The term casting in Java is just a conversion from one data type to another and is usually applied to class hierarchy with inheritance features like upcasting and downcasting. Upcasting is when we take a reference to one class and change it to another class, and downcasting is when we change the reference of one superclass into its respective subclass. It is important to know and apply these concepts while using polymorphism and fully utilizing OOP abilities in Java.
Upcasting is inherently safe (no matter the exact definition we follow), as it means moving to a more “generic” type than another. Another side to downcasting is that it has some risk, and developers will have to check that they are casting the object correctly and that it is an instance of a subclass.
Typecasting in Java
Typecasting is a concept that must be known when working on Java because it involves converting one data type to another. It makes a programmer’s life much easier by allowing them to manipulate and manage all data types. Java mainly has two types of typecasting: Reference typecasting and primitive typecasting.
Primitive and referential typecasting is now basic to fundamental information sorts, such as int, by and large in any case, char, float, etc. In contrast, referential typecasting is the base class for object referrals, which might be any classes or their hierarchies.
Also Read: Type Casting in Java

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Multi Cloud Architecture & DevOps
Master cloud architecture, DevOps practices, and automation to build scalable, resilient systems.
Classifying Typecasting
You also find two more types of typecasting: upcasting and downcasting. Both terminologies are used in the case of a superclass and subclass relationship. They are upcasted from a subclass to a superclass and downcasted from a superclass to a subclass.
Upcasting in Java
The Concept of upcasting in Java can be explained in conjunction with the statement that upcasting is a type of object typecasting where a child object is converted to a parent object using typecasting. It upcasts implicitly, so there’s no need to say anything about the parent class. In upcasting, the benefit is that we have access to all the methods and variables of the parent class. In upcasting, we cannot use all the variables and methods of the child’s class. We can just view certain methods and variables of the child class.
Syntax in Java
Parent parentRef = new Child();
Use Case in Java
Upcasting is often used for polymorphism. For instance, methods or collections designed to work on a parent class can work on different subclasses of that parent class. This method allows for a single method to work with many different types of objects:
public class Parent {
public void display() {
System.out.println("Parent class method");
}
}
public class Child extends Parent {
public void display() {
System.out.println("Child class method");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parentRef = new Child(); // Upcasting
parentRef.display(); // Output: Child class method
}
}
In this example, parentRef can call the overridden display() method in the Child class due to polymorphism, even though the reference type is Parent.
Also Read: Polymorphism in Java
Downcasting in Java
Downcasting is another type of object type casting. When downcasting, a child class is given a parent class reference object. In Java, you cannot pass a parent class reference object as a parameter to a child class; there is no compile time error because Java offers downcasting. When we try to execute it, we get the “ClassCastException.” The question is: Why is the compiler permissive if it’s not possible in Java? Downcasting is sometimes an option in some Java cases. In this case, the essence of the master class is the subclass object.
Syntax in Java
Parent parentRef = new Child();
Child childRef = (Child) parentRef;
Use Case in Java
Downcasting is used if you want to use some methods or fields from the child class after first treating the object with the parent class. Here’s an example:
public class Parent {
public void show() {
System.out.println("Parent class method");
}
}
public class Child extends Parent {
public void play() {
System.out.println("Child class-exclusive method");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parentRef = new Child(); // Upcasting
if (parentRef instanceof Child) { // Checking type before downcasting
Child childRef = (Child) parentRef; // Downcasting
childRef.play(); // Accessing child class-specific method
}
}
}
For example, once we’ve upcasted to the Parent class, we can downcast the Child again to access the play() method, which is inaccessible in the Parent class.
Downcasting allows an instance of a superclass to be retrieved, but we can only access methods specific to a certain subclass. Upcasting, meanwhile, helps convert objects from subclasses to their parents, allowing polymorphism and code flexibility.
Also Read: Data Types in Java

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
Differences Between Upcasting and Downcasting
| Aspect | Upcasting | Downcasting |
| Definition | Upcasting means converting a reference from a subclass object to a superclass object. It’s also called Widening. | Conversion of a superclass reference to a subclass reference is termed downcasting or narrowing. |
| Automatic or explicit | The Java compiler automatically upcasts for us. You don’t have to explicitly cast the object. | Downcasting is not automatic. It requires explicit casting using parentheses syntax (SubclassName). |
| Accessibility | The members of the superclass are only accessible after upcasting. You cannot use methods or fields dealing with the subclass. |
With downcasting, you can reach the superclass and subclass members. The access allows us to use the subclass-specific methods or the fields. |
| Safety | It is safe upcasting because a subclass is an instance of its superclass. There is no ClassCast exception. | Downcasting is a potentially dangerous operation. If the being downcasted object is not an instance of the subclass, it will throw a dreaded ClassCastException. |
| Usefulness | Upcasting tends to allow polymorphic behavior between subclasses and superclasses. | Downcasting is used when we need access to subclass-specific behavior, which is only done with a superclass reference. |
| Flexibility | Upcasting in code enhances its flexibility and scalability by allowing us to treat subclass objects as superclass objects. That is a useful trick when several subclasses contain one specific behavior in the superclass. |
Upcasting makes code more flexible and scalable because it allows the treatment of subclass objects as superclass objects. Such behavior will be inherited by all subclasses that share a common behavior defined in the superclass, and this is good when many subclasses exhibit similar behavior. |
Need of Upcasting and Downcasting in Java
Polymorphism can be done in Java, but we need to do upcasting. This method allows you to treat a subclass object as an instance of its parent class and use various child objects in place of a common parent reference. It’s handy when you write general code that works with parent types but deals with different subclasses.
On the other hand, downcasting is necessary to access subclass-specific methods or properties given by upcasting references. Upcasting makes it easier for an object to implement the same interface at the same location. At the same time, downcasting allows you to pull out the actual object and its unique features. What matters, though, are the runtime exceptions and downcasting, which must be done carefully.
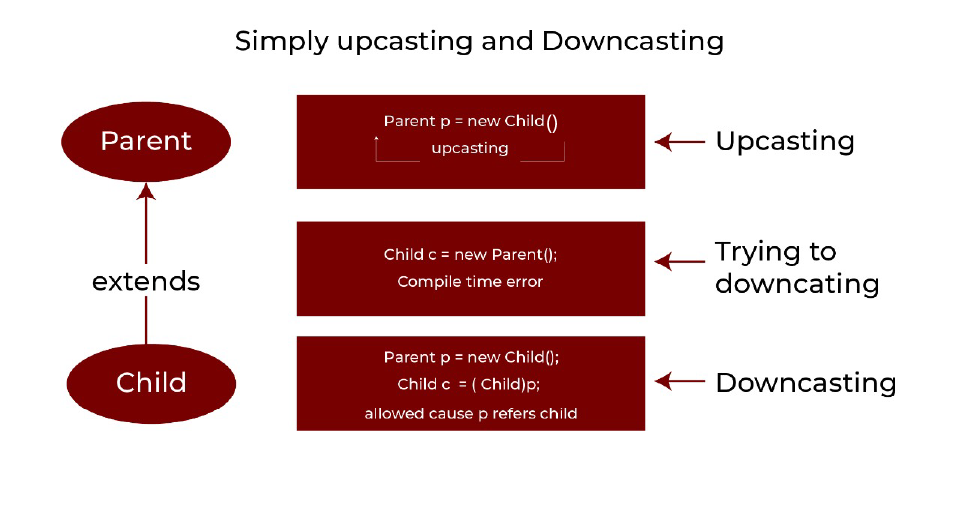
Upcasting permits a Child object to be referenced as a Parent, and downcasting appears as converting it to access Child functionality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, upcasting and downcasting in Java are used in object-oriented programs to operate on objects in class hierarchies. Upcasting in Java allows the flexibility of treating subclasses as instances of their superclass, therefore allowing polymorphic behavior. While powerful, downcasting is usually an option usually used when you need to validate that a particular subclass method or attribute exists and only when the situation warrants the possible runtime exception.
These casting mechanisms make the dynamic and adaptable part of Java’s object-oriented model’s nature contribute to writing more generic and reusable code while maintaining subclasses’ specific features. Enroll in the Certificate Program in Full Stack Development with Specialization for Web and Mobile offered by Hero Vired to get hands-on experience in Java.
How are upcasting and downcasting in Java?
In Java, what is the difference between Upcasting and Typecasting?
Why is upcasting used?
When to use downcast?
What is safe Upcasting or downcasting?
Updated on October 23, 2024
