Do you lose track of your business’s finances?
Wonder where all your money is going and if you’re really profitable?
These are very valid concerns for businesses, small or big. Without a clear picture of your finances, decisions become a guess, and that can be the risky path.
Financial accounting steps in to provide that clear picture. It enables us to see these fine details.
Let’s get a little deeper into the nature and scope of financial accounting and know how it works in the practical running of a business.
What is Financial Accounting?
At its simplest, financial accounting is the process of recording, summarising, and reporting a company’s financial transactions over time.
It allows us to know where money is coming from, where it is going, and whether the business is doing well or not.
Now imagine a local restaurant. They may rake in money from daily customers, but unless they are marking what they spend on expense items, like the cost of ingredients, wages paid to the staff, and rent, then they may be surprised at being barely breaking even.


POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Financial Analysis, Valuation, & Risk Management
Learn financial modeling, valuation techniques, and risk management to drive strategic business decisions.
Nature of Financial Accounting: Key Processes and Characteristics
Financial accounting is not some dull paperwork but a mechanism that keeps businesses operating smoothly and running.
The nature of financial accounting is to monitor transactions involving the flow of money in ways that maintain a healthy balance. We make records of everything that impacts money- from sales to salaries- so that no stone goes unnoticed.
Recording Monetary Transactions: A Core Function of Accounting
The very core of financial accounting is a simple bookkeeping task: recording the transactions. Be it a sale, purchase, or payment, if money is involved, we record it. Every transaction has a story to tell. It is somewhat like an intimate diary for your business to keep track of every little thing your business does.
Unique Example:
Consider the small café in Delhi. They buy milk, sugar, and coffee beans every day. They sell lattes and espressos; besides, they sell some snacks on the side. They keep track of each rupee that goes out or comes in. Thus, they will know at the end of the week how much they have made and whether they need to cut costs or expand.
The transparency of our company’s finances can only be achieved through perfectly written records.
Classification and Consolidation of Financial Information
Now that these transactions have been recorded, they need to be sorted out. The second major step is classification. We classify similar items, such as rent, electricity, or raw materials. Now, when we look back, it’s easy to see where the money went.
Summarising occurs after classification. It is not necessarily essential to analyze hundreds of transactions to understand the big picture. Summarising them into reports that are easy to read helps us identify trends and make better decisions.
Also Read: Limitations of Financial Accounting
Specific Example:
Take a manufacturing business in Mumbai. Every month they have to pay for raw materials, electricity, and labour. They classify these expenses into different categories. Then, at the end of the month, they summarise everything into one report that shows the total expenses, income, and profit.
Accuracy and Transparency: Financial reporting
For finances, transparency is very essential. We need to ensure everything goes right and above board. If this is not done, it may result in costly mistakes in terms of money and trust.
Undeniably, accurate financial reports bring trust, not only within our business but also towards stakeholders, such as investors, partners, or employees. If the numbers don’t add up, it’s not merely a financial loss—it’s an issue of trust.
Unique Example:
A tech start-up in Bengaluru wants investors. However, investors are not going to throw money at them without seeing the numbers. It is financial accounting that ensures that the financial reports of the startup are accurate and transparent and give confidence for investment.
Major Functional Areas of Financial Accounting: Journals, Ledgers, and Summaries
Let’s break down some of the key functional areas of financial accounting.
We start by recording transactions in journals, then classifying them in ledgers, and eventually summarising everything into easy-to-understand financial statements.
Recording and Identifying Financial Transactions
We record transactions here for the first time in journals. It’s the starting point of our accounting process. Each and every financial activity – whether revenue is coming into the business or costs are going out – each one of them finds a record here. This whole process is termed bookkeeping.
Each transaction related to the business, whether it’s a raw material purchase or salary payment, will have to be noted. It is not good practice; it is compulsorily required for some proper tracking of finances.
Special Example:
A retailer of a business located in Chennai will purchase the stock from wholesalers and sell it to customers. Every purchase, including the buying of stock or collecting money from customers, is journalised. In this way, they are completely clear about what is happening to them financially.
Classify Data into Ledgers for Accurate Tracking
After recording the transactions, the next step is their classification. We use ledgers to group similar transactions. The ledgers can be visualised as if separate notebooks were maintained in every area of our finances that we track, whether cash flow, sales, or expenses.
This makes it easy to trace where our money is going and how it is being used. For instance, if we want to check how much we spent on salaries, we just need to check the “salaries” ledger.
Unique Example:
A construction company operating in Hyderabad is paid money in terms of materials, labour, and transportation. All these costs are put into various ledgers. This would inform the construction companies which area is cost-intensive, hence helping them in managing their costs effectively.
Consolidating Information into Financial Statements
Once we have sorted the transactions into ledgers, we summarise them. This is how we end up producing the statements of financial position, which comprise the profit and loss statement as well as the balance sheet. The summaries thus come up to give us and our stakeholders a quick and easy snapshot of the current financial health of the business.
A profit and loss statement is simply an account of whether or not the business is making money or losing it. The balance sheet informs us of what the business owns at what time, as well as what the business owes at the same time.
Unique Example:
A pharmaceutical company in Pune sums up its data at the end of every quarter. It uses a profit and loss statement indicating its profits to its stakeholders. Meanwhile, the balance sheet reveals how much they owe the suppliers and how much cash they have in hand.
Also read: Difference Between Financial Accounting and Management Accounting
Scope of Financial Accounting: Why It Matters to Different Stakeholders
Ever wondered who really cares about all those financial reports?
Is it just for tax purposes or internal use?
The scope of financial accounting goes far beyond just keeping your records in order. It’s about providing critical information to various people who rely on that number in making decisions.
Let’s break it down and see why it matters to them.
Stakeholders Who Require Financial Data
Financial accounting is not just useful for the company’s management. It is required by several stakeholders.
First of all, let’s talk about shareholders. They are interested in whether their money is expanding or shrinking in volume. Profits and losses accounts, balance sheets, and cash flow statements provide them with a glimpse of the company’s health.
They will study the quarterly reports to determine whether the firm is expanding or it is time to change its investment.
Next, we have the creditors.
These will have to decide whether there is much risk involved in lending him money. The financial statements assure them that their loans will be repaid.
Without financial accounting, government authorities would also not know if the businesses were paying their taxes correctly.
Lastly, employees are indirect stakeholders.
They must know whether the company is profitable enough to be able to keep them employed. They may not go through the financial statements; however, their lives hinge on the financial health of the organisation.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance for Financial Reporting
The legal aspect of financial accounting cannot be overlooked.
The law requires businesses to follow the rules and regulations set up by the government and other authorities or bodies.
For example, companies in India have to adhere to Ind AS- Indian Accounting Standards. These standards require that companies prepare and report their financial statements uniformly.
Non-compliance is not just economically unfriendly; it can invite penalties or even litigation.
Apart from the business reasons for transparency, listed companies are regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) to ensure that their financial reporting is in the best interest of their investors.
Broader Implications of Accounting for Finance within Society and Economy
Financial accounting is not confined to influencing businesses and their immediate stakeholders. It has larger-scale impacts on the economy.
When firms publish their financial reports, they contribute to market-wide transparency. These reports help local and international investors know where to place their money.
A transparent business environment can be a way of instilling confidence, which is the backbone of economic development.
Inaccurate financial reporting can trigger scandals, loss of investor confidence, and damage the market as a whole. This is where accounting comes as an essential tool that contributes not only to personal success but also to the greater economic platform.

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
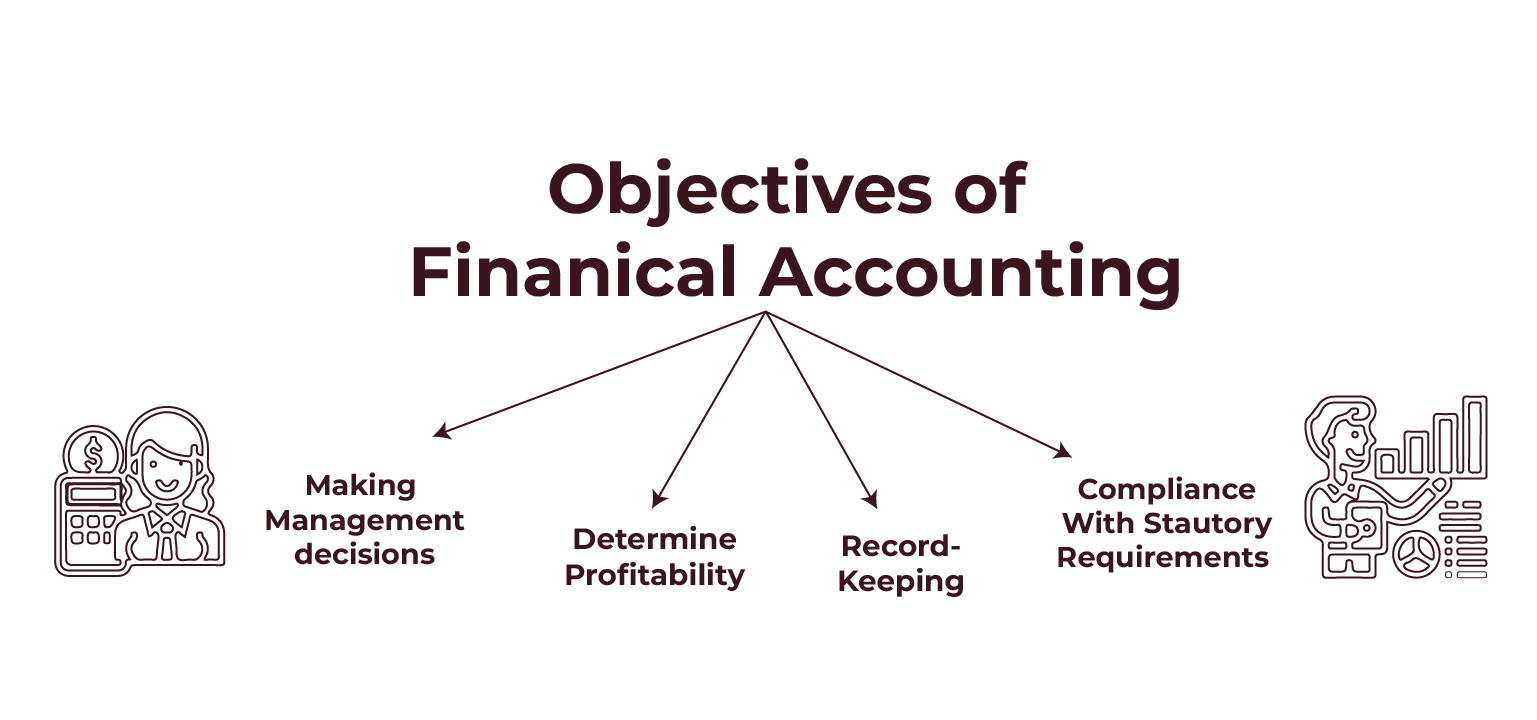
Purpose of Financial Accounting: Motivating Business Performance
Without clear objectives, any process becomes pointless. Financial accounting is no exception as well. It is also driven by specific goals that help businesses stay on course and inform stakeholders of good decisions.
Measuring Profitability and Financial Position
One of the main objectives is to find out whether the business is profitably running or not.
This is typically determined through an analysis of the profit and loss statement, another standard financial statement. It also helps to estimate the company’s general financial standing—what it owns, what it owes, and what it’s worth.
Facilitating Strategic Choices
Financial accounting is not just about numbers. It is about strategic choice.
Do you want to go to another location? Do you need to invest in new equipment? You would like to know whether the business could afford it.
Financial reports give you this clarity.
Financial Planning and Budgeting for Future Growth
Financial accounting lastly helps in financial planning and budgeting.
It gives the required information to enable realistic forecasts and achievable goals. Without it, businesses would essentially be shooting in the dark when it comes to planning their futures.
Limitations of Financial Accounting: Recognizing What It Cannot Do
The nature and scope of financial accounting are highly important but not perfect. There are very obvious limitations we need to acknowledge.
It is purely historical cost accounting. No adjustment is made for inflation or a change in market value.
It provides information regarding the whole business, not individual units or product lines. If you wish to know how much revenue a particular product generates, you will require cost accounting or management accounting.
It focuses on past data, not future projections. Financial accounting is not meant for forecasting or making future predictions.
Also Read: Financial Statement Analysis
Conclusion
The nature and scope of financial accounting is more than being a bookkeeper. It describes financial information because it tracks, organises, and presents financial data to inform the decisions of an organisation.
Actually, financial accounting is the fundamental process by which information flows to investors, creditors, and employees by meeting the needs of various legal mandates. It identifies financial strengths and weaknesses, helps in strategic decisions, and increases business planning for the future.
Although this has its limitations, like focusing only on historical data, it is still important for business transparency and accountability.
As a business grows, so do their actions. It is essential that financial accounting always acts as a source for understanding one’s financial health and success in the long term.
If you are willing to increase your knowledge of financial accounting, you can enrol in the Financial Analysis, Valuation, & Risk Management course by Hero Vired. This course provides practical insights and advanced tools that help you make better financial decisions and improve business performance while managing risks effectively.
Is financial accounting useful for decision-making?
Is financial accounting only suitable for big corporations?
Why is financial accounting important for small businesses?
Updated on October 22, 2024
