Strategic management is an essential component of any organization, and hardly any aspect does not involve consideration of its operating environment. The environment in strategic management comprises all measurable and immeasurable factors within and outside the organisation, which affect the company’s decisions, performance, and capacity to meet its objectives.
These factors are divided into various parts that define an organization’s strategy. The components of the environment in strategic management are typically divided into two broad categories: Two broad categories describe the explicit content of the strategy process: the external environment and the internal environment.
What is a Business Environment?
The business environment involves factors, internal and external to the firm, that affect it regarding operation, management decisions, and profitability. These may be economic, social, technological, political, legal, or environment-related.
The business environment can be divided into two key categories:
- Internal Environment: This comprises all the variables the firm can truly manage. Such factors are reasonably stable and can be negotiated by the company to exclude influences that have adverse effects on operation.
- External Environment: It covers factors beyond the company’s influence. They are often unpredictable since a company cannot influence or forecast change in them. Something that may suddenly negatively or positively affect a company’s activities remains unpredictable.

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Strategic Management & Business Essentials
Develop strategic thinking, leadership skills, and business acumen to excel in management roles.
Components of Business Environment
The business environment is generally divided into two main types: the external and internal environment. There is also a possibility of varying these types to embrace many factors that influence business functioning and outcomes. Here’s a breakdown of the different types:
Internal Environment
The internal business environment consists of several internal forces or elements within a business that are within the business’s ambit about force.
- Value: This business ethical belief steers the business in accomplishing its mission and objective. The value system embraces all the structures that comprise a business’s legal framework: organizational culture, climate, workflows, management strategies and organizational standards.
- Vision, Mission, and Objectives: Business’s vision, mission and objective deal with what an entity intends to do in the future. That is why the business is created.
- Organisational Structure: They explain how the activities coordinate within the organizational system to accomplish its objectives. They consist of the regulation governing organizational affairs, the authority and mandate of subordinates, how the work is distributed, and the movement of information within the various strata of an organization.
- Human Resources: Human resources form all the employees and other personnel associated with the business. It forms the organisation’s most valuable asset, as success or failure depends on it.
- Physical Resources and Technological Capabilities: It encompasses fixed assets and the operational skills that determine its strategic capacity and the business’s growth potential.
External Environment
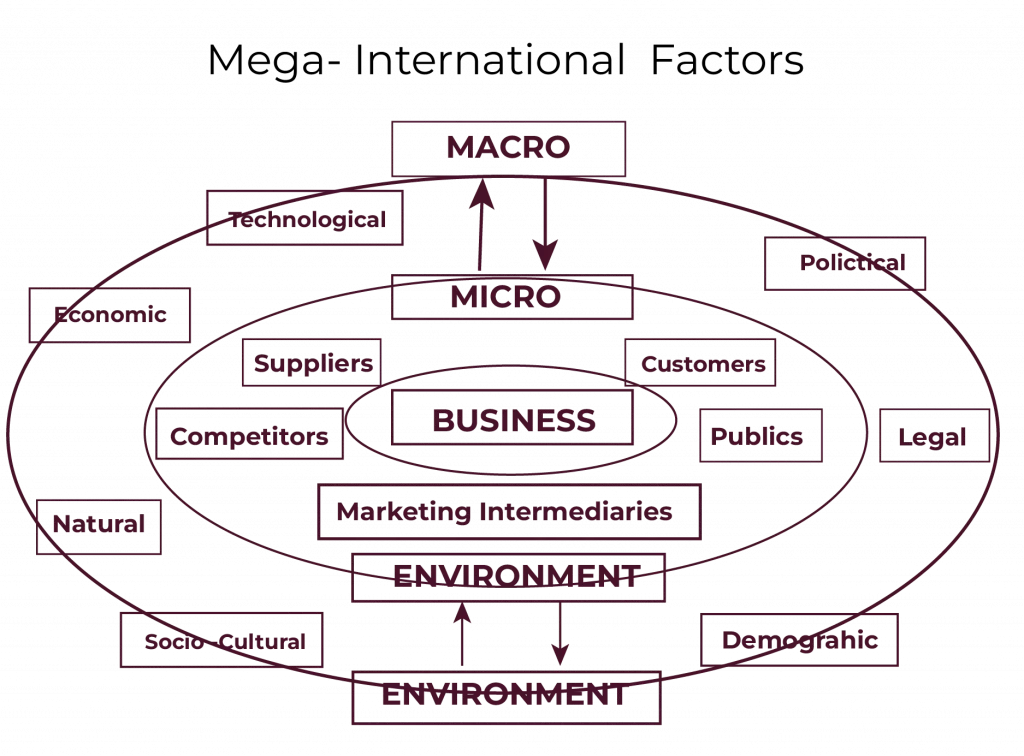
The external environment happens outside the business and affects its operations and decision-making process. These factors are the microenvironment and the macro environment in which the business operates.
- Micro Environment
- Macro Environment
Micro Environment
Micro environment refers to the close outside conditions that affect the business since it directly impacts the firm’s routine operational activities. They are beyond the control of the business but are considered while managing the business to avoid any business losses.
- Competitors: Other businesses that can acquire market and resource shares that the present business has.
- Suppliers: Essential sources that provide the resources necessary for the company’s products and practices.
- Partners: All kinds of collaborative entities helping customer service: consultancy firms, advertising agencies, etc.
- Public: Entities that can affect the company’s customer service.
- Customers: The set of customers for which the company provides products or services in exchange for revenue.
- Media: It is used as a media, a marketing, or a communication platform.
- Intermediaries: Facilitating groups that transfer products or services to customers.
Macro Environment
Larger industry forces influence business but cannot necessarily be managed by the business. Key components include:
- Political Factors: Government policies, laws, and order situations influence the business landscape.
- Economic Environment: Inflation, employment level, interest rate and economic growth rate.
- Social and Cultural Environment: Consumer behaviour characteristics or preferences, societal norms or behaviour, alterations to life patterns, and changes in population profile.
- Technological Environment: Solutions or ideas implemented in organisations or within production or service delivery processes.
- Legal Factors: These industry-specific laws and regulations govern business practices.
- Environment: Environmental conditions influencing the organization include regulatory systems, sustainable development and natural resources.
Also Read: Exploring the Objectives and Goals of Strategic Management
Importance of Business Environment
- Helps in Decision Making: Knowledge of the business environment plays a significant role in formulating policies that bear on all aspects of an organization, from setting the price of products to developing the product itself.
- Identifies Opportunities and Threats: The manager can identify new opportunities and threats and the surrounding environment through various factors such as market trends and regulatory or legal factors.
- Enhances Strategic Planning: Business environment knowledge empowers organizations to predict future changes and obstacles or circumstances they are likely to face and then develop strategic plans.
- Encourages Innovation and Adaptation: Recognising changes in current technology, customs, or competition enables business organisations to change and introduce new ideas relevant to the market.
- Regulatory Compliance: Legal and political factors guide legal requirements and procedures that affect the business environment to prevent firms from falling foul of the law and bearing the resulting consequences.
Also Read: What is Environmental Scanning in Strategic Management
Features of Business Environment
The business environment is the internal and external conditions that shape the business venture and its performance. Knowing its characteristics is vital for organizations to prepare and compete in a more challenging environment. Here are the key features of the business environment:
- Dynamic Nature: The business environment can be volatile depending on technological development, market forces, legislation changes, and consumer preferences. Hence, the organizations need to be dynamic enough to address those changes suitably.
- Interrelated Elements: Several parts of the business environment, like the economic, political, social, and technological environment, are entwined. The relationship of the task requirements shows that a change in one factor has a carryover effect on other changes.
- Complexity: It consists of various elements such as competition, legal policies, environment, culture, etc. Analyzing such a significant complexity can be possible only within the framework of an integrated approach.
- Uncertainty: It is markedly uncertain as to what the business environment will look like in the coming years. Fluctuations in the political environment, international business environment, and environmental calamities are some factors that create uncertainties in doing business.
- Relativity: The business environment differs from one location to another and sector to another. Locality is an important consideration as it occurs in a given culture and setting, as well as economic and political strengths and weaknesses unique to that region.
- Influence on Decision-Making: It means that a business entity’s success, at its core, depends more on how effectively it can scan and respond. It is common to define decision-making in an organizational context as being influenced by factors such as the market, competitors, and technologies.

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
Examples of a Business Environment
- Google’s open management: The management at Google goes the extra mile by practicing an open-style management technique that enhances the creation of ideas by employees.
- Tesla’s resource availability: The resource availability at Tesla includes innovative technology, engineers and resources to develop electric cars.
- Apple’s leadership approach: Despite the mentioned approaches and strategies, Apple successfully applies its leadership approach to the corporation’s strategic design and development of innovative products and market domination.
- Netflix’s flexible work environment: Netflix provides flexibility at work, which increases innovation because people can easily adjust to changes in the market.
Also Read: Your Guide to the Stages & Process of Strategic Management
Conclusion
Strategic Management of the elements used to implement strategic management are important in business. The internal environment lays the organizational culture, structure, resource and capabilities systems, which define how strategies are developed and implemented. On the other hand, the organization environment, which includes the microenvironment, which they have to cope with, includes customers, suppliers and competitors, and the Macro environment, which comprises the economic, political, and technological factors, are both opportunities and risks in the business. Want to learn more about the components of the environment in strategic management? Consider pursuing the Certificate Program in Strategic Management and Business Essentials Hero Vired offers in collaboration with INSEAD.
What is the external environment?
What is the internal environment?
What is PESTEL?
How does organizational culture impact strategy?
What is SWOT analysis in strategic management?
Updated on February 19, 2025
