Method overloading in Java allows a subclass to provide a specific implementation for a method already defined in its superclass. This feature allows a subclass to provide a specific implementation of a method already defined in its superclass, enhancing the flexibility and extensibility of your code. This article will guide you through the practical uses of method overriding in Java, a fundamental concept in Object-Oriented Programming.
What is Method Overriding?
Method overriding is an object-oriented programming language feature that allows a subclass to provide a specific implementation for a method already defined in its superclass. Although the method in a subclass has the same name, return type, and parameters as the method in its superclass, the method in the subclass overrides the method in the superclass.

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Multi Cloud Architecture & DevOps
Master cloud architecture, DevOps practices, and automation to build scalable, resilient systems.
Rules of Method Overloading in Java
- Final methods can not be overridden: In Java, if we don’t want a method to be overridden in the subclass, We declare it as a final keyword.
The following program demonstrates the final keyword program.
Program
class ParentClass {
final void show(){
System.out.println("Show Display Something") ;
}
}
class ChildClass extends ParentClass{
void show(){
System.out.println("Show Display Something");
}
}
class Main{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Final KeyWord Example") ;
ChildClass ob = new ChildClass() ;
}
}
Output
Main.java:8: error: show() in ChildClass cannot override show() in ParentClass
void show(){
^
overridden method is final
- Static methods can not be overridden(Method Overriding vs Method Hiding)
When a developer defines a static method with the same signature as a static method in the base class. It is known as a method of hiding. The following table describes what happens when you define a method with the same signature as a method in a super-class.
| Superclass Instance Method | Superclass Static Method | |
| Subclass Instance Method | Overrides | Generates a compile-time error |
| Subclass Static Method | Generates a compile-time error | Hides |
Program
class Parent {
static void addition(int x, int y){
System.out.println("Addition ="+(x+y)) ;
}
void subtraction(int x, int y) {
System.out.println("Subtraction = "+(x-y)) ;
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
static void addition(int x, int y){
System.out.println("Addition = "+(x+y));
}
@Override public void subtraction(int x, int y){
System.out.println("Subtract = "+(x-y)) ;
}
}
// Driver class
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Parent ob = new Child() ;
ob.addition(30, 40);
ob.subtraction(50, 40);
}
}
Output
Addition =70
Subtract = 10
- Private methods can not be overridden
We cannot override private methods in the subclass. Because the scope of private methods is limited to the class, we cannot access them outside the defined class.
Program
class SuperClass{
private void privateMethodExample(){
System.out.println("Private Method Example in Java") ;
}
public void publicMethodExample(){
System.out.println("This is a public method in SuperClass");
}
}
class SubClass extends SuperClass{
private void privateMethodExample(){
System.out.println("This is a private method in SubClass") ;
}
public void publicMethodExample(){
System.out.println("This is a public method in SubClass");
privateMethodExample();
}
}
class Main{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Private Method Example ") ;
SuperClass ob = new SuperClass() ;
ob.publicMethodExample() ;
SubClass ob2 = new SubClass() ;
ob2.publicMethodExample();
}
}
Output
Private Method Example
This is a public method in SuperClass
This is a public method in SubClass
This is a private method in SubClass
- The overriding method must have the same return type (or subtype)
After Java 5.0 was released, it is possible to have different return types for an overriding method in the child class, but the child’s return type should be a subtype of the parent’s return type. This phenomenon is known as the covariant return type.
The following program demonstrates the overriding method.
Program
class SuperClass {
public Object ObjectFuntion()
{
System.out.println(
"This is the method in SuperClass");
return new Object();
}
}
class SubClass extends SuperClass {
public String StringFunction()
{
System.out.println(
"This is the method in SubClass");
return "Hello, World!";
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SuperClass obj = new SuperClass();
obj.ObjectFuntion();
SubClass obj2 = new SubClass();
obj2.StringFunction();
}
}
Output
This is the method in SuperClass
This is the method in SubClass
- Invoking overridden method from sub-class
Using the super keyword, we can use all the parent class methods in the overriding method.
The following program uses the super keyword in the sub-class.
Program
class SuperClass {
void show() {
System.out.println("Superclass show method");
}
}
class ChildClass extends SuperClass {
@Override void show(){
super.show();
System.out.println("Child show method");
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
SuperClass ob = new ChildClass();
ob.show() ;
}
}
Output
Superclass show method
Child show method
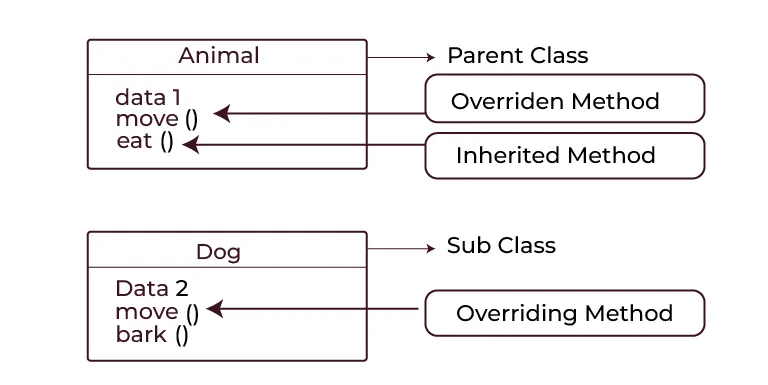
Example of Method Overriding
The following program demonstrates method overriding in Java.
Program
// Superclass
class Animal {
void sound() {
System.out.println("Animal makes a sound");
}
}
// Subclass
class Dog extends Animal {
@Override
void sound() {
System.out.println("Dog barks");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal myDog = new Dog();
myDog.sound(); // Output: Dog barks
}
}
Output
Dog barks
The above program’s ‘Dog’ class overrides the ‘sound’ method of the ‘Animal’ class. When a sound method is called on an ‘Animal’ reference pointing to a ‘Dog’ object, the overridden method in the ‘Dog’ class is executed. This demonstrates the runtime polymorphism.
Uses of Method Overriding
Let’s discuss the uses of Method Overriding in the Java language.
- Runtime Polymorphism: Method overriding achieves runtime polymorphism in Java. It allows a method to behave differently based on the object that invokes it.
- Code Reusability: By overriding methods, subclasses can reuse the interface provided by the superclass while providing a specific implementation. This promotes code reusability and cleaner code architecture in the Java program.
- Enhancing Functionality: In Overriding, the Subclass can enhance or modify the behaviour of methods inherited from the superclass. It makes it possible to extend the functionality without altering the superclass code.
- Frameworks and Libraries: Method overriding is extensively used in frameworks and libraries where default methods are provided in base classes, and users can override these methods to customise behaviour.

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned about method overriding in Java. It is a powerful feature that enables subclasses to customise or completely replace the behaviour of methods defined in their superclasses. By following the rules of method overriding, developers can leverage this mechanism to achieve polymorphism, which enhances code flexibility and promotes reusability. Understanding and effectively using method overriding is essential for mastering object-oriented programming.
What is method overriding in Java?
Can a private method be overridden?
Can a static method be overridden?
Can we override a ‘final’ method?
Can an abstract method be overridden?
Updated on July 31, 2024
