This development is crucial since a central pillar of strategic management, the BCG Matrix, was invented in the 1970s and is crucial in choosing the corporate strategy. Developed by the Boston Consulting Group, this powerful tool categorizes products into four quadrants based on their market growth and share. By understanding the strategic position of each product, businesses can make informed decisions about resource allocation, investment priorities, and portfolio optimization.
Apple is a prime example of a company that is effectively leveraging the BCG Matrix. Apple has identified its Stars, Cash Cows, Question Marks, and Dogs by analyzing its product portfolio. This analysis has enabled the company to allocate resources strategically, invest in promising products like the iPhone and Apple Watch, and phase out less profitable ones.
What is Strategic Management?
Strategic management is a systematic approach to planning, organizing, leading, and controlling an organization’s resources to achieve its long-term goals. It involves analyzing the external environment, assessing internal strengths and weaknesses, and formulating and implementing strategies to gain a competitive advantage. For instance, a tech startup might use strategic management to identify emerging market trends, develop innovative products, and allocate resources to high-potential areas.

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Strategic Management & Business Essentials
Develop strategic thinking, leadership skills, and business acumen to excel in management roles.
The Need for Strategic Tools
In today’s rapidly changing business landscape, businesses need effective tools to make informed decisions and stay ahead of the competition. Strategic tools help organizations analyze their internal and external environments, identify opportunities and threats, and develop strategies to capitalize on strengths and mitigate weaknesses. The BCG Matrix is a powerful tool to help businesses assess their product portfolios and make strategic choices.
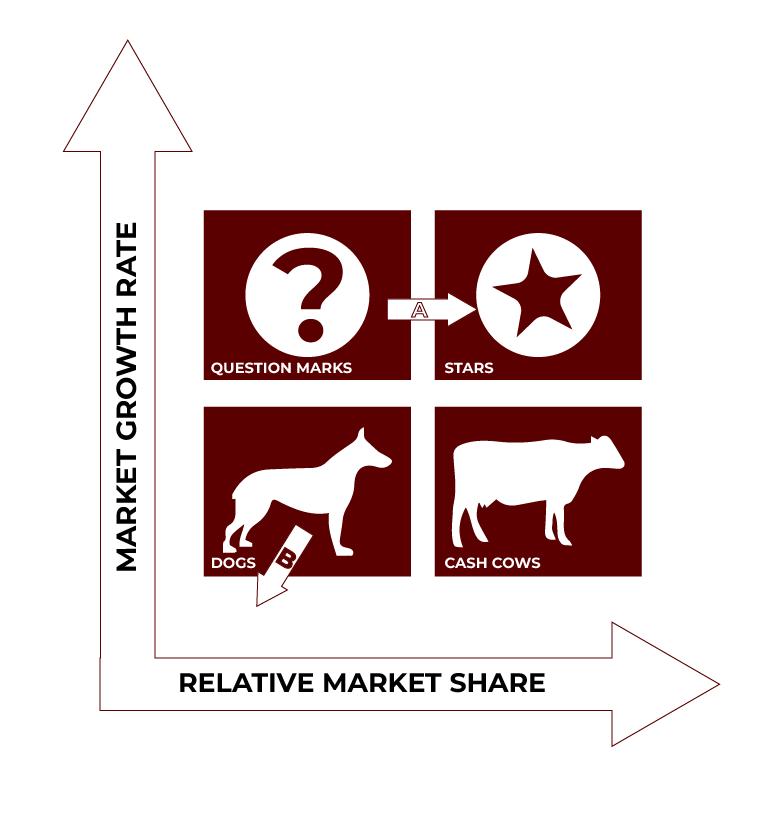
Introducing the BCG Matrix
The BCG Matrix, a cornerstone of strategic management, was developed by the Boston Consulting Group in the 1970s. This powerful tool categorizes products or business units into four quadrants based on market growth rate and relative market share. By understanding the strategic position of each product or unit, businesses can make informed decisions about resource allocation, investment priorities, and portfolio optimization.
Read also: Importance of Strategic Management
The Four Quadrants of the BCG Matrix
Stars
- High market growth, high market share
- Example: Apple’s iPhone, Tesla’s electric vehicles
- Strategic Implications: These are the most sought-after goods or divisions. They must make large investments to sustain market dominance and support future expansion. Strategies often involve:
- Product differentiation: Continuously innovating to offer unique features and benefits.
- Market expansion is the process of breaking into new markets and geographical areas.
- Strategic alliances: Working together with other businesses to improve market position.
Cash Cows
- Low market growth, high market share
- Example: Coca-Cola’s classic soda products, Microsoft’s Office Suite
- Strategic Implications: Cash Cows generate significant profits with relatively low investment. Strategies often focus on:
- Maintaining market share: Through a unified brand and marketing strategy.
- Optimizing production and distribution: To reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Using the generated cash: To fund other business units, invest in research and development, or return to shareholders through dividends.
Question Marks
- High market growth, low market share
- Example: A new product launch by a tech startup, a new line of sustainable products by a traditional company
- Strategic Implications: Question Marks have the potential to become Stars, but they require careful evaluation and investment. Strategies often involve:
- Selective investment: Focusing on the most promising products.
- Aggressive marketing and promotion: To build brand awareness and attract customers.
- Monitoring performance: To assess their potential and make timely adjustments.
Dogs
- Low market growth, low market share
- Example: A legacy product line that is no longer profitable, a niche product with limited market potential
- Strategic Implications: Dogs often consume resources without generating significant returns. Strategies often involve:
- Divestment: Selling or phasing out the product.
- Harvesting: Maximizing short-term cash flows by reducing costs.
- Maintaining: If the product has strategic value, such as complementing other products or maintaining customer relationships.

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
How to Use the BCG Matrix
Step-by-Step Guide
- Identify the Strategic Business Units (SBUs): Determine which products or services you want to analyze. SBUs can be individual products, product lines, or divisions within the company. For example, a tech company might identify its SBUs as smartphones, laptops, tablets, and software.
- Assess Market Growth Rate: Evaluate the market growth rate for each SBU. This involves analyzing industry reports, market trends, and economic indicators to understand market dynamics. For instance, the smartphone market might be experiencing moderate growth, while the tablet market might be slowing down.
- Determine Relative Market Share: Examine each SBU’s market share about its biggest rival. This metric helps gauge the competitive position of each product. For example, if Apple had a higher market share than Samsung in smartphones, it would have been positioned higher on the relative market share axis.
- Plot SBUs on the Matrix: Place each SBU in the corresponding quadrant of the BCG Matrix based on their relative market share and market growth rate. For example, a tech company might have a high-growth, high-share smartphone business (Star), a low-growth, high-share laptop business (Cash Cow), a high-growth, low-share tablet business (Question Mark), and a low-growth, low-share smartwatch business (Dog).
- Develop Strategic Implications: Formulate strategies based on the position of each SBU in the matrix. For instance, allocate more resources to Stars, optimize Cash Cows for profitability, invest selectively in Question Marks, and consider divesting Dogs. For example, invest heavily in Stars like the iPhone, optimize Cash Cows like the iPad, invest selectively in Question Marks like the Apple Watch, and consider divesting or harvesting Dogs.
Also Read: Stages & Process of Strategic Management
Advantages of the BCG Matrix
The BCG Matrix offers several advantages:
- Simplicity and Clarity: The concept is straightforward to understand, making it a valuable tool for strategic planning.
- Opportunity Assessment: It helps efficiently evaluate available opportunities and devise strategies to optimize their potential.
- Resource Allocation: It guides businesses in determining how to best allocate resources to maximize future growth and profitability.
- Portfolio Analysis: It offers a structure for evaluating and contrasting various items in a portfolio.
Read Also: Benefits of Strategic Management
Real-World Case Studies
Apple
Apple is a classic example of a company that has effectively used the BCG Matrix to manage its product portfolio.
- Stars: The iPhone has been a dominant Star for many years, requiring continuous innovation and investment to maintain its market leadership. Apple consistently invests in R&D to develop new features and functionalities for the iPhone while expanding into new markets.
- Cash Cows: The iPad initially launched as a Star but has transitioned into a Cash Cow, generating steady revenue. Apple focuses on optimizing production and distribution to maintain profitability for the iPad.
- Question Marks: The Apple Watch is a mark of significant growth potential in the wearables market. Apple invests strategically in the Apple Watch, aiming to capture a larger market share and transform it into a Star.
- Dogs: Apple TV is often categorized as a Dog due to its limited market share and growth prospects. Apple may consider harvesting the product for short-term cash flow or divesting it if it doesn’t align with its long-term strategy.
Amazon
Amazon has utilized the BCG Matrix to diversify its business and enter new markets.
- Stars: Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a Star, experiencing significant growth in the cloud computing market. Amazon invests heavily in AWS to expand its service offerings and maintain its competitive edge.
- Cash Cows: Amazon’s core retail operations, while still experiencing some growth, can be considered Cash Cows. They generate substantial revenue that Amazon can use to invest in other areas.
- Question Marks: Amazon has several questions, such as those about its healthcare and grocery delivery ventures. The company carefully evaluates these businesses, investing in those with the most promising future.
- Dogs: It’s challenging to pinpoint specific Dogs in Amazon’s portfolio as they may keep some products for strategic reasons, even if they are low performers.
These are just a few examples, and the specific categorization of products within the BCG Matrix will vary depending on the company and its industry.
Limitations of the BCG Matrix
- Oversimplification: The BCG Matrix simplifies complex business situations into a two-dimensional model, which may only capture some of the nuances of a product’s performance. It primarily focuses on market growth and share, potentially overlooking factors like profitability, competitive dynamics, and technological trends. To address this, it’s essential to consider additional factors and qualitative analysis.
- Market Definition Challenges: Defining markets and shares can be challenging, especially in dynamic industries. Markets can evolve rapidly, and competitive landscapes can shift. This can impact the placement of SBUs on the matrix and subsequent strategic decisions.
- Time Horizon Considerations: The BCG Matrix may not fully account for the long-term potential of products. A product categorized as a Dog today might have future growth potential due to technological advancements or changing consumer preferences. It’s crucial to consider the long-term viability of products and avoid premature divestment.
- Alternative Frameworks: While the BCG Matrix is a valuable tool, it’s essential to consider other frameworks to gain a more comprehensive understanding of a business’s portfolio. The GE McKinsey Matrix and the AD Little Matrix provide alternative perspectives by incorporating additional factors like industry attractiveness and competitive position.
Read also: Strategic Management Process
Comparing the BCG Matrix and Ansoff Matrix
While the BCG Matrix is a powerful tool for analyzing a company’s product portfolio, it’s important to consider other strategic frameworks. One such framework is the Ansoff Matrix.
Ansoff Matrix
The Ansoff Matrix is a strategic planning tool that helps businesses identify growth opportunities by considering new products and markets. Four quadrants are used to classify growth strategies:
- Market Penetration: Selling existing products to existing markets. New markets.
- Product Development: Selling new goods to markets that already exist.
- Diversification: Selling new products to new markets.
Read also: Nature and Scope of Strategic Management
Comparing the Two Matrices:
| BCG Matrix | Ansoff Matrix |
| Its main objective is to analyze the current product portfolio of a business. | Focuses on identifying growth opportunities for a company. |
| Categorizes products based on market growth rate and market share. | Classifies growth tactics according to markets and products. |
| Helps in resource allocation and investment decisions. | Helps in making strategic decisions about product development, market penetration, market development, and diversification. |
Conclusion
The BCG Matrix is a powerful tool to help businesses better understand their product portfolios and make strategic decisions that drive growth and profitability. Businesses can allocate resources effectively, prioritize investments, and optimize their portfolios by categorizing products based on market growth and market share.
While the BCG Matrix is a valuable tool, it’s important to recognize its limitations and use it with other strategic frameworks. Businesses can develop more comprehensive and effective strategies by combining the BCG Matrix with tools like SWOT analysis and Porter’s Five Forces.
Ultimately, the success of any strategic initiative depends on its implementation and continuous monitoring. By regularly reviewing and updating their strategic plans, businesses can adapt to changing market conditions and ensure long-term success. Learn about Strategic Management professionally with the Certificate Program in Strategic Management and Business Essentials With Insead by Hero Vired.
Who founded the Boston Consulting Group (BCG)?
What is the BCG Matrix?
- Stars: High-growth, high-share products.
- Cash Cows: Low-growth, high-share products.
- Question Marks: High-growth, low-share products.
- Dogs: Low-growth, low-share products.
What are the advantages of the BCG Matrix?
- Simplicity: It's easy to understand and apply, making it a valuable tool for strategic planning.
- Focus: It helps businesses prioritize products and allocate resources effectively.
- Flexibility: It can be adapted to various industries and business contexts.
- Actionable Insights: It provides clear strategic implications for each product category.
What are the four major growth strategies?
- Market Penetration: Increasing market share in existing markets with existing products.
- Product Development: Introducing new products into existing markets.
- Market Development: Entering new markets with existing products.
Why is BCG so influential?
Updated on November 13, 2024
