The C++ language has inline functions, a key feature that replaces function calls with the actual function code during compilation, thereby reducing overhead. This function effectively embeds the code at the call site, playing a crucial role in improving the quality of our code. In this article, we will learn about the Inline Function in C++ language, understanding its syntax, application, advantages, and limitations. By mastering this function, we can significantly enhance the readability and maintainability of our code, a skill that every C++ programmer should strive for.
What is the Inline function in C++?
An inline function can be defined using the ‘inline’ keyword. It suggests to the compiler that it should attempt to insert the function’s code directly into the calling code rather than executing to insert the function’s code directly into the calling code. It can improve the performance by avoiding the overhead of function call mechanisms such as stack allocation, parameter passing and return address management.
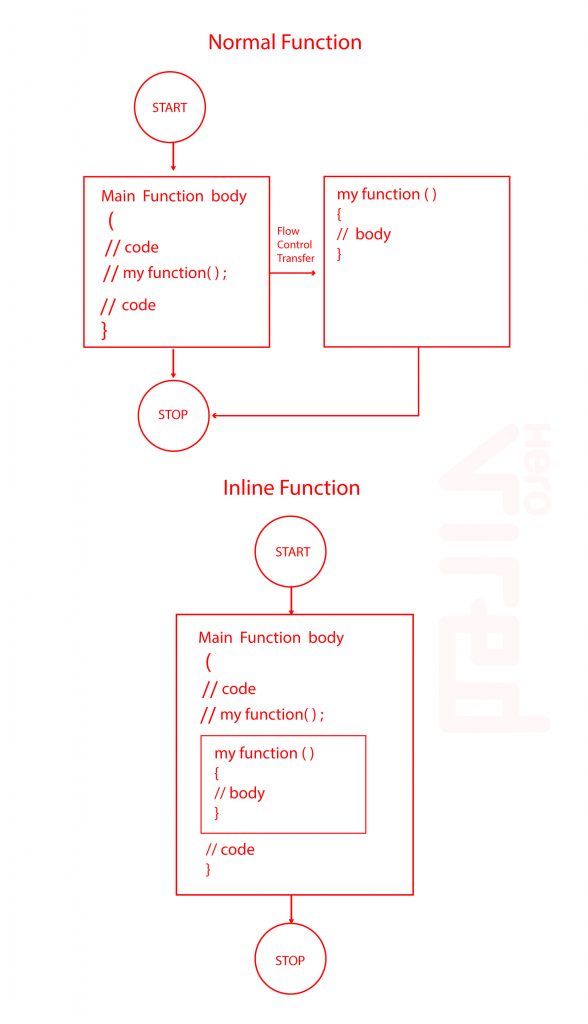
The following image shows “how the inline function works”.

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Multi Cloud Architecture & DevOps
Master cloud architecture, DevOps practices, and automation to build scalable, resilient systems.
Syntax of Inline Function in C++
inline returnType functionName(parameters) {
// function body
}
Example
inline int add(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
These are the common situations where the compiler may not perform inlining in such circumstances
- If our function contains the loop, for example, while and do-while loop.
- If a function contains the stack variables
- If our function is recursive.
- If a function return type is other than void and the return statement does not exist in a function body.
- If our function contains a switch or goto statement.
Applications of Inline Functions in C++
In this section, we will discuss the Inline function in C++ language.
- Boost Efficiency: The primary use of the inline function is to increase a program’s efficiency. This function embedding the function’s code at the caller site eliminates the need for Function call overhead, such as jumping to the function and returning from it. This functionality saves both execution time and stack space in development. It makes your program faster and more resource-efficient.
- Avoiding Complex Functions: By using the inline function, we can avoid complex functions. Complex functions are those functions which have loop-heavy, recursive, or involve significant computation and are generally not good candidates for inlining.
- Streamlined Functions: In the critical section of code where speed is the most important factor in development, we can use the inline function. It can provide speed efficiency. Developers can enhance the overall performance of time-sensitive operations within their application by using the streamline function.
Why are Inline Functions Used?
Inline functions in C++ are utilised primarily to enhance performance and streamline code organisation. By instructing the compiler to replace the function call with the actual code of the function at the calling function. It is just like a shortcut for small tasks. Instead of telling the computer to a different part of the program to something simple. You can just put the code right where you need it. This makes the code more efficient and faster because It doesn’t have to keep jumping around.

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
Advantages of using the Inline function in C++
In this section, we will see the advantages of the Inline function in C++ language. Here are some common advantages of the Inline function.
- Increased Execution Speed: One of the primary advantages of using inline functions in C++. It boosts the program execution speed. This is because inline functions eliminate the overhead associated with the function calls.
- Reduced Function Call Overhead: By avoiding the overhead of function calls, such as parameter passing and stack frame allocation, the inline function can make your code more efficient, especially for small and frequently called functions.
- Code Size Optimization: Inline functions in C++ also reduce the size of executables by eliminating redundant function call instructions. This can result in more efficient memory usage and better cache performance, particularly where our resources are limited.
- Encapsulation and Readability: Inline functions can improve code organisation and readability by encapsulating functionality directly where It’s used. It makes the code more modular and easier to understand, reducing the need for extensive comments and documentation.
Limitations of using Inline Function in C++
The inline function is a very powerful feature for optimising function performance. It calls the function frequently. However, there are some limitations of the inline function. In this section, we will discuss some limitations.
- Increased Executable Size: Inline Function can increase the larger executable size, especially when we use lengthy code blocks. This is because the code for an inline function is copied to every point in the code where the function is called from a single location.
- Debugging Challenges: The inline function makes debugging more challenging because the function‘s code is across multiple locations in a single program. This can make it harder to trace the flow of execution and identify the source of bugs
- Increased Compile Time: Inlining can lead to longer compile times, especially for large projects. This is because the compiler needs to duplicate the function code at each call site, which increases the code size that needs to be processed during the compilation.
- Memory Thrashing: Excessive use of the inline function can increase the executable file size, leading to memory thrashing. Memory thrashing occurs when the system spends a significant amount of time swapping data between physical memory and disk storage. It degrades the performance of the overall system
Example of Inline Function in C++
The following program demonstrates the inline function example
Program
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
inline int subtract(int x, int y) {
return x – y;
}
inline int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
// Main Function
int main() {
cout << add(33, 11) << endl;
cout << subtract(200, 15) << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
44
185
Inline Functions and Classes
In this section, we will implement the Inline function using the C++ classes. It enhances efficiency by embedding function code directly into the calling location, reducing function call overhead. By default, functions defined inside a class definition are inline. It is recommended to declare them within the class and define them externally with the inline keyword for clarity.
The following program demonstrates the inline function and class.
Syntax
class Calculator {
public:
int subtract(int x, int y);
};
inline int Calculator::subtract(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
Program
#include <iostream>
class MathOperations {
public:
//Function declarations
inline int add(int x, int y);
inline int subtract(int x, int y);
inline int multiply(int x, int y);
inline float divide(int x, int y);
};
inline int MathOperations::add(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
inline int MathOperations::subtract(int x, int y) {
return x – y;
}
inline int MathOperations::multiply(int x, int y) {
return x * y;
}
inline float MathOperations::divide(int x, int y) {
if (y != 0) {
return static_cast(x) / y;
} else {
std::cerr << “Error: Division by zero!” << std::endl;
return 0;
}
}
int main() {
MathOperations calc;
int a = 343, b = 3433;
std::cout << “Given numbers: a = ” << a << “, b = ” << b << std::endl;
std::cout << “Addition: ” << calc.add(a, b) << std::endl;
std::cout << “Subtraction: ” << calc.subtract(a, b) << std::endl;
std::cout << “Multiplication: ” << calc.multiply(a, b) << std::endl;
std::cout << “Division: ” << calc.divide(a, b) << std::endl;
return 0;
}
Output
Given numbers: a = 343, b = 3433
Addition: 3776
Subtraction: -3090
Multiplication: 1177519
Division: 0.0999126
Cons of using Macros in C++ language
In this section, we will see the cons of macros. This makes them a less preferred option for modern C++ programming. Here’s easy to understanding breakdown of the problems associated with errors
- Debugging Challenges: Macros are expanded before compilation, making it harder for developers to debug the whole code. The expanded code may differ significantly from the original source, leading to confusion when trying to diagnose issues.
- Readability and Maintainability: Macros can make code less readable and maintainable, especially when they are used extensively in coding. Understanding the behaviour of macros often requires referring to their definitions.
- No Type Safety: Unline functions and macros do not perform type checking or enforce necessary type conversion. This results in errors that are caught only at runtime, making the code less safe and predictable.
- Proper use of Inline Functions: Inline functions must be small and used sparingly. Overusing inline functions or making large functions inline can lead to code bloat, potentially negating any performance benefits.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned about inline functions in the C++ language. These functions offer a valuable mechanism for improving code performance and organisation. By using inline functions, we can replace function calls with actual code at the call site; inline functions eliminate the overhead associated with function calls, leading to faster execution and reduced memory usage. Overall, understanding the principles, advantages, and limitations of inline functions empowers developers to make informed decisions about their usage, ensuring optimal performance and maintainability in C++ codebases.
What is an inline function in C++ language?
When should I use an inline function in C++?
What are the advantages of using inline functions in C++?
Are inline functions the same as macros in C++?
Updated on September 6, 2024
