Over the past few years, data science has become one of the most promising and easily adaptable industries that deal with technology. This field entails looking for patterns in data and developing the logic that can help drive businesses, governments, and organizations. Over the last decade or more, data science has branched out into different forms based on the specialization, industry, and approach used in analyzing data. This article will explore all the types of data science and its advantages and disadvantages.
What is Data Science?
Data science is a scientific method/rigorous discipline that deals with ‘analytics’ or computing facts from data. In inextricably integrating elements of statistics, calculating, computer science, and materials of a specific problem area, data science allows for the analysis of essential data, correct decisions, and even the prediction of tendencies in the future.

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Multi Cloud Architecture & DevOps
Master cloud architecture, DevOps practices, and automation to build scalable, resilient systems.
Importance of Data Science?
Let’s see the importance of data science.
- Informed Decision-Making: It enables data-driven decisions by analyzing trends and insights, reducing risks.
- Driving Innovation: This sparks advancements in healthcare, finance, and technology.
- Operational Efficiency: This optimizes workflows, automates tasks, and reduces costs.
- Competitive Advantage: This helps businesses stay ahead by understanding market trends and customer behaviour.
- Scientific Research: It facilitates data analysis for hypothesis testing and knowledge discovery.
Popular Data Science Types
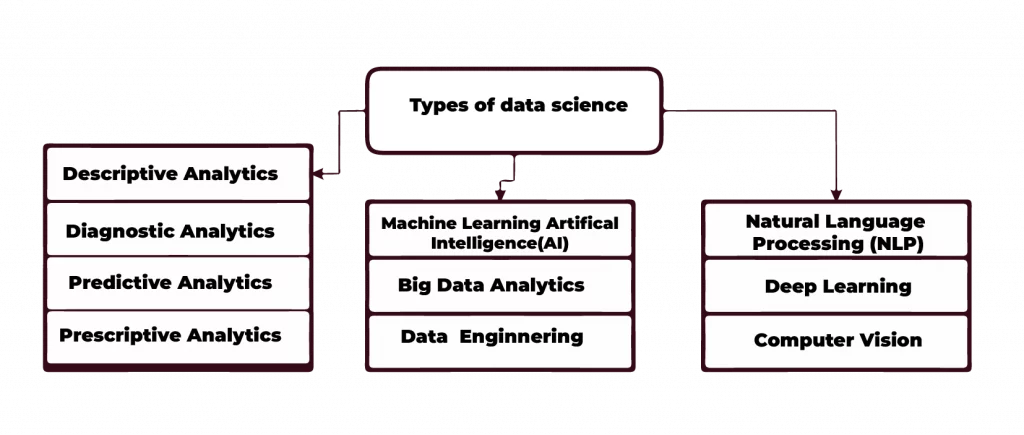
Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics tells about the ‘what’, and diagnostic analytics tells the ‘why’. This is the study of patterns to identify factors leading to observed behaviours and events. Diagnostic analytics involves methods like correlation analysis and root cause analysis that help to understand drivers, giving previous results reasons.
Benefits
- Enhanced Data Understanding: Descriptive analytics allows data scientists to evaluate data variations, occurrences, and frequencies and to discover other important yet unnoticed patterns, for instance, customer preferences or process constraints. This understanding is useful when formulating a strategy and managing data solution development.
- Effective Visualization: Descriptive analytics translates multiple layers of information into simpler graphic displays, including charts, graphs or dashboards. These visuals are important for conveying information to people with little knowledge about data science.
- Trend Identification: In data science projects, identifying trends is critical. Descriptive analytics reveals patterns over time, such as sales growth, customer churn rates, or website traffic, allowing businesses to adjust strategies.
Diagnostic Analytics
Descriptive analytics forms the first level of data analysis in data science. It tends to analyse past occurrences to determine what has transpired. Descriptive analytics help understand past behaviour and activity patterns based on statistical methods and graphical presentation, giving the organization a snapshot of their data.
Benefits
- Deeper Insights: Diagnostics analytics show deep information about data by detecting reasoning from ‘what’ to ‘why;’. It helps reveal why, how, what, where, when, and which trends, deviations, and phenomena so you can make the right decision based on information supporting a case’s arguments and not a presumption.
- Improved Problem-Solving: You can first determine the source of what you consider a problem, which diagnostics analytics allows you to do. Therefore, you have a possibility for directed actions aimed at preventing the root of problems and resulting in sensible solutions and sustainable improvements.
- Process Optimization: Following a diagnostic analysis, more light must be shed on bottlenecks and workflow efficiencies. One can learn from how operations fail to adopt better techniques to enhance the operation’s efficiency and reduce waste.
Predictive Analytics
That is why predictive analytics concerns future events, using historical data to predict the unknown future based on the known past. This system uses statistical and learning methods to predict behaviours, trends, and results. It is valuable in strategic business processes and assists business organisations in predicting market trends, customer patterns, and risks.
Benefits
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Thus, predictive analytics enables organizational management to make the right decisions based on data. Because it will give awareness of the future trends and possibilities, it makes the decision-making process to select the right option more confident.
- Improved Forecasting: Organizations can predict customers’ demand, sales or behaviour. For instance, retail businesses can determine the demand for inventories during the holidays, eliminating the possibility of lacking certain products or having excess of other products.
- Cost Optimization: Cost optimization is another aspect made possible through the analysis of predictive analytics to detect waste. For example, in manufacturing, it will be able to forecast when machinery is likely to break down. Therefore, it will be repaired or replaced before it causes a problem.
Prescriptive Analytics
Prescriptive analytics takes the concept further because it provides proactive forecasts for future trends and suggests a course of action for reaching a specific goal. It entails using optimisation and simulation algorithms to offer direction on decision-making and possible solutions to existing issues or approaches towards handling future issues.
Benefits
- Improved Decision-Making: Prescriptive analytics provides decision-makers with actionable suggestions for decision-making, informing them of the best course to take. This erases guesswork and allows decisions that are oriented to the organizational goals in place.
- Optimization of Resources: Organizations can make the best use of available resources. For instance, in manufacturing, prescriptive analytics tells the right materials to use, the optimum way of applying them and people’s time.
- Enhanced Productivity: Thus, prescriptive analytics, providing recommendations for a change in processes, increases efficiency. For example, it can either improve how supply chains are managed by determining the best routes that can be utilized and the best time for delivery to be made.
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Modern-day data science trends include machine learning and AI, and the main aim of these modern science departments is to design algorithms that can learn and develop themselves. Artificial intelligence, machine learning and robotics are all concerned with making machines capable of reasoning, learning from data, and making decisions independently, without human intervention. Machine learning and AI are ideals that have started changing industries worldwide, making predictions more accurate, automating the execution of activities, and incubating evolution.
Benefits
- Enhanced Efficiency and Automation: It is noteworthy that with ML and AI, all manual work is performed automatically, and a specialist is free to engage in meaningful activities.
- Improved Decision-Making: Technology and AI systems look for patterns in large data sets to inform decision-makers.
- Personalization: This article defines how machine learning algorithms provide user experiences based on user activities.
Big Data Analytics
Big data analysis, on the other hand, means dealing with large volumes of data that cannot, in one way or the other, be handled by standard data processing tools. This approach uses techniques in mathematical computations to identify patterns, relationships, and trends in large datasets, making it easier for organizations to analyze data from different areas.
Benefits
Big data analytics offers many real-world advantages, and let’s understand with examples.
- Informed Decisions: Big Data Analytics assists them in knowing the most appropriate products to avail in hopes of capturing the market. It frees up space, helps minimise wastage, and ensures customers are satisfied hence, profits remain high.
- Enhanced Customer Experiences: That is where Big Data Analytics comes into play, making those product suggestions spot on. It is like employing the service of a private assistant who would go ahead and source goods based on what he knows we like.
- Optimized Logistics: Big Data Analytics is used by FedEx to send your packages in less time and without affecting the surrounding environment—the fast but kind to the planet version.
Data Engineering
Data engineering allows the creation of the framework and instruments for data acquisition, storage, and analysis. It is more about the specifics of data gathering and structuring, which could be clearer, more complex, and heavy on the nuts and bolts of getting data ready for analysis. The data engineer is responsible for the construction and upkeep of the framework of data science endeavours.
Benefits
- Enhanced Data Quality: Data engineering is a process that, through rigorous validation, transformation, and cleaning processes, provides data used for analysis that is accurate, robust, and error-free. Better business outcomes require better-quality data.
- Faster Data Access: Data pipelines and storage systems are designed to decrease data scientists’ and analysts’ access time to necessary data. It accelerates processes and decision-making for analytics.
- Scalability: Data engineering supports scaling data systems to handle growing data volumes and complexity. It is crucial for businesses dealing with big data and real-time analytics.
Natural Language Processing(NLP)
Natural Language Processing is a subcategory of data science that works to make computers comprehend, analyse, and synthesise text and speech. It uses them for text and speech conversion to make efficient communication between humans and machines, and it is used in activities such as sentiment analysis, chatbots, language translation, and so on.
Benefits
- Improved Communication: NLP brings Humans and Machines together to better interact with them through voice commands, chatbots and virtual assistants. This increases both the usability and accessibility of the user experience.
- Enhanced Customer Support: NLP-powered Automated chatbots and virtual assistants respond instantly to customer queries, decreasing waiting time and improving service quality. Apart from handling repetitive tasks, they also free up human agents to handle complex issues.
- Data Analysis at Scale: The NLP processes and analyses unstructured data, such as customer reviews, social media posts, and survey responses, to extract valuable insights. This helps businesses understand customer sentiment, market trends and brand perception.
Deep Learning
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that attempts to mimic real learning, particularly from experience. Machine learning is a type of artificial intelligence that leverages neural networks with many layers to figure out complex patterns in data. At the same time, it’s very good at finding patterns in seemingly random data sets like images, sounds, and text to advance the fields of computer vision and speech recognition.
Benefits
- Handles Complex Data: The most recent (ascension) of these perennials in Sriram’s garden are interconnected with each other, producing bulbils (or bulb forms), and grouped (in a crawling fashion, rather than a bunch like those in the photo) as a single entity. That’s why it is good for jobs like image recognition, speech processing and natural language understanding.
- Automated Feature Extraction: Deep learning is not like traditional machine learning algorithms. Deep learning eliminates manual feature engineering. It automatically picks up the most important feature in the data and passes it on to the model-building process.
- Superior Accuracy: Typically, deep learning models solve tasks, such as image classification, speech recognition, and language translation, with ‘better’ accuracy than traditional methods. It becomes even more true when huge quantities of labelled data are available.
Computer Vision
Computer vision aims at enabling machines to read and understand the visual world. We apply deep learning models to images and videos to allow computers to recognize objects, faces, and scenes—describing what you see and allowing computers to act based on what they see. Elastic allows scientists in industry to build sophisticated visual systems that can transform industries by turning insight into action through capabilities including automated inspection, surveillance, and augmented reality.
Benefits
- Enhanced Accuracy: Computer Vision leverages advanced algorithms to minimize human errors in critical applications, such as medical diagnosis, quality inspection, and facial recognition systems. With its precision, it gives reliable results.
- Improved Security: Computer Vision brings great strength to security: facial recognition, intrusion detection, behavioural analysis, etc. They increase organizational security and public safety.
- Cost Efficiency: Automating visual inspections and analysis can help businesses reduce costs by reducing manual intervention, saving them money, and increasing operational efficiency. Also, it reduces losses from defective products and missing errors.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Data Science
A detailed comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of data science is presented in tabular form.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Data science provides actionable insights by analysing trends and patterns, enabling better decision-making. | If sensitive data is managed, there are privacy problems, and breaches won’t be handled well. |
| Information personalisation in services and products increases customer satisfaction (for example, recommendation of books). | Starting and sustaining data science entails more capital investment in technologies for analysis, software and human capital. |
| Predictive analytics streamlines business processes, reduces waste, and increases profitability. | For this reason, poor quality or even biased data can cause wrong conclusions and wrong decision-making. |
| It drives innovation by anticipating new trends, opportunities, and market ‘gaps’. | Overly complex models might perform well on training data but need to generalise to new data. |

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
Conclusion
Data science specialisations help tackle complex data challenges and deal with them within businesses in different industries. Regardless of the specialisation – in data engineering, business analytics, machine learning, or data visualization – whatever is done to derive value from data is different. Together, these roles produce insights that inform organisations about what to do, how to be efficient, or how to create effective and innovative products and services.
With continued development within the field, data scientists can pick, based on their interests and strengths, to bring their prowess in data-driven solutions to add to the creation of data-driven solutions for society and businesses. Consider pursuing the Certification Program in Data Analytics with Microsoft offered by Hero Vired for further knowledge.
What is a Data Analyst?
What does a Data Engineer do?
What is a Data Scientist?
Updated on November 26, 2024
