During this digital age where connections prevail, protecting sensitive data must remain the highest priority. Security oboucryptographic methods alongside network defence serve essential functions to protect data while blocking cyber threats against communication and system infrastructure. This article dives deeply into the key concepts, importance, and application of cryptography and network security.
What is Cryptography?
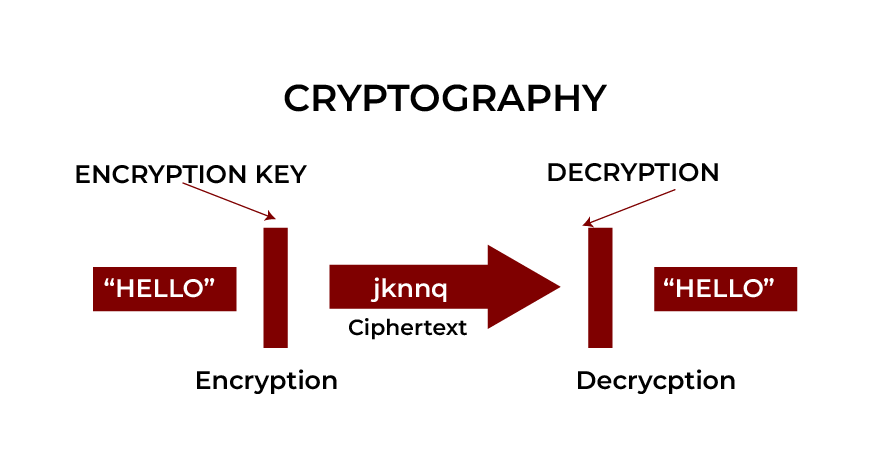
Cryptography is the foundational practice of information encryption and decryption for defending communication when known threats are present. Cryptography offers authorized access to sensitive information through algorithmic encryption of plaintext data. The primary objectives of cryptography include:
- Confidentiality: The secure transfer of information depends on preventing unauthorized groups from accessing it.
- Integrity: It lowers the risks of unwanted changes throughout data transmission or storage periods.
- Authentication: The communication process requires identity confirmation of participating entities.
- Non-repudiation: The technology ensures no unauthorized entity can reject participation during exchanges or communication.
Also Read: What is Public-key Cryptography?

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Multi Cloud Architecture & DevOps
Master cloud architecture, DevOps practices, and automation to build scalable, resilient systems.
Types of Cryptography
- Symmetric-Key Cryptography: This cryptography method uses The same key for encryption and decryption. It is efficient for large amounts of data but requires secure key sharing.
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
- Data Encryption Standard(DES)
- Asymmetric-key cryptography uses a pair of keys—a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. It is widely used in secure communication.
- RSA(Rivest-shamir-adleman)
- Elliptic Curve Cryptography(ECC)
- Hash Functions: Cryptographic hash functions convert data into a fixed-length hash value, ensuring data integrity. Popular hash algorithms include.
- SHA-256
- MD5
What is Network Security?
The deployment of Network Security depends on multiple policies and practices alongside strategic measures to defend computer systems and data from unauthorized manipulation or destruction. Network security applies multiple protective mechanisms and technological tools to prevent unauthorized entry into network systems and prevent resource control failures.
Also Read: Why the Future is Bright for the Crypto, Blockchain, and Web 3.0 Domains
Types of Network Security
Network security consists of various measures designed to protect a computer network from unauthorized access, misuse, modification, or denial of service. The different types of network security include.
- Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks. They filter incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined security rules.
- VPN(Virtual Private Networks): VPNs encrypt data transmitted over public or private networks, ensuring secure communication between remote users and the organization’s network.
- Access Control: Access control restricts unauthorized users from accessing network resources. This is enforced using authentication mechanisms like passwords, biometrics, and role-based access.
Also Read: Implementing of Data Encryption Standard, DES Algorithm in Cryptography
Objectives of Network Security
- Confidentiality: The network distribution mechanism ensures authorized users and systems have exclusive access to sensitive data.
- Integrity: Data remains protected from unauthorized modification or corruption during the transmission and storage phases.
- Availability: Access to authorized users must always be supported by the availability of network services and network resources as needed.
Components of Network Security
- Firewall: The firewall implements security rules to check and limit all network traffic entering or leaving the system.
- Antivirus and Anti-malware Software: The network security tools defend against harmful software, including viruses, worms, and ransomware.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention System(IDPS): The system identifies unauthorized system access attempts and suspicious network behavior while blocking both entities.
- Virtual Private Network(VPN): The virtual private network encryption protects internet data transmission to secure remote network access.
- Access Control: A strong access control method allows only permitted network users to reach their designated system resources.
- Network Segmentation: Dividing the network sections stems from segmentation to restrict potential security breach consequences.
- Data Loss Prevention(DLP): The solution consists of monitoring activated mechanisms that defend sensitive data by safeguarding against both unauthorized transmission and leaks.

82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
Importance of Cryptography and Network Security
Importance of Cryptography
Cryptography focuses on securing information through encoding, ensuring that only authorized entities can access or understand it. Its significance includes.
- Data Confidentiality: Electronic encryption protects sensitive data by securing information through communication through emails, online banking, and messaging applications.
- Data Integrity verifies that data has not been altered during storage or transmission. It ensures the trustworthiness of financial transactions and legal documents.
- Authentication confirms the identity of users, systems, and devices. It underpins secure login systems, digital certificates, and multi-factor authentication.
- Securing Emerging Technologies: The safeguarding blockchain, IoT, and cloud computing innovation. This supports advancements in secure quantum computing solutions.
Importance of Network Security
- To protect sensitive information from cyber-attacks.
- This is very important to secure sensitive data from cyber-attacks and ensure the network is usable and trusted.
- The network security protocols the client’s data by ensuring the system is not slowed down due to redundant tools and data.
- It protects the network from ransomware, a common attack that blocks access to data until the ransom is paid.
Applications of Cryptography and Network Security
Network security, combined with cryptography, powers organizations’ numerous functional sectors to protect data and system reliability while achieving secure communication. The securing system and operational effectiveness remain dependent on implementing these systems throughout the contemporary digital system.
Cryptography Applications
- Secure Communication: Implementing cryptography protects platform communication channels, including the messaging systems of apps like WhatsApp and Signal. The cryptographic system protects communications by encryption, which allows authorized readers to decrypt messages without permitting interception.
- Data Protection: Sensitive data is encrypted cryptographically, ensuring protection throughout storage and transmission times. The encryption standards AES(Advanced Encryption Standard) and RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) secure confidential data protection across databases with cloud storage applications and data transmission services.
- Authentication System: The authentication mechanisms verify user identities using cryptographic methods. Password hashing, two-factor authentication, and digital certificates are prime examples of cryptography, which ensures secure access to systems and resources.
- Digital Signatures: Digital Signatures authenticate the origin and integrity of electronic documents. They are extensively used in financial transactions, legal contracts, and software distributions, assuring authenticity and non-repudiation.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology employs cryptographic principles to maintain secure and immutable records of transactions. Public key cryptography and hashing algorithms ensure transparency and integrity in cryptocurrencies and decentralized systems.
- Electronic Voting: Cryptography enables secure digital voting through data protection mechanisms and anonymous election participation, stopping manipulation attempts.
- E-Commerce Security: Online shopping platforms use cryptographic protocols like SSL( Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS( Transport Layer Security) to encrypt sensitive data, such as credit card information, ensuring safe and trustworthy transactions.
- Government and Military Applications: Cryptography has been instrumental in securing sensitive government and military communications. Advanced encryption methods protect classified data from cyberattacks and espionage.
Applications of Network Security
Network security implements diverse technologies and practices to defend data integrity and system accessibility throughout interconnected network environments. The sector depends heavily on the widespread applications of this technology.
- Enterprise Security: Centro Guadalajara depends on firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and Virtual Private Networks to protect network systems against cyber threats so operation continues without interruption.
- Cloud Security: Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) enable businesses to protect their networks from cyber threats while providing continuous operational capabilities.
- Cloud Security: The growth of cloud computing as a standard practice makes establishing robust cloud environment protection measures necessary. Network security systems protect cloud-based data and data processing against breaches and unauthorized access.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Security: The Internet of Things comprises smart home systems and industrial sensors whose vulnerability leads cyber attackers to target them. These devices perform safely through robust network security features and prevention systems against unauthorized control.
- Healthcare Security: Network security solutions from healthcare organizations protect patient medical information and fulfil HIPAA requirements to maintain patient data confidentiality standards.
- Educational Institutions: Schools and universities protect research information and personal records through network security to build reliable educational platforms online for learning activities.
- Critical Infrastructure Security: Public services remain at risk of disruption when power grids, water supply networks, and transportation systems depend on secure networks to stop potential cyber threats.
Conclusion
Information security applications span multiple domains, and network security implements cryptography to provide confidential communication and protect data with system reliability assurances. These systems are crucial for preserving trust and operational efficiency in digital environments. Consider enrolling in the Certificate Program in Cybersecurity Essentials & Risk Assessment with Microsoft to deepen your understanding of cybersecurity principles and risk assessment. This program equips you with the skills needed to excel in the ever-evolving field of cybersecurity.
What is the primary goal of cryptography?
How do firewalls contribute to network security?
What is the difference between symmetric and asymmetric cryptography?
Why is network security essential for businesses?
Updated on February 3, 2025
