Financial risk, as a component of individual financial and risk management, is a situation where persons or institutions may lose money or face negative financial outcomes for one reason or another. When dealing with governments, businesses, and even individuals, managing and avoiding different financial risks is much easier if they are distinguished. Drawing on literature, this article aims to disseminate knowledge about the key financial risks and the consequences of their presence.
What is Financial Risk?
Financial risk is the possibility of a definite value loss of financial assets, such as cash or assets, due to the impact of internal or external factors. Since these risks are inherent to financial decision-making processes, they also affect the properties of financial reports, such as the health of the individual, corporate, or government. Stakeholders, however, are aware of these risks and can do their best to mitigate them.

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Financial Analysis, Valuation, & Risk Management
Learn financial modeling, valuation techniques, and risk management to drive strategic business decisions.
Different Types of Risks Encountered by Firms
Probability may be defined as the likelihood of an unfavorable or unfavorable event. Risk is defined as any action or activity resulting in loss. Below are various types of risks that a firm might encounter and which it must unlock. Risks can be broadly classified into Organizational Risk, Non-Organizational Risk, and economic risk.
- Business Risk: Such risks are assumed by business enterprises themselves in an attempt to maximize shareholder value and profits. For instance, marketing a company that invests in a new product to increase sales involves high-cost risks.
- Non-business risks are outside the firms’ micro and macro environments. Political and economic instabilities, for example, can be considered non-business risks.
- Financial Risk: As the term implies, financial risk is the risk that leads to financial loss for firms. It derives commonly from fluctuations and losses in the financial markets and factors such as stocks, currency, rates of interest, etc.
Types of Financial Risks
Financial risk is one of the critical risks that companies anticipate for any business venture. Market risk is the cause of financial risk and can encompass everything. Hence, several categories are usually adopted when categorizing financial risk. They include:
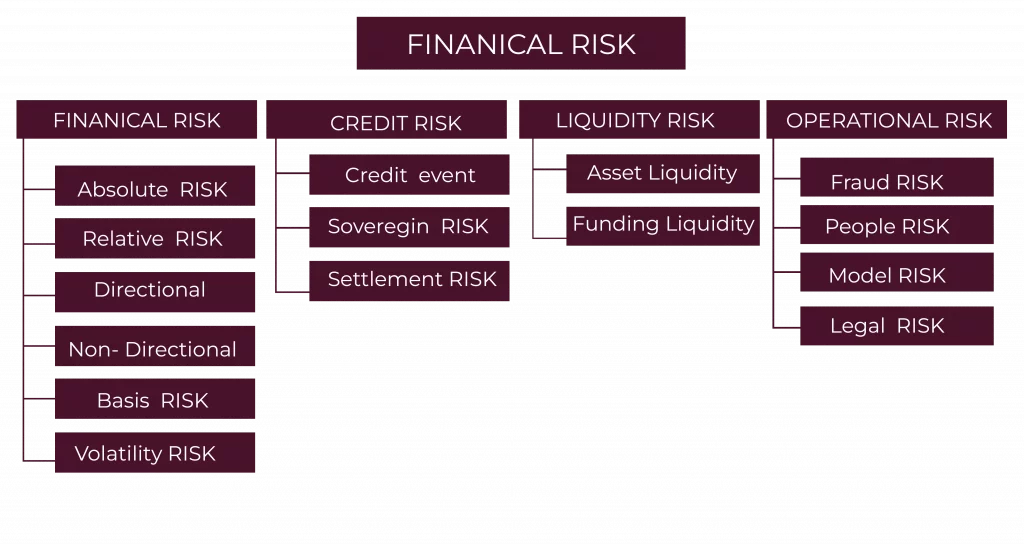
- Market Risk occurs when the prices of financial instruments change. Market risk can be categorized as Directional or non-directional. Directional risk arises when the stock price, rates of interest, and other factors change. Non-directional risk can be volatility risk.
- Credit Risk occurs when one party defaults and fails to meet the agreed obligation to the other party. Credit risk can be divided into sovereign risk and settlement risk. Sovereign risk, frequently due to troublesome foreign exchange policies, may be defined as. On the other hand, settlement risk occurs when one counterparty has made a payment while the other has not.
- Liquidity Risk is surely the result of a failure to complete transactions. Asset liquidity risk and funding liquidity risk are two types of liquidity risk. Asset liquidity risk occurs when there are insufficient buyers or sellers on sell or buy orders.
- Operational Risk is based on mismanagement or technical failure. Fraud risk and model risk are also classified as operational risk. Lack of controls exposes us to fraud risk, while model risk is the correct model application.
- Legal Risk: Legal restrictions, such as lawsuits, create financial risk. A company takes a legal risk whenever it has to bear financial losses resulting from legal proceedings.
Financial Risks for Businesses
Financial risks for a business are the potential risks arising from external (external) and internal factors, such as market volatility, operational inefficiencies, or macroeconomic shifts. Market risk is one of the largest categories and results when stock prices, interest rates, exchange rates or commodity prices decrease and cause a company’s financial standing to become worse. To name one, businesses might be hit with equity risk from ever-changing stock prices, interest rate risk from changing borrowing costs, currency risk from unsteady exchange rates in foreign trade or commodity risk when raw material prices fluctuate.
Credit risk is another important financial risk that arises when customers default on payment. It can overstrain cash flow and may stem from delayed payments, the bankruptcy of a major client, or a situation where a single buyer whose creditworthiness is uncertain is underwritten. Together, these risks underline the crucial role of effective financial management in avoiding losses and consequently stabilizing the business.

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
Financial Risks for the Market
Market risk is caused by variable changes, including stock prices, interest rates, foreign exchange rates, and commodity prices. These external, largely uncontrollable risks are pivotal to financial markets and investment strategies.
Types of Market Risks
- Equity Risk: Equity risk is volatility in stock prices. Equity risk, in other words, is a shareholder’s equity in stock investments that decline due to bad market conditions, company-specific problems, or economic decline by definition.
- Interest Rate Risk is always the risk that shifting interest rates will change the value of an investment. This indicates that when the interest rate rises, the value of bonds also changes, and the price of an asset that constitutes a fixed-income portfolio will be adjusted.
- Currency Risk: Currency risk—also called foreign exchange risk or recession against the group—results from wavy changes in foreign exchange rates affecting buying or selling things denominated in a foreign currency. This is particularly relevant for large multinational businesses and global investors.
- Commodity Risk: Prices for commodities like oil, gold, and agricultural products are a commodity risk. This risk is relevant to commodity producers, consumers, and investors in commodity markets.
Financial Risks for Governments
In plain words, financial risks to governments include risks that imperil their financial stability. Other situations involve governments facing event risks that create unfavourable economic environments. Most of the risks, however, arise from factors like changes in global markets, political upheavals, changes in commodity prices, catastrophic events, and fluctuations in public policies and regulations.
For instance, market risks are still significant to governments, including international borrowing for government debt, and changes in interest or exchange rates affect national borrowing costs. In other words, it implies that the government will fail its debt obligations and be exposed to credit risk, thus with uncertain credit rating to borrow to finance projects. Passed that is the second liquidity risk because if the government does not get enough money to cope with its short-term commitments, it has a fiscal problem. As a result, financial instability is faced by operational risks like poor spending by the government and corruption.
For example, fluctuations in governmental measures may involve structural shifts in taxation systems, social reforms, and public expenditures, which impact the economy. Financial risks such as these must be controlled so that governments can increase economic growth, make people happy, and discharge their financial obligations.
Financial Risks for Individuals
In simple terms, the risks affecting governments’ financial stability are called financial risks. These include the challenges and uncertainties that governments may face that will result in adverse economic conditions. Most of the time, these risks arise from factors such as changes in global markets, political instability, and changes in commodity prices, as well as the impact of natural disasters and changes in public policy or regulation.
Market risk is a big concern to governments, especially government borrowing from international markets and fluctuations in interest or exchange rates that can impact national debt servicing costs. Government failure to meet debt obligations can lead to credit risk, such that the government may not be able to have a certain level of credit rating and borrow to fund projects. Liquidity risk also comes in that if the government doesn’t have enough cash flow to pay its short-term obligations, it may have a fiscal crisis. Operational risks in connection with inefficiencies in government spending and corruption can also undermine financial instability.
Also, sudden changes in government policies may generate political and policy risks. These may entail changes in tax structures, social programs, and public spending priorities and affect economic performance. These financial risks must be managed so that governments can continue to generate economic growth, protect citizens’ welfare, and meet their financial commitments.
Pros and Cons of Financial Risk
| Pros of Financial Risks | Cons of Financial Risks | Governments facing high financial risk may incur higher borrowing costs, as lenders may demand higher interest rates to offset the perceived risk. | This awareness of financial risks can lead to improved fiscal policies and more prudent budgeting and spending. | High financial risk can lead to economic instability and affect public services: investment and growth.
| The financial risk management practices encourage regular monitoring and evaluation of government finances. | Addressing financial risks might lead to cuts in essential public services or social programs, affecting citizens. |
| The financial risks can push governments to adopt long-term economic planning and sustainability strategies. | The risk leads to borrowing or debt issuance, resulting in a growing national debt straining future financial resources. |
Why is understanding financial risk important for businesses?
Why is understanding financial risk important for businesses?
What is market risk, and how does it affect businesses?
Can financial risks be eliminated?
What industries are most affected by financial risks?
Updated on December 28, 2024
