-scale applications.
Advantages of POP
Faster Execution for Simple Programs
- Functions in POP are called directly, leading to quicker execution.
Better for Low-Level System Programming
- POP provides direct hardware access, which is crucial for system programming and embedded software.
Lower Memory Consumption
- POP does not store objects or class metadata, reducing RAM usage.
- Suitable for memory-constrained environments like microcontrollers and embedded systems.
Easier to Debug in Small Applications
- Since POP follows a linear execution model, debugging is simpler.
Disadvantages of POP
No Data Security Due to Global Variable Access
- Any function can modify global variables, increasing security risks.
Code Duplication Increases Development Time
- Since POP lacks inheritance, functions must be rewritten for different use cases.
Hard to Scale for Large Applications
- As the program grows, managing multiple functions becomes complex.
Not Suitable for Object-Based Modelling
- POP cannot represent complex entities efficiently.
Detailed Comparison: Key Difference Between OOP and POP
This table highlights the main difference between OOP and POP, making it easier to decide which approach suits a particular project.
| Feature | Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) | Procedure-Oriented Programming (POP) |
| Approach | Bottom-up (Objects first, then methods) | Top-down (Main function first, then sub-functions) |
| Code Reusability | High – Supports inheritance, polymorphism | Low – Functions must be rewritten for different use cases |
| Encapsulation | Supported – Data is protected within objects | Not supported – Global variables are accessible to all functions |
| Security | High – Encapsulation restricts data access | Low – Data is shared globally and can be modified anywhere |
| Scalability | Suitable for large applications | Hard to scale due to increasing function dependencies |
| Memory Usage | Higher – Objects and classes consume more memory | Lower – Functions execute directly without extra storage |
| Performance | Slower for small tasks due to object overhead | Faster for small programs since there is no object creation |
| Complexity | More complex due to objects, classes, and methods | Simpler – Functions execute sequentially |
| Modularity | High – Divides code into reusable objects | Low – Functions are not tied to reusable structures |
| Data Handling | Uses access specifiers (private, protected, public) | All functions share global data, increasing security risks |
| Error Handling | Better – Uses exception-handling mechanisms | Limited – Requires manual error-checking in functions |
| Suitable for | Large projects like banking apps, game development, web applications | System-level programming, embedded systems, operating systems |
| Parallel Development | Easier – Different teams can work on different classes | Harder – Modifying one function can affect the entire program |
| Abstraction | Supported – Hides complex implementation details | Not supported – Every function must be manually defined |
| Flexibility | High – Code can be modified without affecting other parts | Low – Changes in one function can impact the entire structure |
| Example Languages | Java, C++, Python, C# | C, FORTRAN, Pascal, Shell scripting |
Conclusion
The difference between OOP and POP lies in how they handle data, security, scalability, and performance. OOP follows a modular approach, focusing on objects and helping with code reuse and encapsulation. It is primarily used in building large applications like bank systems, game development, and web apps. Procedure-oriented programming runs step by step, making it faster and more efficient for system programming, embedded systems, and scientific computing.
OOP provides better security through encapsulation. On the other hand, POP users miss out on access controls, hence making it unsuitable for those applications which require data protection. The selection of OOP vs POP depends on the project’s need, performance requirements, and future scalability. An understanding of both paradigms helps make the right decisions for software development.
Mastering application development requires knowledge of both OOP and POP. The Certificate Program in Application Development by Hero Vired provides hands-on training in modern programming techniques. It imparts industry-relevant skills needed to build scalable and efficient applications. Explore the course now and take another step forward in your career.
Which programming method is better: OOP or POP?
Is it possible to integrate OOP and POP into a single program?
Why is OOP considered more secure than POP?
Which programming languages support both OOP and POP?
Is POP outdated, or does it still have use cases?
Updated on March 6, 2025
