The prominent difference between Encapsulation and Abstraction lies in the the way they are used in java, Lets understand how Abstraction vs Encapsulation works in java.
How Abstraction Works in Java
In Java, abstraction defines the character sets and behaviours representing a complex system. However, this doesn’t involve the implementation details and is achieved through using abstract classes and interfaces.
An abstract cast is typically used as a base for all other classes and can’t be instantiated. While interfaces involve a collection of abstract constants and methods defining a class contract for implementation.
Overall, abstraction proves helpful in Java as it allows you to create more manageable and straightforward code, making the process more scalable, readable and maintainable.
If you have grown some interest in cloud engineering, the best idea would be to opt for a Cloud engineering course .
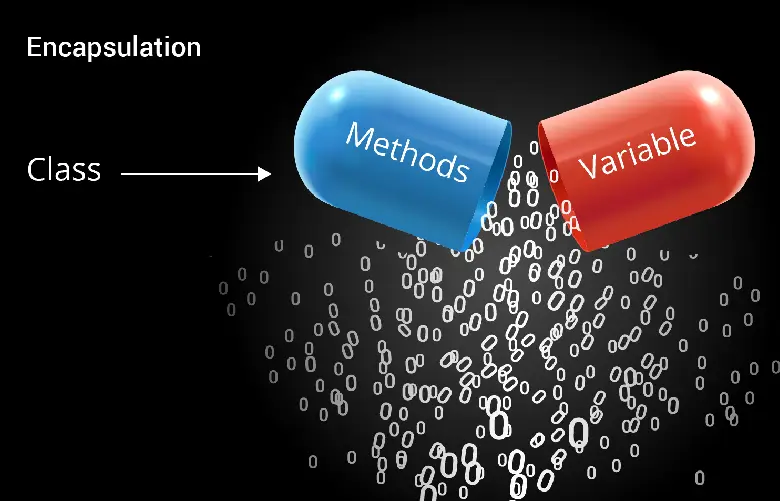
How Encapsulation Works in Java
Encapsulation involves hiding the details of an object’s implementation, limiting access to its internal state. Achievement of this is done with the use of access modifiers like public, private and protected.
It works in Java by improving a code’s scalability, security and maintainability of a code. Making the modification process easier without affecting other application parts.
Example Difference Between Abstraction and Encapsulation
You can better understand the difference between Encapsulation vs Abstraction with an example. The major difference between abstraction and encapsulation in Java is that encapsulation is used for the internal wrapping of the codes on the other hand abstraction is used for making the user-end less complex which is free from unwanted codes.
Examples of Abstraction in Java
Let’s understand better the difference between Encapsulation vs Abstraction with an example.
Abstract Classes: This class can’t be instantiated and may contain one or more methods. It is a method that is not implemented but only declared.
Interfaces: This is a collection of abstract methods that doesn’t specify how a set of behaviors will be implemented but just defines them.
Generics: It allows one to create parameterized classes and methods, where the type of the parameter is not specified until the class or method is instantiated. One significant difference between Abstraction and Encapsulation in Java is how they represent data. Encapsulation wraps data and codes for necessary information and Abstraction represents only useful data.
Examples of Encapsulation in Java
Let’s understand better the difference between Encapsulation vs Abstraction with an example.

Private Access Modifiers: These restrict access to a class’s methods and fields. Only methods residing inside the class can have access.
Getter and Setter Methods: This method is used to modify and access the field of a class.
Immutable Objects: The state of these objects can’t be changed after their creation. Another key difference between Abstraction and Encapsulation in Java is the way programs are partitioned.
Let’s deep dive into the major difference between Abstraction vs Encapsulation in terms of Advantages & Disadvantages.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Using Abstraction in Java
Let us see the difference between abstraction and encapsulation with respect to their advantages and disadvantages in detail.
Advantages of abstraction in Java:
- Reduce the code’s complex nature.
- Proves benefits in achieving modular programming.
- Increases code’s flexibility
- Promotes the reuse of the expected functionality of the code.
Disadvantages of abstraction in java:
- In the case of too many layers of abstraction, it can lead to unwanted complexity.
- Can also result in code bloat
- It can sometimes decrease performance primarily due to the additional overhead of working with abstract interfaces or classes.
- Can make debugging complex due to the presence of additional abstraction layers.
Advantages of Using Encapsulation in Java
Encapsulation offers numerous benefits to programmers; these are:
- Enhanced code maintainability
- Better security
- Better organisation of the code
- Improved code performance
- Promotes the reuse of the code
Similarities in Abstraction vs Encapsulation
Apart from the difference between abstraction and encapsulation in java the two also shares some similarities, which are mentioned below:
- Both revolves around object-oriented programming concept.
- Both help in hiding details and enhance the quality of code
- Both promote code reusability and modular programming
- Both make use of access modifiers for controlling the data visibility
- Both prevent unauthorized access to data