Data is increasingly used to make business decisions. Read about it, and you’ll find terms like data analysis and data analytics used interchangeably, but they’re not quite the same. The differences between these two terms will help characterize their large roles in the data science domain. Both are about working with data, but only one is on a large scale, complex and with a goal of insight.
What is Data Analytics?
Analysis of data related to a large set of data is known as data analytics and is used to discover important information and trends. It encompasses the use of statistical computational and other techniques in processing large volumes of data to derive some conclusions favourably for business efficiency, predicting the next future trend or solving a particular pre-defined problem.
Components of Data Analytics
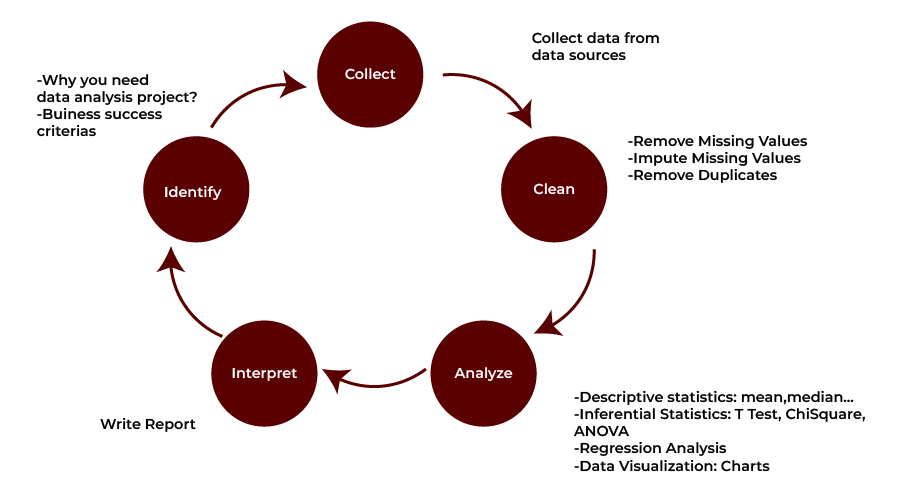
- Data Collection: This refers to a process of collecting data from different sources like databases, APIs, web scraping, sensors, and different digital interfaces. It includes numeric and categorical data in tabular forms like spreadsheets or SQL databases, text, image, video data, JSONs, or XMLs.
- Data Cleaning and Preprocessing: Primary data, in this case, is undirected and has variations; therefore, cleaning forms part of the process. Specific activities include dealing with ‘?’ and or ‘NA’ entries, deleting similar records, editing data and standardizing the data type. Other activities may include normalization of the data (scaling numerical values) and encoding of some categorical variables for use in analysis.
- Data Exploration and Analysis: In this process, it is necessary to investigate and aggregate the data in an effort to discover relationships, associations and trends. Preprocessing encompasses the process of understanding the nature of the data by applying descriptive statistics (mean, median, variance and the like) and data visualization (graphs and charts).
- Statistical Analysis and Hypothesis Testing: Cross-sectional data involves, in this phase, testing assumptions or hypotheses with statistical methods. Regression analysis is used to establish associations between variables, and hypothesis testing includes a t-test, chi-square test, and F-test that will tell us whether we observe some patterns or differences in the statistically significant data. This step is crucial when one wants to draw conclusions from the data.
Read also: Data Analyst Interview Questions

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Data Science & AIML
Learn Data Science, AI & ML to turn raw data into powerful, predictive insights.
What is Data Analysis?
According to the above discussion, the analysis of data is critical since most decisions are made not by guesswork but through well-conducted and analyzed data. In general, the analysis of data is beneficial, whether it is aimed at future trends, at the optimization of business processes, or at the study of the habits of consumers.
Difference between Data Analytics and Data Analysis
| Data Analytics | Data Analysis |
| It is the process of inspecting, cleaning, and modeling data to discover useful information. | A broader field that involves using various techniques and tools to analyze data for business decision-making. |
| We have to understand and interpret data to answer specific questions or solve problems | We have to predict future trends, optimize processes, and guide strategic decisions based on data insights. |
| It often uses simpler methods like statistical analysis, correlation, and basic visualizations. | More complex, including machine learning, big data analytics, and advanced statistical modelling. |
| Basic tools like Excel, Python (for simple tasks), or R for statistical analysis. | Advanced tools like Tableau, Power BI, Python (with libraries like Pandas, Scikit-learn), Hadoop, Spark, etc. |
| Reports, charts, and summaries that explain patterns or trends in data. | Actionable insights, predictions, recommendations, and optimized decision-making frameworks. |
| Data Engineers, primarily business stakeholders, managers, etc. | Data scientists, analysts, researchers, etc. |
Read also: Data Science vs. Data Analytics
Which is the Better Option: Data Analytics or Data Analysis?
Data analysis or data analytics is a better option for you if your goals, data complexity, and available resources make your choice. Data analysis is appropriate when what you want to know can be answered by simpler methods and tools, usually from past or present data, and questions such as where there are trends, patterns, and abnormalities. Because of this, it’s more accessible, faster, and less resource-intensive, and it’s a good choice for smaller datasets or short-term problem-solving. Then, data analytics can be useful if you are trying to forecast future outcomes, optimize processes, or make data-driven decisions at scale. As such, it uses advanced techniques such as machine learning and big data processing — both of which make it a better choice for larger, more complex datasets and long-term strategic planning. Data analytics represents a much deeper, more predictive form of insight when you have the requisite expertise and resources, but data analysis continues to be an important analytical tool for understanding the past and taking immediate action in the present.
Read also: Python for Data Analysis

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
Conclusion
In other words, the fundamental difference between data analysis and data analytics is just in the range of difficulty. I will define data analysis as a sharp or, at times, less complicated method of data evaluation to arrive at conclusions or, more accurately, answer precise questions. It includes simple procedures such as tabulation, categorization and even simple statistical methods of data analysis.
Data analysis, on the other hand, is a broader concept than data analysis and encompasses the use of complicated techniques, for example, data mining, predictive analysis, automation, and the like, in order for individual recurrent data to be found and used to make decisions. It is commonly employed for analyzing big data and might be useful to predict further trends among companies or improve a production process.
So, data analysis is a specific aspect of data analytics, but data analytics is a loose term that encompasses various methods and tools that are suited for strategic and prospective decision-making. Learn about data analytics professionally with the Certification Program in Data Analytics with Microsoft by Hero Vired.
Do I need programming skills for data analysis?
Which tool is used for data analysis?
Can data Analytics be done without data analysis?
Can Data Analytics be done without clean data?
Can Data Analysis be a part of Data Analytics?
Updated on November 13, 2024
