A factorial of a non-negative integer n is the product of all positive integers less than or equal to n. it is represented by n!. For instance, the factorial of 5 is:
5! = 5×4×3×2×1=120
Why are factorials so important? Here are some fields in which the concept of factorial is used extensively:
Uses of Factorials in Mathematics
- Permutations & Combinations
- Probability
- Series Expansion
- Calculus
- Algebra
- Number Theory
Uses of Factorials in Computer Science
- Algorithm Analysis
- Data Structures
- Cryptography
- Dynamic Programming
- Combinatorial Problems
- Graph Theory
- Statistical Models
The following article will examine five distinct approaches to writing a factorial program in Java and compare the time and space complexity of each approach.
Also Read: Java Tutorial
Factorial Program in Java: Different Methods with Detailed Code Examples
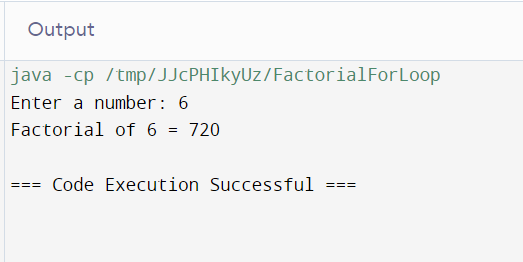
Method 1: Factorial Calculation Using For Loop
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FactorialForLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int number = sc.nextInt();
long factorial = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= number; i++) {
factorial *= i;
}
System.out.println("Factorial of " + number + " = " + factorial);
}
}
Output:
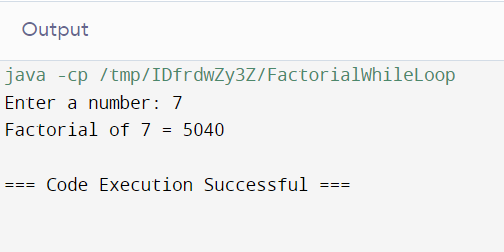
Method 2: Factorial Calculation Using While Loop
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FactorialWhileLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int number = sc.nextInt();
long factorial = 1;
int i = 1;
while (i <= number) {
factorial *= i;
i++;
}
System.out.println("Factorial of " + number + " = " + factorial);
}
}
Output:
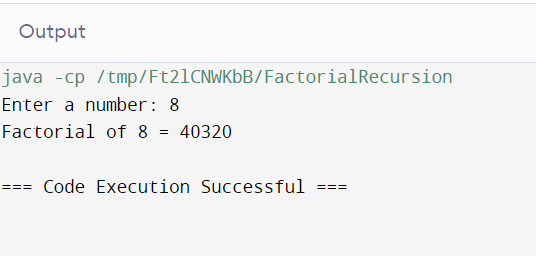
Method 3: Factorial Calculation Using Recursion
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FactorialRecursion {
static int factorial(int n) {
if (n == 0)
return 1;
else
return (n * factorial(n - 1));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int number = sc.nextInt();
int result = factorial(number);
System.out.println("Factorial of " + number + " = " + result);
}
}
Output:
Method 4: Using BigInteger for Factorial Calculation of Large Numbers
When dealing with large numbers, the BigInteger class in the java.math package is our friend. It helps us avoid overflow issues.
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FactorialBigInteger {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int number = sc.nextInt();
BigInteger factorial = BigInteger.ONE;
for (int i = 1; i <= number; i++) {
factorial = factorial.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(i));
}
System.out.println("Factorial of " + number + " = " + factorial);
}
}
Output:
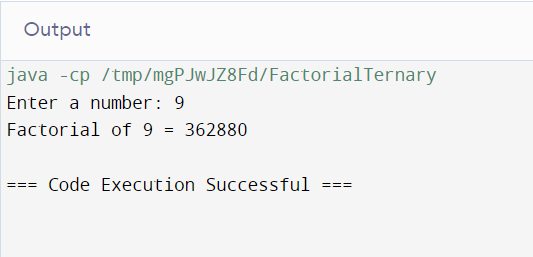
Method 5: Factorial Calculation Using One-Liner Ternary Operator
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FactorialTernary {
int factorial(int n) {
return (n == 1 || n == 0) ? 1 : n * factorial(n - 1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int number = sc.nextInt();
FactorialTernary obj = new FactorialTernary();
System.out.println("Factorial of " + number + " = " + obj.factorial(number));
}
}

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Multi Cloud Architecture & DevOps
Master cloud architecture, DevOps practices, and automation to build scalable, resilient systems.
Evaluating the Efficiency of Various Techniques
Let’s examine the time and space complexity of each technique we covered so that you can decide which approach to take into account while creating a factorial program in Java.
Time Complexity Analysis
Understanding how long each method takes to run helps us choose the right one.
- For Loop:
- Time complexity: O(n)
- This means the time it takes grows linearly with the size of the input.
- While Loop:
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Similar to the for loop, the time increases linearly.
- Recursion:
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Although recursion calls itself repeatedly, it still operates in linear time.
- BigInteger:
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Even though it handles large numbers, it performs in linear time.
- One-Liner Ternary Operator:
- Time complexity: O(n)
- It’s compact but still linear in execution time.
Space Complexity Analysis
Space complexity tells us how much memory each method uses.
- For Loop:
- Space complexity: O(1)
- This method uses a constant amount of memory, regardless of the input size.
- While Loop:
- Space complexity: O(1)
- Like the for loop, it uses a constant amount of space.
- Recursion:
- Space complexity: O(n)
- Recursion uses more memory because each call adds a layer to the stack.
- BigInteger:
- Space complexity: O(n)
- Handling large numbers means more space is needed.
- One-Liner Ternary Operator:
- Space complexity: O(n)
- This method also adds to the stack with each call, using more space.
Common Errors and How to Avoid Them
Let’s discuss a few common challenges that we should avoid when writing a factorial program in Java.
- Integer Overflow:
- Problem: Using int or long for large numbers can lead to overflow.
- Solution: Use BigInteger for large values.
- Infinite Recursion:
- Problem: Recursion can spiral out of control if the base case isn’t properly defined.
- Solution: Always ensure you have a clear base case to end the recursion.
- Off-by-One Errors:
- Problem: Incorrect loop conditions can cause calculations to be off.
- Solution: Double-check loop boundaries and conditions.
- Improper Input Handling:
- Problem: Not validating input can cause the program to crash.
- Solution: Always check for valid, non-negative integers before processing.
- Memory Limits:
- Problem: Recursion or large computations can hit memory limits.
- Solution: For large computations, consider iterative methods and use BigInteger.
Also Read: Structure of Java Program
Conclusion
In this guide, we’ve walked through several ways to write a factorial program in Java. From for loops to recursion, and even using BigInteger for those massive numbers. Each method has its strengths and trade-offs. Choosing the right one depends on your specific needs—whether it’s minimising memory use or handling large values efficiently.
Why use BigInteger for large numbers?
Can factorial be calculated for negative numbers?
Which method is most efficient for calculating factorials?
What are some practical uses of factorials?
Updated on July 26, 2024